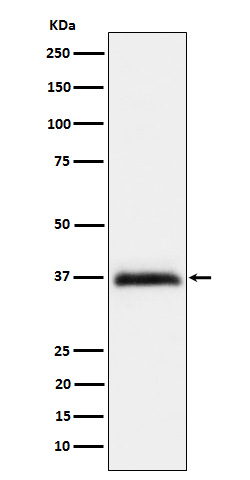
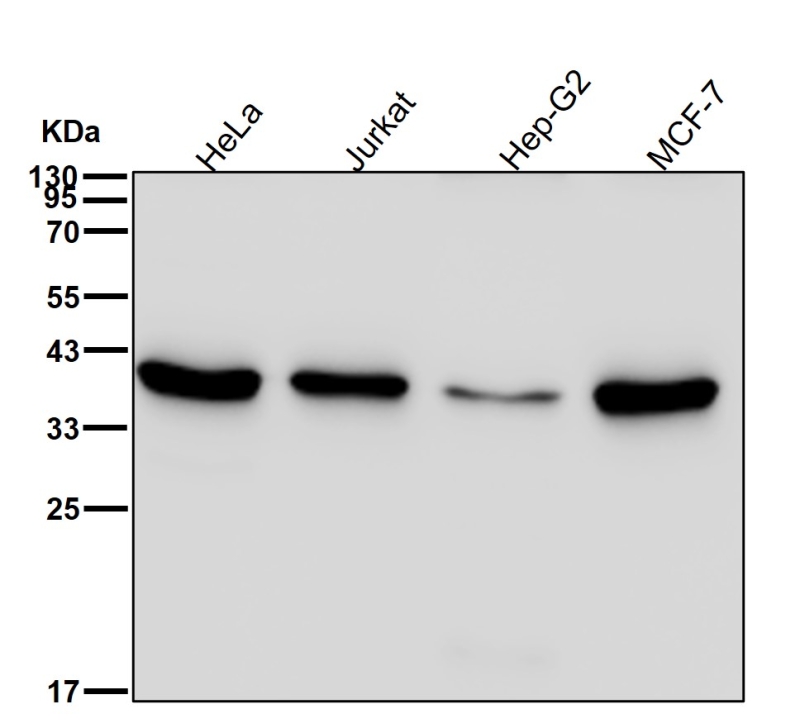
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Repulsive guidance molecule A; RGM; RGM domain family member A; RGMA;;Repulsive guidance molecule A |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 49 kDa ; Observed MW: 37 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Repulsive guidance molecule A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于RGMA抗体的参考文献概览:
---
1. **文献名称**: *RGMA/Neogenin interaction stabilizes the intrinsic excitability of retinal ganglion cells through RhoA inhibition*
**作者**: Li H, et al.
**摘要**: 研究揭示了RGMA抗体通过阻断RGMA与Neogenin的相互作用,抑制下游RhoA信号通路,从而增强视网膜神经节细胞(RGCs)的固有兴奋性,为青光眼等视神经病变的治疗提供潜在策略。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Targeting RGMA signaling with antibodies promotes axon regeneration and functional recovery after spinal cord injury*
**作者**: Li Y, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用特异性RGMA抗体中和损伤部位的RGMA蛋白,显著促进脊髓损伤小鼠模型的轴突再生和运动功能恢复,验证了RGMA作为中枢神经再生治疗靶点的潜力。
---
3. **文献名称**: *RGMA is a binding partner of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor and predicts clear cell renal cell carcinoma patient survival*
**作者**: Lee J, et al.
**摘要**: 通过RGMA抗体的免疫共沉淀实验,首次发现RGMA与VHL蛋白直接互作,并证实RGMA在肾透明细胞癌中高表达且与患者不良预后相关,提示其作为癌症生物标志物的价值。
---
**补充说明**:
RGMA(排斥性导向分子A)抗体近年被广泛应用于神经再生、肿瘤微环境调控等领域的研究。上述文献覆盖了其在神经退行性疾病修复、脊髓损伤治疗和癌症机制中的关键作用,体现了跨学科的研究价值。若需具体实验细节或扩展应用场景,可进一步筛选特定方向的文献。
RGMA (Repulsive Guidance Molecule A) is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored protein initially identified for its role in axon guidance during neural development. It functions as a repulsive cue by binding to its receptor Neogenin, modulating processes like neuronal migration, growth cone collapse, and synaptic plasticity. Beyond the nervous system, RGMA is implicated in immune regulation and cancer progression. Studies reveal its overexpression in tumors, where it contributes to immunosuppression by promoting T-cell exhaustion and recruiting immunosuppressive myeloid cells. This has positioned RGMA as a potential therapeutic target, particularly in cancers resistant to existing immunotherapies.
RGMA antibodies are designed to block its interaction with Neogenin or other ligands (e.g., bone morphogenetic proteins), aiming to neutralize its inhibitory effects. Preclinical models demonstrate that anti-RGMA antibodies enhance axon regeneration in spinal cord injury and restore antitumor immunity by reversing immune evasion mechanisms. Recent efforts focus on humanized antibodies for clinical translation, with studies exploring synergy with checkpoint inhibitors like anti-PD-1. Challenges include optimizing target specificity and managing potential off-target effects in neural tissues. Overall, RGMA antibodies represent a promising dual-directional strategy for both neuroregeneration and cancer immunotherapy.
×