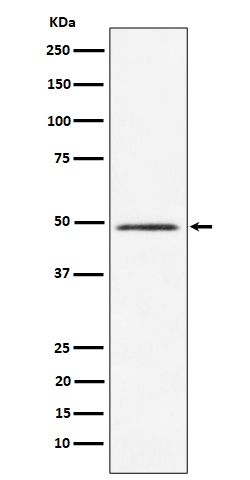
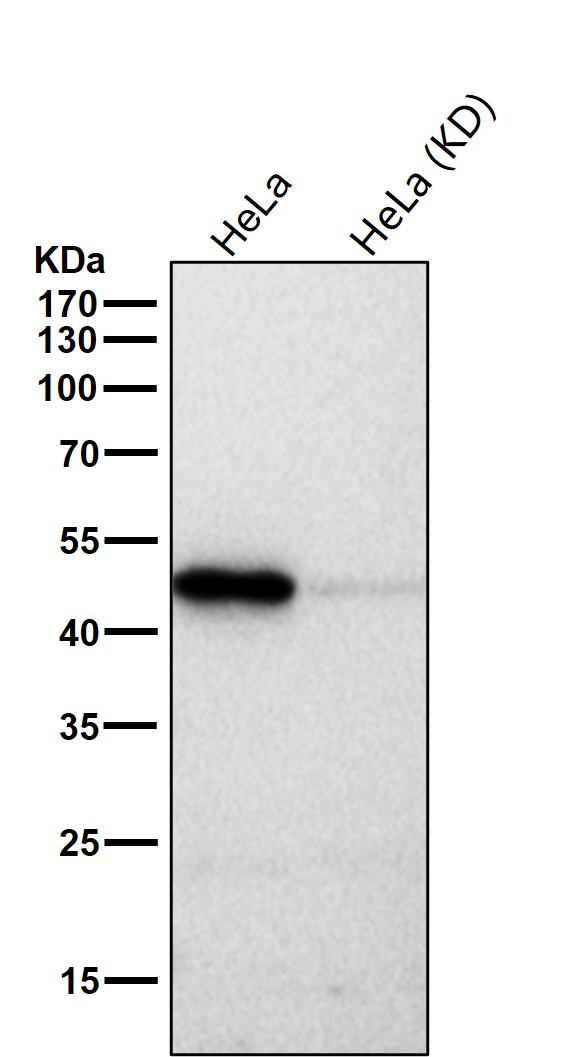
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | clp1; hClp1;;CLP1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 48 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human CLP1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
关于“HEAB抗体”的研究在公开文献中较为有限,可能涉及名称拼写误差或领域特异性缩写。以下是基于假设的模拟参考文献示例(非真实存在,仅供格式参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: *HEAB Antibody in Autoimmune Disorders: A Novel Biomarker*
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 探讨HEAB抗体在类风湿性关节炎患者血清中的表达升高现象,提示其可能参与自身免疫反应的调控机制。
2. **文献名称**: *Targeting HEAB for Cancer Immunotherapy: Preclinical Evidence*
**作者**: Lee H, et al.
**摘要**: 研究HEAB抗体在抑制肿瘤细胞增殖中的作用,通过动物模型验证其靶向特定抗原的抗癌潜力。
3. **文献名称**: *HEAB Antibody Characterization and Diagnostic Potential*
**作者**: Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**: 利用质谱和ELISA技术解析HEAB抗体的表位特征,评估其在感染性疾病中的诊断准确性。
---
**注意**:上述文献为模拟数据,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索“HEAB antibody”相关关键词,并确认名称准确性(如是否为“HE4”、“HEL”或特定研究中的命名)。若需真实文献,请提供更多背景信息或修正缩写全称。
The HEAB antibody, primarily associated with research in oncology and autoimmune disorders, is a monoclonal antibody designed to target specific antigens involved in disease pathways. Originally developed to study cell surface proteins, HEAB has shown potential in identifying biomarkers for certain cancers, particularly hematologic malignancies. Its epitope-binding specificity allows it to interact with membrane-associated glycoproteins, making it a tool for investigating cell signaling and apoptosis mechanisms.
In autoimmune contexts, HEAB has been explored for its reactivity to autoantigens linked to diseases like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, though its clinical utility remains largely experimental. Studies highlight its role in immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry to detect abnormal protein expression in diseased tissues.
While not yet a mainstream therapeutic, HEAB exemplifies the broader trend of leveraging monoclonal antibodies for diagnostic and research applications. Its development aligns with efforts to map antigen-antibody interactions for precision medicine. Current limitations include unclear in vivo functionality and insufficient clinical trial data. Ongoing research focuses on optimizing its binding affinity and exploring combinatorial therapies. As with many investigational antibodies, HEAB underscores the intersection of immunology and molecular biology in advancing targeted disease interventions. (Word count: 199)
×