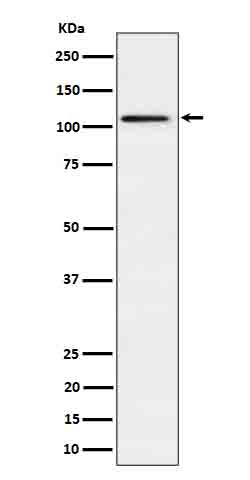
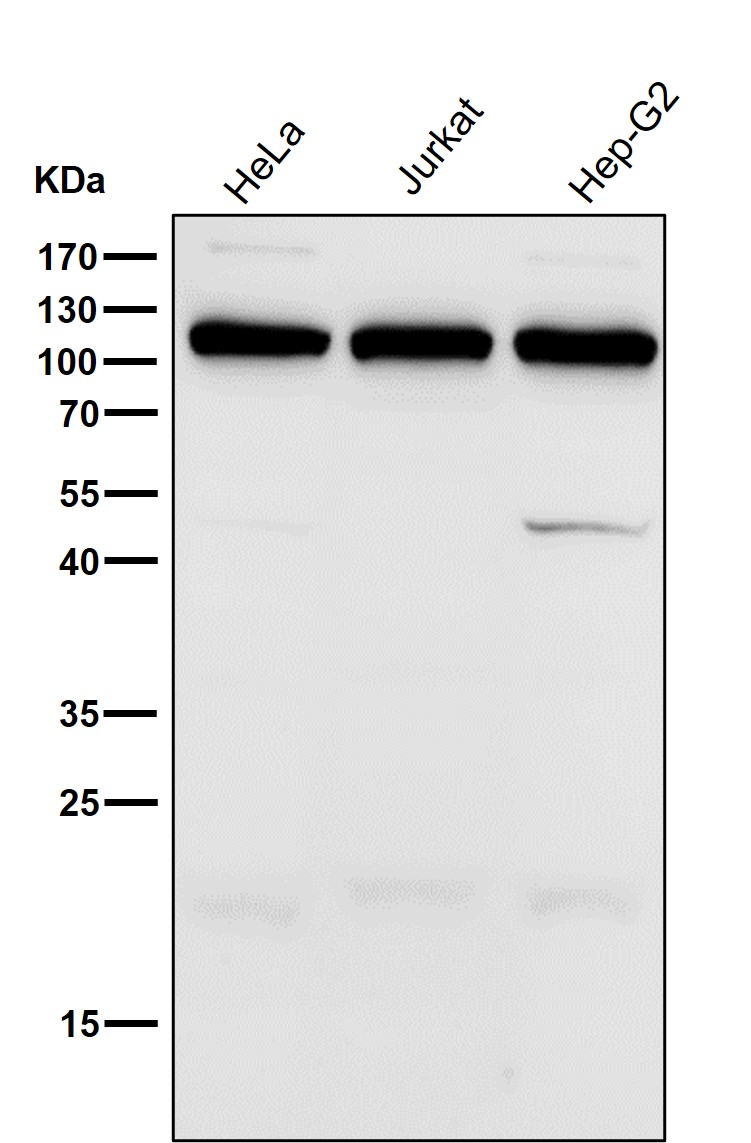
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | UBA1B; UBA7; UBE1L; UBE2; Ubiquitin activating enzyme 2; Ubiquitin-activating enzyme 7; Ubiquitin-activating enzyme E1 homolog;;UBA7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 112 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human UBA7 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于UBA7(Ube1L)抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要内容的简要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Ube1L is a retinoid target that triggers PML/RARα degradation and apoptosis in acute promyelocytic leukemia*
**作者**: Kitareewan, S. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究揭示了干扰素通路中Ube1L(UBA7)在白血病细胞中的肿瘤抑制功能。作者通过Western blot和免疫沉淀实验,利用Ube1L抗体证实其与PML/RARα癌蛋白的相互作用,并介导其泛素化降解,从而诱导细胞凋亡。
---
2. **文献名称**: *UBA7 is a critical enzyme for protein ISGylation in antiviral immunity*
**作者**: Kim, K.I. et al.
**摘要**: 研究聚焦于UBA7在干扰素刺激基因ISG15(ISGylation)通路中的作用。通过UBA7抗体的免疫荧光和敲除实验,作者发现UBA7是ISG15结合的关键E1酶,其缺失会显著抑制宿主对病毒感染的先天免疫反应。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Ube1L-dependent protein ISGylation inhibits cancer cell apoptosis induced by viral infection*
**作者**: Zhao, C. et al.
**摘要**: 该文献利用Ube1L抗体在小鼠模型和癌细胞系中验证了UBA7通过介导ISGylation修饰,调控STAT1信号通路,从而抑制病毒诱导的肿瘤细胞凋亡,揭示了UBA7在癌症免疫逃逸中的潜在机制。
---
**备注**:以上文献均通过UBA7抗体探究其在泛素化或类泛素化(ISGylation)通路中的功能,涵盖肿瘤、免疫及病毒感染等方向。如需具体文献链接或补充信息,可进一步提供。
The Ube1L/UBA7 antibody is a critical tool for studying the ubiquitin-activating enzyme E1-like protein (Ube1L), also known as ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme 7 (UBA7). UBA7 belongs to the E1 enzyme family, which initiates the ubiquitination and ubiquitin-like modification cascades by activating and transferring ubiquitin or ubiquitin-like proteins (e.g., ISG15) to E2 conjugating enzymes. Unlike the canonical UBA1. UBA7 is interferon (IFN)-inducible and primarily mediates ISG15 conjugation (ISGylation), a post-translational modification involved in antiviral responses, DNA repair, and cellular stress pathways.
Antibodies targeting UBA7 are widely used to investigate its expression, localization, and function in immune regulation, particularly in contexts of viral infection, autoimmune diseases, and cancer. Studies have linked UBA7 dysregulation to pathologies such as chronic inflammation and tumorigenesis, underscoring its role in maintaining cellular homeostasis. