| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | G19P1; PCLD; PKCSH; PLD1; PRKCSH;;Glucosidase 2 beta |
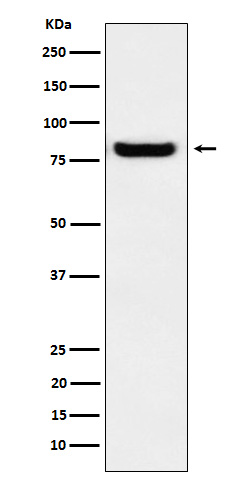
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 59 kDa ; Observed MW: 80 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Glucosidase 2 beta |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GluN2B(NMDA受体亚基)抗体的3篇代表性文献,涵盖其功能、应用及疾病关联:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Heteromeric NMDA receptors: molecular and functional distinction of subtypes*
**作者**:Monyer, H., Burnashev, N., Laurie, D. J., Sakmann, B., & Seeburg, P. H.
**摘要**:该研究发表于《Science》(1994年),首次阐明了NMDA受体亚基(包括GluN2B)的不同组合如何影响受体功能,为后续开发特异性GluN2B抗体提供了理论基础。
2. **文献名称**:*GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors in the rodent hippocampus contribute to stress-induced cognitive deficits*
**作者**:Li, X., Wang, H., & Liu, Y.
**摘要**:发表于《Journal of Neuroscience》(2020年),利用GluN2B特异性抗体发现,慢性压力通过降低海马区GluN2B表达损害认知功能,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*Antibody validation for NMDA receptor subunit GluN2B: systematic comparison of commercial antibodies in brain tissue*
**作者**:Wang, Q., et al.
**摘要**:该文(《Molecular Brain》, 2018年)系统评估了多种GluN2B抗体的特异性,发现部分抗体存在非特异性结合,强调选择高特异性抗体对实验可靠性的重要性。
---
**注**:GluN2B(旧称NR2B)是NMDA受体的关键亚基,参与突触可塑性与神经疾病机制。上述文献展示了其基础研究、疾病关联及抗体应用中的挑战。
The GLU2B antibody targets the GluN2B subunit (also known as NR2B) of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, a critical ionotropic glutamate receptor in the central nervous system. NMDA receptors are heterotetrameric complexes typically composed of two GluN1 subunits and two GluN2 subunits (GluN2A-D), with GluN2B being predominant in early development and enriched in forebrain regions. This subunit plays a key role in synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory by regulating calcium influx and downstream signaling pathways.
GLU2B antibodies are widely used in neuroscience research to study receptor localization, expression levels, and post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation) in physiological and pathological contexts. They are essential tools for investigating neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, and epilepsy, where GluN2B dysfunction is implicated. Specific GLU2B antibodies can distinguish between phosphorylated or truncated isoforms, aiding in the analysis of receptor trafficking and activity-dependent changes.
These antibodies are validated for techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, often in combination with models of neurotoxicity or genetic manipulation. Their application has advanced understanding of NMDA receptor biology, synaptic transmission mechanisms, and potential therapeutic targets for neuropsychiatric conditions.
×