| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Cspg3; Ncan; NEUR; Neurocan core protein;;Neurocan |
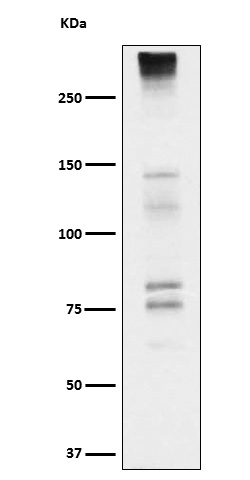
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 143 kDa ; Observed MW: 130270 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Neurocan |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Neurocan抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**: "Purification and characterization of developmentally regulated chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans expressed in embryonic brain"
**作者**: Rauch U. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究纯化了胚胎大鼠脑中的Neurocan蛋白,并制备了特异性抗体。通过免疫化学分析,揭示了Neurocan在神经发育过程中的时空表达模式,证实其作为硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖在中枢神经系统细胞黏附中的调控作用。
2. **文献名称**: "Neurocan is upregulated in injured brain and in cytokine-treated astrocytes"
**作者**: Asher R.A. et al.
**摘要**: 文章利用Neurocan抗体检测其在脑损伤后的表达变化,发现Neurocan在胶质瘢痕中显著上调,且炎性因子(如TGF-β)可诱导星形胶质细胞分泌Neurocan,提示其参与抑制轴突再生。
3. **文献名称**: "The chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans neurocan and phosphacan are expressed by reactive astrocytes in the chronic CNS glial scar"
**作者**: Matsui F. et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化结合Neurocan抗体,研究证明Neurocan在慢性胶质瘢痕中由反应性星形胶质细胞持续表达,可能通过抑制神经元突触可塑性影响中枢神经系统的修复。
4. **文献名称**: "Binding of tenascin-R and neurocan to phosphacan creates a ternary complex influencing neurite extension"
**作者**: Milev P. et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用Neurocan抗体探究其与tenascin-R、phosphacan的相互作用,发现三者形成的复合物可调节神经元突触生长,为Neurocan在神经再生中的抑制机制提供了分子层面的解释。
这些文献均涉及Neurocan抗体的实验应用,涵盖发育、损伤修复及分子机制等领域。
Neurocan antibodies are essential tools in neuroscience research, specifically targeting neurocan, a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan (CSPG) predominantly expressed in the central nervous system (CNS). Neurocan, a member of the lectican family, plays critical roles during brain development by regulating neuronal migration, axon guidance, and synaptic plasticity. It is highly abundant in the extracellular matrix (ECM) of developing brains but decreases in adulthood, though its expression can be upregulated following CNS injury or in neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease. Neurocan interacts with other ECM components and cell surface receptors, influencing cell adhesion and signaling pathways.
Antibodies against neurocan enable researchers to detect and study its spatial-temporal distribution, functional interactions, and involvement in pathological processes. They are widely used in techniques such as immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and immunofluorescence to visualize neurocan in tissue sections or cultured cells. These antibodies have been instrumental in exploring neurocan’s dual role: while it inhibits axonal regeneration post-injury by creating a growth-restrictive environment, it also supports neuroprotection and ECM remodeling. Additionally, neurocan antibodies aid in investigating its potential as a biomarker for neurological disorders and in evaluating therapeutic strategies targeting CSPGs to enhance neural repair. Most neurocan antibodies are raised against specific epitopes in its core protein, ensuring specificity across species like humans, mice, and rats.
×