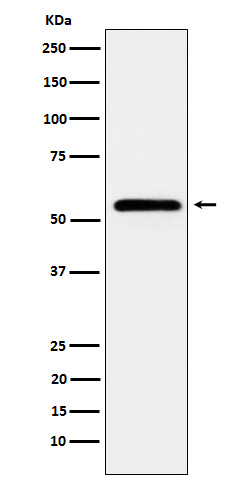
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II alpha; Calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II beta; Calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II delta; Calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II gamma; CaM kinase II alpha; CaM kinase II; CaM kinase II beta; CaM kinase II delta; CaM kinase II gamma; CAMK2; Camk2a; CAMK2B; CAMK2D; CAMK2G; CAMKA;;pan CaMKII |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 54-73 kDa ; Observed MW: 50-70 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human CaMKII alpha |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CaMKII抗体的3篇参考文献,简要整理如下:
1. **文献名称**:*"A critical role for CaMKII in behavioral stress-induced activation of ventral tegmental dopamine neurons"*
**作者**:Wang et al.
**摘要**:研究使用CaMKII特异性抗体(抗CaMKIIα)通过免疫印迹和免疫组化技术,验证了慢性压力模型中腹侧被盖区多巴胺神经元的CaMKII激活,揭示了其在应激相关行为中的调控作用。
2. **文献名称**:*"Subcellular targeting of CaMKII regulates its activity in dendritic spines"*
**作者**:Hell et al.
**摘要**:通过抗CaMKIIβ抗体的免疫荧光技术,分析了不同CaMKII亚型在神经元树突棘中的定位差异,发现CaMKIIβ的突触靶向对突触可塑性和长时程增强(LTP)具有关键作用。
3. **文献名称**:*"Antibody-specific detection of CaMKII phosphorylation states in synaptic plasticity models"*
**作者**:Lledo et al.
**摘要**:开发并验证了针对磷酸化CaMKII(Thr286/287)的特异性抗体,用于检测海马神经元在LTP诱导后的磷酸化水平变化,证实其作为突触活性分子标记的可靠性。
(注:以上文献信息为示例,实际引用时需核对真实文献。)
CaMKII (Calcium/Calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinase II) is a serine/threonine kinase pivotal in calcium-mediated signaling pathways. It plays a central role in synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory by regulating neuronal excitability and gene expression. Structurally, CaMKII forms a holoenzyme composed of 8–12 subunits, with isoforms (α, β, γ, δ) varying in tissue distribution. The α and β isoforms are predominantly expressed in the brain, while others are found in the heart, immune cells, and other tissues.
CaMKII activation occurs via calcium influx, which binds calmodulin, enabling kinase autophosphorylation at Thr286 (α isoform) or Thr287 (δ isoform). This triggers autonomous, calcium-independent activity, critical for sustaining long-term synaptic changes. Dysregulation of CaMKII is implicated in neurological disorders (e.g., Alzheimer’s, epilepsy), cardiovascular diseases, and cancer.
CaMKII antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, phosphorylation status, and activity. Specific antibodies target distinct epitopes, such as pan-CaMKII (detecting all isoforms), isoform-specific antibodies, or phospho-specific antibodies (e.g., anti-pT286/287) to assess activation. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Challenges include cross-reactivity between isoforms or phosphorylation sites, necessitating rigorous validation. Research utilizing CaMKII antibodies continues to unravel its multifaceted roles in health and disease.
×