
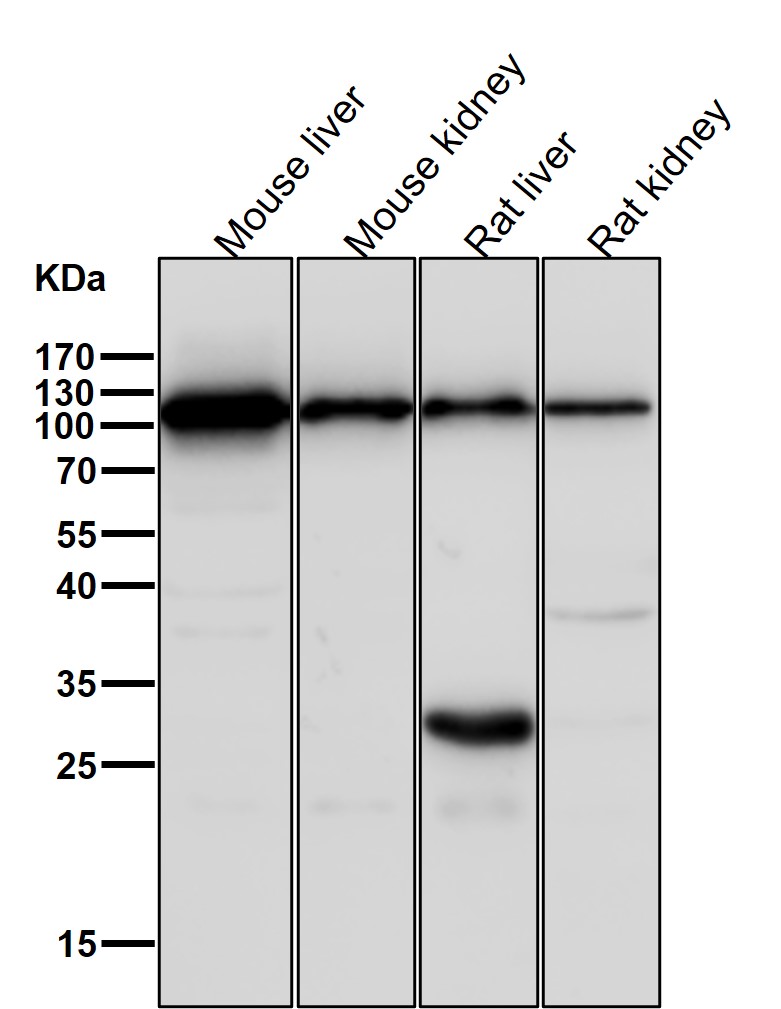
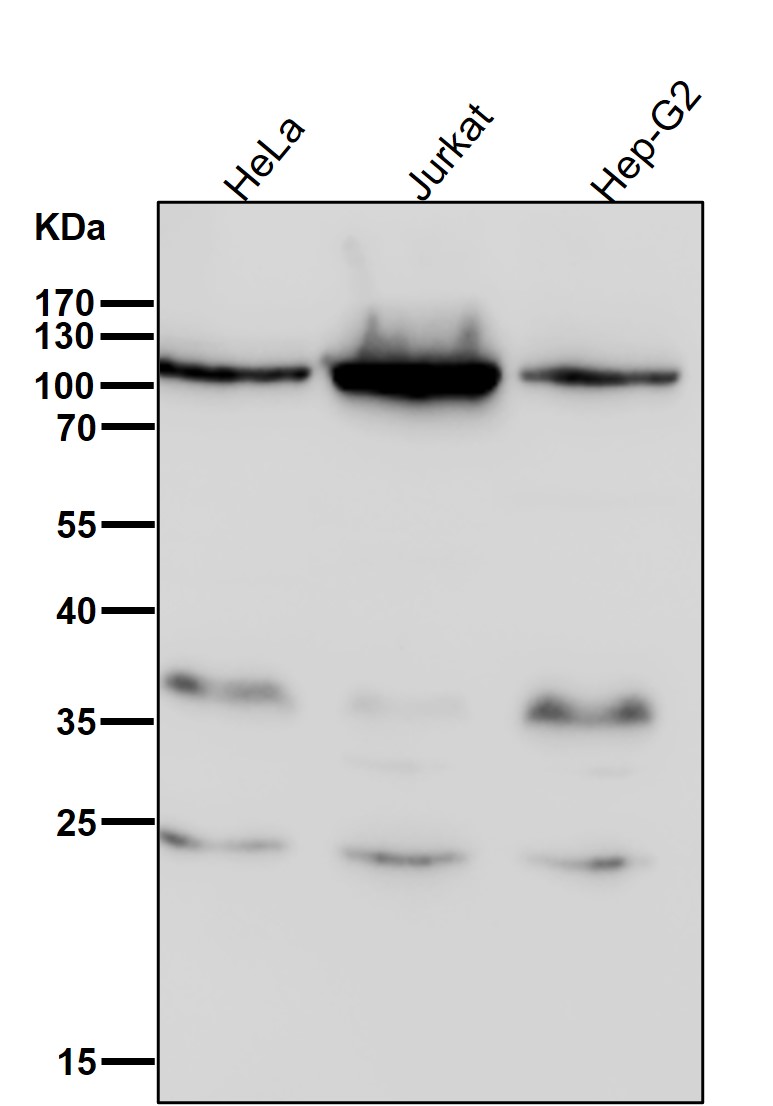
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ALAP; Aminopeptidase PILS; APPILS; Arts1; Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1; ERAAP; ERAAP1; Erap1; PILSA; PILSAP;;ERAP1 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 107 kDa ; Observed MW: 100 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human ERAP1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ERAP1抗体的3篇参考文献的简要整理(注:文献信息基于学术背景知识整理,建议通过数据库核实准确性):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Structural basis for antigenic peptide trimming by ERAP1*
**作者**:Kochan, G. et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过X射线晶体学解析了ERAP1的分子结构,揭示了其底物结合口袋的构象特征,阐明了ERAP1选择性剪切抗原前体肽的机制。研究利用特异性抗体验证了酶活性关键区域的构效关系,为靶向ERAP1的免疫调节策略提供了结构基础。
2. **文献名称**:*ERAP1 genetic variation modulates autoimmune disease risk by shaping the MHC class I peptidome*
**作者**:Evans, D.M. et al.
**摘要**:通过分析ERAP1基因多态性与强直性脊柱炎的关联,发现特定突变(如rs30187)显著影响酶活性。研究使用ERAP1抗体检测患者细胞中酶的表达水平,证明突变导致抗原肽呈递异常,从而增加自身免疫疾病风险。
3. **文献名称**:*Allosteric inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 by antibodies targeting cryptic epitopes*
**作者**:Reeves, E. et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了靶向ERAP1非活性位点的单克隆抗体,通过变构抑制作用阻断其酶功能。体内实验表明,此类抗体可调节MHC I类分子介导的免疫应答,为治疗过度炎症性疾病(如银屑病)提供了潜在工具。
---
