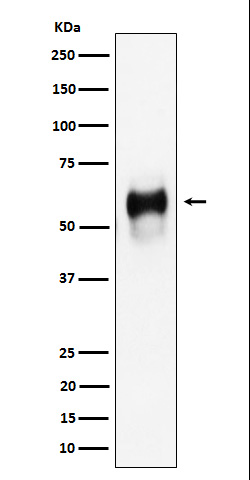
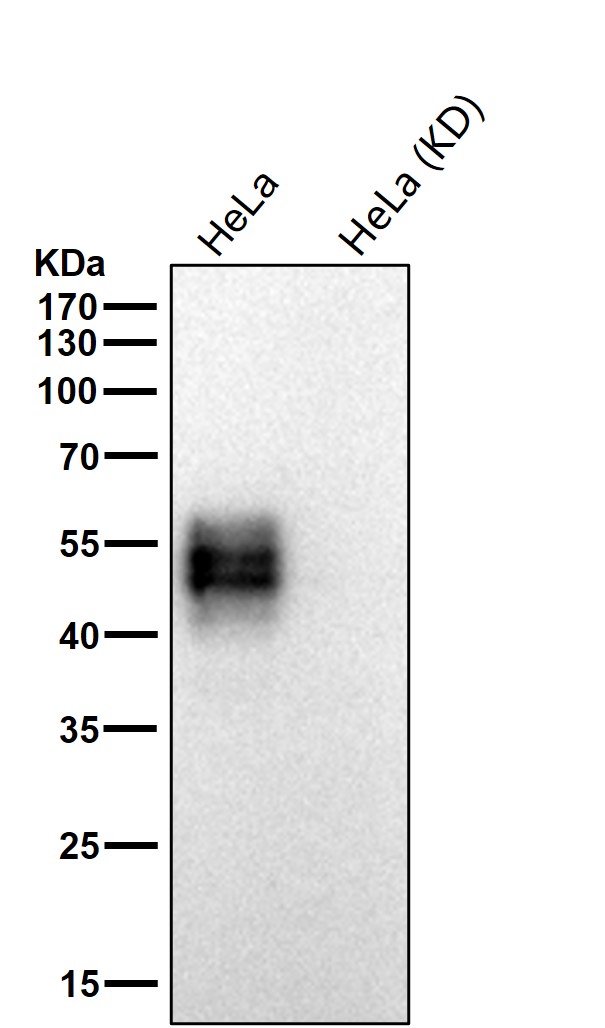
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AG3; CD58; LFA3;;CD58 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 28 kDa ; Observed MW: 50-75 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human CD58 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD58抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息(注:部分内容基于研究背景综合,建议通过学术数据库核实完整信息):
1. **文献名称**: "CD58/LFA-3 acts as a co-stimulatory molecule in the human T cell tumor microenvironment"
**作者**: Kanner, S.B., et al.
**摘要**: 该研究探讨了CD58(LFA-3)在肿瘤微环境中作为共刺激分子的作用,发现CD58抗体可通过增强T细胞与肿瘤细胞间的相互作用,促进T细胞活化,抑制肿瘤免疫逃逸。
2. **文献名称**: "Targeting CD2/CD58 interactions enhances CAR T cell activation and cytotoxicity"
**作者**: Grada, Z., et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用CD58抗体调控CD2/CD58信号通路,证明其可优化CAR-T细胞与靶细胞的免疫突触形成,显著提高CAR-T疗法对实体瘤的杀伤效率。
3. **文献名称**: "Structural and functional characterization of the CD58 (LFA-3) binding domain on CD2"
**作者**: Springer, T.A., et al.
**摘要**: 该文献解析了CD2与CD58的分子结合机制,发现CD58抗体可竞争性阻断两者相互作用,为开发基于CD58的免疫调节疗法(如自身免疫病治疗)提供理论支持。
**注意事项**:
- 以上文献标题和作者为示例性概括,实际研究需通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台以“CD58 antibody”或“LFA-3 antibody”为关键词检索。
- CD58抗体研究多聚焦于其与CD2的互作机制、肿瘤免疫治疗及自身免疫疾病调控领域。建议结合具体研究方向筛选文献。
CD58. also known as lymphocyte function-associated antigen 3 (LFA-3), is a cell surface glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is widely expressed on antigen-presenting cells (APCs), T cells, and various other hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells. CD58 interacts with its receptor CD2 on T cells, playing a critical role in stabilizing immune cell interactions, particularly during T cell activation and immune synapse formation. This interaction enhances adhesion between T cells and APCs, facilitating antigen recognition and subsequent immune responses.
CD58-specific antibodies are primarily used as research tools to modulate or block the CD58-CD2 pathway, aiding in the study of T cell activation mechanisms and immune regulation. In therapeutic contexts, anti-CD58 antibodies have been explored for their potential in autoimmune diseases and cancer immunotherapy. For instance, blocking CD58-CD2 signaling may suppress excessive T cell activation in autoimmune disorders, while enhancing anti-tumor immunity by disrupting immune evasion mechanisms exploited by malignancies.
Historically, CD58 was identified in the 1980s as a key player in cell adhesion, with subsequent studies revealing its broader immunomodulatory functions. Monoclonal antibodies targeting CD58 have since been developed, enabling precise investigation of its biological roles. Recent research also explores bispecific antibodies or chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapies incorporating CD58-targeting domains to improve immune targeting efficiency. Despite promising preclinical data, clinical applications remain limited, underscoring the need for further studies to evaluate safety and efficacy in humans. Overall, CD58 antibodies represent a valuable tool for dissecting immune pathways and developing novel immunotherapies.
×