| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ACAD3; ACADS; Bcd1; SCAD;;ACADS |
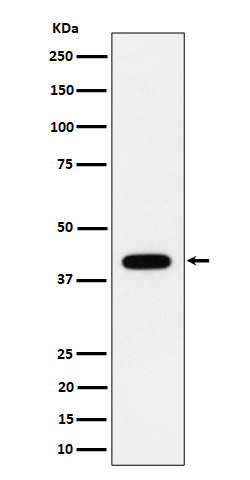
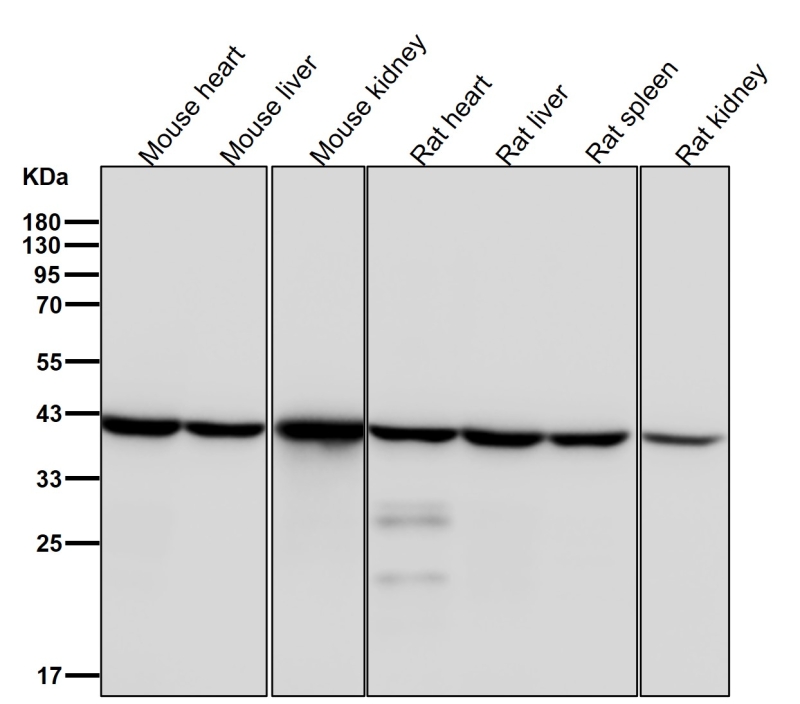
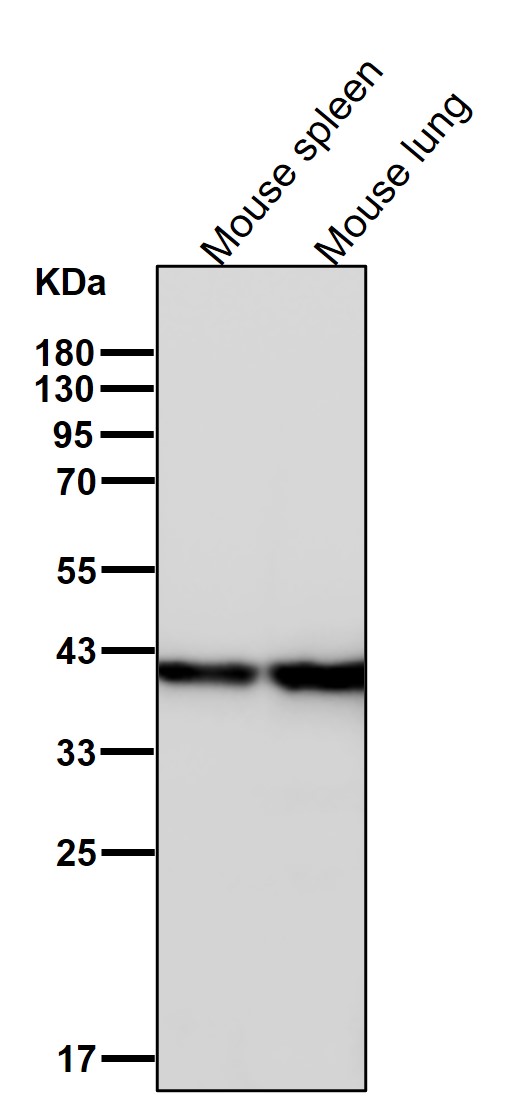
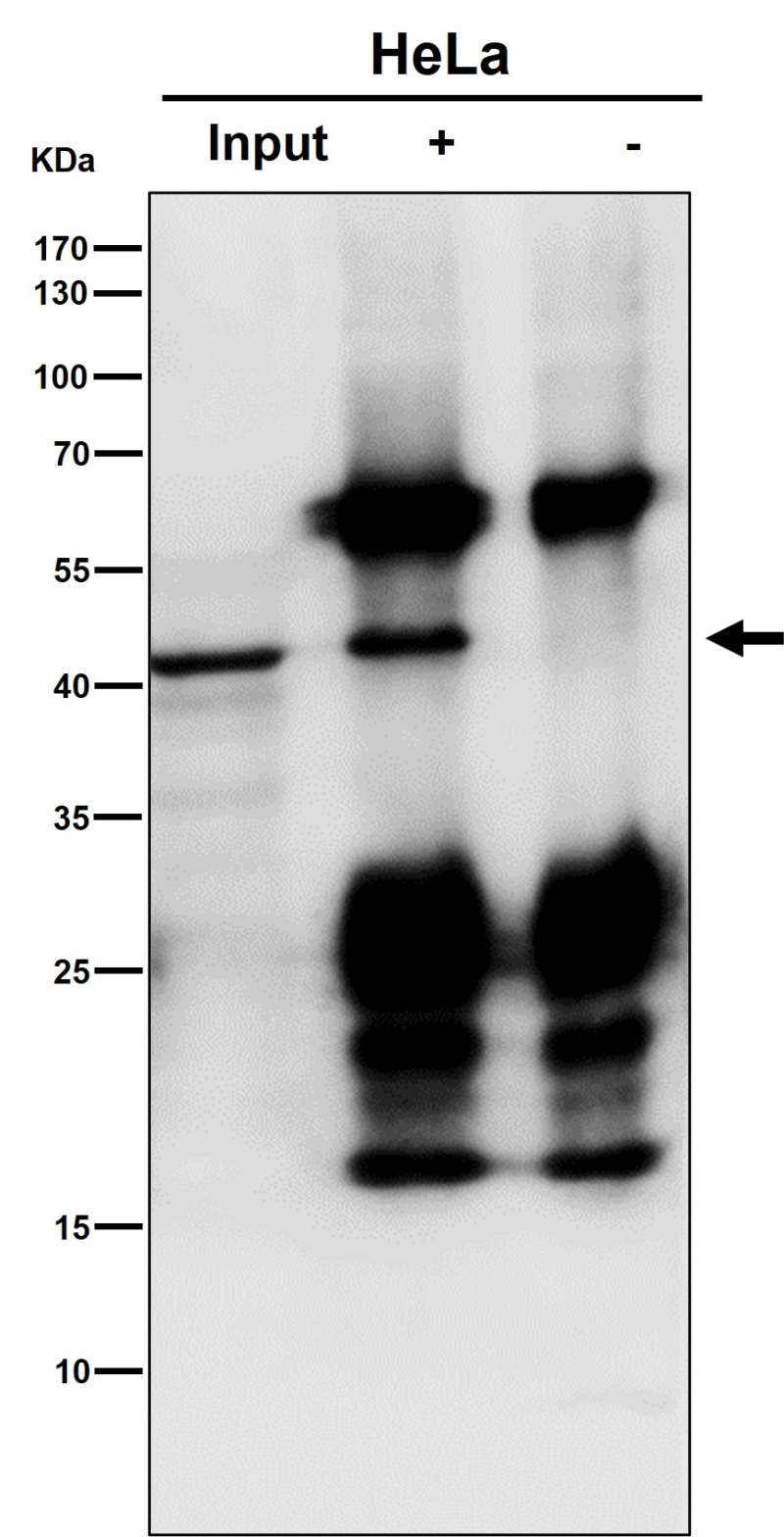
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 44 kDa ; Observed MW: 40 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human ACADS |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ACADS/SCAD抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (SCAD) deficiency: molecular and biochemical perspectives*
**作者**:Gregersen N, et al.
**摘要**:该研究系统分析了SCAD缺乏症的分子机制,揭示了ACADS基因突变(如c.625G>A和c.511C>T)导致酶活性降低的分子基础,并讨论了抗SCAD抗体在体外功能验证实验中的应用。
2. **文献名称**:*Clinical and biochemical heterogeneity in SCAD deficiency*
**作者**:Tein I, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过病例分析发现SCAD缺陷患者的临床表型差异显著,提出利用抗SCAD抗体进行蛋白质印迹(Western blot)检测,可辅助诊断患者肌肉或成纤维细胞中SCAD蛋白的表达水平异常。
3. **文献名称**:*SCAD deficiency: diagnostic challenges and the role of newborn screening*
**作者**:Pedersen CB, et al.
**摘要**:探讨了SCAD缺陷在新生儿筛查中的局限性,提出结合血酰基肉碱谱分析与抗SCAD抗体的免疫检测技术,可提高该病的早期诊断准确性,并减少假阳性结果。
---
以上文献均聚焦于ACADS/SCAD的分子机制、临床诊断及抗体应用,涵盖基础研究到临床实践的关键内容。
