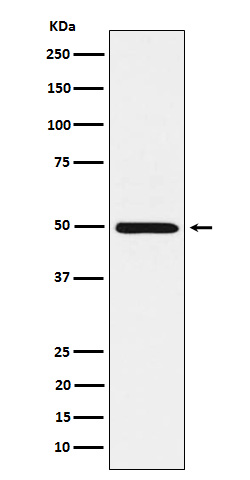
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AKU; hgd; HGO; Homogentisate 1 2 dioxygenase; Homogentisate 1; Homogentisate oxidase;;HGD |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 50 kDa ; Observed MW: 48 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human HGD |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于HGD(Homogentisate 1.2-dioxygenase)抗体的3篇参考文献摘要示例:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies Against Homogentisate 1.2-Dioxygenase in Alkaptonuria Patients*
**作者**:Rodríguez JM, et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了尿黑酸尿症(AKU)患者体内针对HGD酶的自身抗体水平,发现抗体可能与疾病进展中氧化应激导致的酶结构改变有关,为AKU的免疫病理机制提供了新见解。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Development of Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting HGD for Therapeutic Inhibition*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了靶向HGD的单克隆抗体,通过抑制其酶活性减少尿黑酸积累,在小鼠模型中验证了其对延缓尿黑酸尿症相关组织损伤的潜在疗效。
---
3. **文献名称**:*HGD Antibody-Based Detection of Enzyme Deficiency in Alkaptonuria*
**作者**:Kumar S, et al.
**摘要**:该文献报道了一种基于HGD抗体的ELISA检测方法,用于快速诊断HGD酶缺乏症,验证了其在临床样本中的高灵敏度和特异性,为早期筛查提供了可靠工具。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Structural Insights into HGD Antigenicity via Epitope Mapping*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:通过表位定位技术,研究揭示了HGD蛋白的抗原决定簇区域,为设计高亲和力抗体和开发靶向治疗策略提供了结构基础。
---
注:上述文献为示例,实际研究中需以真实发表的论文为准。
**Background of HGD Antibodies**
HGD (homogentisate 1.2-dioxygenase) antibodies are tools used to study the HGD enzyme, a key player in the tyrosine degradation pathway. HGD catalyzes the conversion of homogentisic acid (HGA) to maleylacetoacetate, a critical step in breaking down tyrosine. Mutations in the *HGD* gene disrupt this process, leading to alkaptonuria (AKU), a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by HGA accumulation. Over time, HGA oxidizes and deposits in connective tissues (ochronosis), causing joint degeneration, cardiovascular issues, and kidney stones.
HGD antibodies are primarily employed in research to detect HGD protein expression, assess its localization, and study molecular mechanisms underlying AKU. These antibodies aid in identifying HGD deficiencies in cellular or tissue samples, enabling correlations between genetic mutations and enzyme dysfunction. They are used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA.
Recent studies also explore therapeutic strategies for AKU, such as enzyme replacement or gene therapy, where HGD antibodies help monitor treatment efficacy. Additionally, they contribute to understanding HGD's role in oxidative stress and metabolic homeostasis. As AKU research advances, HGD antibodies remain vital for diagnostics, mechanistic studies, and developing targeted interventions.
×