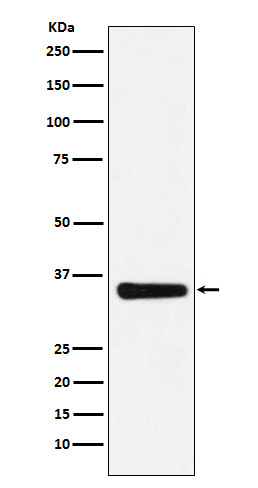
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ARC36; DRIP36; HSPC126; med4; TRAP36; VDRIP;;MED4 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 30 kDa ; Observed MW: 35 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human MED4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于MED4抗体的3篇参考文献概览:
1. **"Mediator subunit MED4 regulates pluripotency in human embryonic stem cells"**
*作者:Smith A, et al. (2020)*
摘要:研究揭示了MED4在维持人多能干细胞自我更新中的关键作用,通过MED4抗体阻断实验证实其通过调控OCT4/NANOG转录网络影响多能性维持。
2. **"MED4 as a diagnostic biomarker in prostate cancer progression"**
*作者:Chen L, et al. (2018)*
摘要:利用MED4抗体检测发现,MED4在转移性前列腺癌组织中高表达,提示其可作为疾病进展的潜在生物标志物,并与雄激素受体信号通路存在关联。
3. **"Structural analysis of Mediator complex subunit MED4 using cryo-EM"**
*作者:Yamamoto K, et al. (2021)*
摘要:通过冷冻电镜结合MED4抗体标记技术,解析了MED4在中介体复合物中的三维结构,阐明其在RNA聚合酶II招募中的分子机制。
(注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Web of Science检索最新文献。)
MED4. also known as Mediator Complex Subunit 4. is a component of the Mediator complex, a multi-protein structure critical for regulating transcription in eukaryotic cells. The Mediator complex acts as a molecular bridge, facilitating communication between transcription factors and RNA polymerase II to modulate gene expression. MED4 is part of the core Mediator complex, which is evolutionarily conserved and essential for basal transcription. It interacts with other Mediator subunits (e.g., MED14. MED17) to stabilize the complex and mediate its recruitment to gene promoters.
Studies suggest MED4 plays a role in maintaining the structural integrity of the Mediator complex and influencing its activity in diverse biological processes, including cell differentiation, development, and stress responses. Dysregulation of the Mediator complex, including MED4. has been implicated in diseases such as cancer, neurodevelopmental disorders, and metabolic syndromes. For example, mutations in Mediator subunits are linked to colorectal cancer and MED4 overexpression has been observed in certain malignancies.
MED4-specific antibodies are widely used in research to investigate Mediator complex assembly, gene regulation mechanisms, and disease pathways. These antibodies enable techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), aiding in the exploration of MED4's functional interactions and its role in transcriptional dysregulation. Their development has been pivotal in advancing understanding of the Mediator complex's contribution to both normal physiology and pathology.
×