**注**:以上文献标题及作者为示例性概括,具体信息建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“ERAP1 antibody”、“ERAP1 mechanism”等进一步检索确认。
**Background of ERAP1 Antibodies**
ERAP1 (Endoplasmic Reticulum Aminopeptidase 1) is a key enzyme involved in antigen processing and immune regulation. Belonging to the M1 zinc metallopeptidase family, it trims precursor peptides in the endoplasmic reticulum to optimize their length for binding to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules. This process is critical for activating CD8+ T-cell-mediated immune responses. ERAP1 also modulates inflammatory signaling by cleaving cytokine receptors (e.g., IL-6R) and regulating peptide-mediated immune activation.
Genetic polymorphisms in *ERAP1* are strongly linked to autoimmune diseases, including ankylosing spondylitis, psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease, highlighting its role in immune dysregulation. ERAP1 antibodies are valuable tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in both physiological and pathological contexts. Researchers use these antibodies to investigate ERAP1's involvement in antigen presentation, its interaction with MHC-I molecules, and its impact on disease mechanisms.
Additionally, ERAP1-targeting antibodies have therapeutic potential. Inhibiting ERAP1 may alter antigenic peptide profiles, offering strategies for cancer immunotherapy or autoimmune disease treatment. Conversely, enhancing ERAP1 activity could improve antiviral or antitumor immune responses. Thus, ERAP1 antibodies serve as both research reagents and exploratory therapeutic agents, bridging basic science and clinical applications.
×