ACADS/SCAD antibodies target short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (SCAD), a mitochondrial enzyme encoded by the *ACADS* gene. SCAD plays a critical role in fatty acid β-oxidation, catalyzing the dehydrogenation of short-chain acyl-CoA derivatives (e.g., butyryl-CoA) to produce energy via the electron transport chain. Deficiencies in SCAD activity, often due to *ACADS* mutations, are linked to SCAD deficiency (SCADD), an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder. SCADD may present with variable symptoms, including hypotonia, developmental delays, and metabolic crises triggered by fasting or illness, though some individuals remain asymptomatic.
ACADS/SCAD antibodies are primarily used in diagnostic and research settings to assess SCAD protein expression and stability. In clinical diagnostics, these antibodies help detect reduced or absent SCAD levels via techniques like Western blot or immunohistochemistry, supporting the confirmation of SCADD alongside genetic testing. Research applications include studying the molecular mechanisms of SCADD, such as misfolding of mutant SCAD proteins or impaired interactions with molecular chaperones. Additionally, these antibodies aid in exploring therapeutic strategies, like chaperone therapy, to stabilize dysfunctional SCAD variants. Their role extends to broader studies on fatty acid metabolism disorders and mitochondrial dysfunction, contributing to understanding genotype-phenotype correlations in SCADD.
×