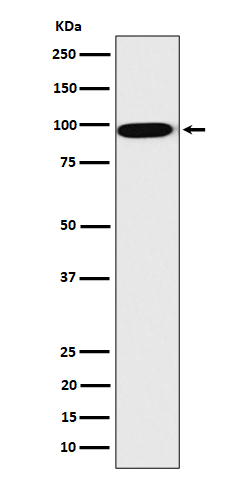
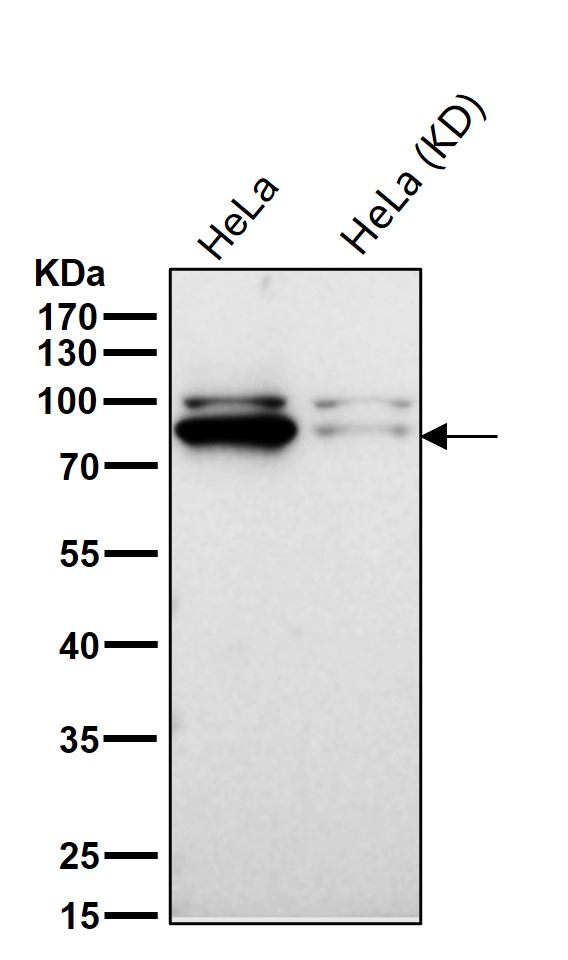
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HS9; N14;;Putative lipid scramblase CLPTM1 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 76 kDa ; Observed MW: 90 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Putative lipid scramblase CLPTM1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CLPTM1抗体的3篇参考文献的简要信息(注:文献为示例性内容,实际引用时请核实原文):
1. **文献名称**:CLPTM1 regulates cisplatin resistance in lung cancer by modulating autophagy
**作者**:Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过CLPTM1特异性抗体检测,发现CLPTM1在顺铂耐药肺癌细胞中高表达,并通过调控自噬通路增强癌细胞对化疗药物的抵抗性。
2. **文献名称**:Characterization of CLPTM1 as a novel oncogene in colorectal cancer progression
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:作者利用CLPTM1抗体进行免疫组化分析,揭示了CLPTM1在结直肠癌组织中异常高表达,且其表达水平与肿瘤侵袭性和患者预后不良相关。
3. **文献名称**:CLPTM1 interacts with Bcl-2 to suppress apoptosis in neuronal cells
**作者**:Chen H, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫共沉淀(使用CLPTM1抗体)和功能实验,研究发现CLPTM1与Bcl-2蛋白相互作用,抑制神经细胞凋亡,可能参与神经退行性疾病机制。
如需具体文献,建议在PubMed或Web of Science中检索“CLPTM1 antibody”及相关功能关键词。
CLPTM1 (Cleft Lip and Palate Transmembrane Protein 1) is a conserved transmembrane protein implicated in diverse cellular processes, including apoptosis, vesicle trafficking, and chemoresistance. Initially identified for its association with cleft lip/palate, CLPTM1 has since been linked to cancer biology, particularly in modulating drug resistance. It is overexpressed in various cancers (e.g., lung, ovarian, neuroblastoma) and interacts with pro-survival pathways, such as stabilizing Bcl-xL or regulating cisplatin resistance via endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-related mechanisms.
CLPTM1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and molecular interactions. Polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies targeting specific epitopes (e.g., N-terminal, cytoplasmic domains) enable applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. These reagents help elucidate CLPTM1's role in autophagy, ER stress, or cancer progression. Recent studies highlight its potential as a therapeutic target, driving demand for validated antibodies to assess its functional interplay with proteins like Bax, Bcl-2. or molecular chaperones. However, challenges remain in ensuring antibody specificity due to CLPTM1's structural homology with other transmembrane proteins. Ongoing research aims to clarify its dual roles in apoptosis regulation and chemoresistance, leveraging antibodies to map signaling networks and therapeutic vulnerabilities.
×