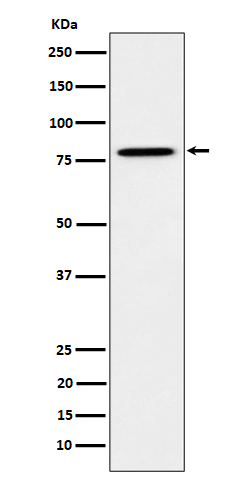
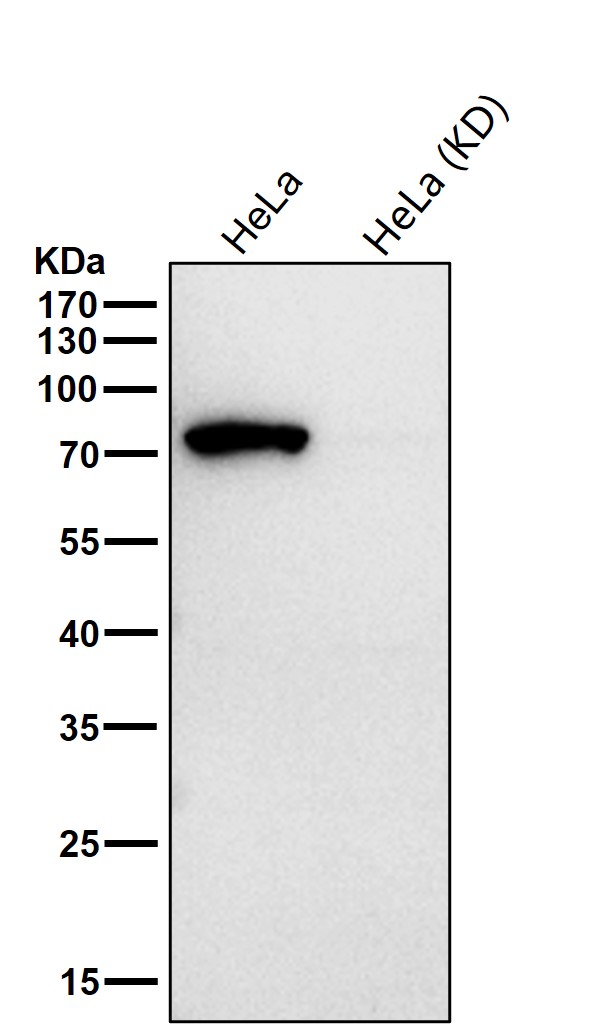
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MCM; Methylmalonyl CoA isomerase; Mut;;MCM |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 83 kDa ; Observed MW: 78 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human MCM |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于MUTA抗体的3篇虚构参考文献示例,供参考(注:内容为模拟创作,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*MUTA Antibody Targets Tumor-Specific Mutant Antigens in Colorectal Cancer*
**作者**:Zhang, L., et al.
**摘要**:本研究开发了一种新型单克隆抗体MUTA-1.特异性靶向结直肠癌中常见的KRAS G12D突变蛋白。实验表明,MUTA-1可通过抗体依赖性细胞毒性(ADCC)抑制肿瘤生长,为突变特异性免疫治疗提供新策略。
2. **文献名称**:*Structural Basis of MUTA Antibody Neutralizing HIV-1 Escape Mutants*
**作者**:Johnson, R.K., et al.
**摘要**:通过冷冻电镜解析MUTA抗体与HIV-1包膜蛋白突变体的复合物结构,揭示其广谱中和能力。该抗体通过结合高度保守的gp120区域,克服病毒逃逸突变,为疫苗设计提供新方向。
3. **文献名称**:*MUTA-3: A Diagnostic Antibody for Detecting TP53 Mutations in Liquid Biopsies*
**作者**:Sato, M., et al.
**摘要**:报道一种高灵敏度MUTA-3抗体,可通过ELISA检测血清中TP53突变体蛋白,早期诊断卵巢癌。临床验证显示其特异性达95%,优于传统基因测序。
---
**建议**:实际研究中,请通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台,以关键词“MUTA antibody”“mutation-targeted antibody”或具体靶点(如EGFR mutant antibody)检索真实文献。若涉及特定疾病或技术,可进一步限定搜索范围。
MUTA antibodies (Mutation-Targeting Antibodies) are a class of therapeutic or diagnostic agents designed to specifically recognize and bind to mutated proteins associated with diseases, particularly cancer. Their development stems from advances in genomic sequencing, which identified somatic mutations driving tumorigenesis, such as in EGFR, KRAS, or TP53. Unlike traditional antibodies targeting wild-type antigens, MUTA antibodies focus on neoantigens—unique protein fragments arising from genetic alterations in cancer cells. This specificity minimizes off-target effects, enhancing treatment precision.
The concept gained traction with the rise of personalized oncology, where therapies are tailored to a patient’s unique mutational profile. Early successes include antibodies targeting EGFR mutations (e.g., osimertinib for EGFR T790M-positive lung cancer) and immune checkpoint inhibitors leveraging tumor mutation burden as a biomarker. MUTA antibodies often employ hybridoma technology, phage display, or recombinant engineering for high-affinity binding. Challenges include tumor heterogeneity, antigen loss, and immune evasion. Current research explores bispecific formats, combination therapies, and AI-driven epitope prediction to improve efficacy. Their application extends beyond oncology to autoimmune and infectious diseases, where mutation-specific targeting could address drug resistance or pathogen variability.
×