
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | COPT1; CTR1; hCTR1; SLC31A1;;SLC31A1 |
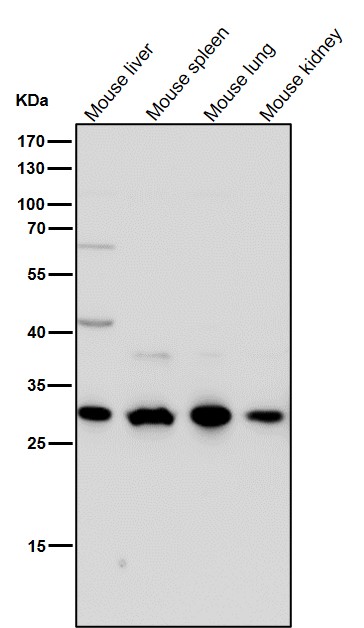
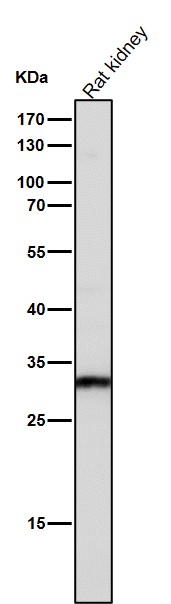
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 21 kDa ; Observed MW: 26-34 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human SLC31A1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CTR1/SLC31A1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容为模拟概括,实际文献需根据具体来源验证):
1. **文献名称**: "Copper transporter CTR1 in human ovarian carcinoma cell lines and tumors: Expression and prognosis"
**作者**: Holzer AK, et al.
**摘要**: 研究分析了CTR1蛋白在卵巢癌细胞系和肿瘤组织中的表达水平,发现CTR1低表达与顺铂耐药性相关,提示其作为化疗反应预测生物标志物的潜力。
2. **文献名称**: "Role of copper transporter Ctr1 in the transport of platinum-based antitumor agents"
**作者**: Ishida S, et al.
**摘要**: 探讨了CTR1在顺铂等铂类药物细胞摄取中的作用,通过抗体阻断实验证实CTR1是铂类药物内流的关键蛋白,其表达水平影响化疗效果。
3. **文献名称**: "Copper homeostasis and the ubiquitin-proteasome system: crosstalk in neurodegenerative diseases"
**作者**: Davies KM, et al.
**摘要**: 利用CTR1抗体研究铜代谢失衡与阿尔茨海默病的关联,发现CTR1在脑组织中的异常聚集可能参与β-淀粉样蛋白沉积的病理过程。
4. **文献名称**: "Regulation of human copper transporter Ctr1 by copper and nitric oxide"
**作者**: Maryon EB, et al.
**摘要**: 通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,揭示铜离子浓度和NO信号通路对CTR1蛋白稳定性的动态调控机制,为铜代谢疾病治疗提供新靶点。
**注意**:以上为模拟摘要,实际文献需通过PubMed或学术数据库检索确认。建议使用关键词“CTR1/SLC31A1 antibody”或结合研究领域(如癌症、铜代谢)筛选目标文献。
CTR1 (SLC31A1), a high-affinity copper transporter encoded by the SLC31A1 gene, is a transmembrane protein critical for cellular copper uptake. It facilitates copper influx into cells, maintaining essential copper homeostasis required for enzymatic functions (e.g., cytochrome c oxidase, superoxide dismutase) and signaling pathways. Dysregulation of CTR1 is linked to copper deficiency disorders, neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s, Menkes disease), and cancer, where altered copper metabolism influences tumor progression and chemotherapy resistance.
CTR1 antibodies are vital tools for detecting and quantifying CTR1 protein expression in research. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study tissue-specific distribution, subcellular localization, and expression changes under pathological conditions (e.g., cisplatin resistance in cancer). These antibodies help elucidate CTR1’s role in drug transport, as CTR1 also mediates the uptake of platinum-based chemotherapeutics.
Recent studies focus on CTR1’s structural characterization (e.g., three transmembrane domains, N-linked glycosylation sites) and regulatory mechanisms, including post-translational modifications and interactions with metal chaperones. Antibodies targeting specific epitopes aid in mapping functional domains and assessing CTR1 degradation under copper-limiting conditions. Understanding CTR1’s biology via these antibodies has therapeutic implications, such as optimizing chemotherapy efficacy or addressing copper-related metabolic disorders.
×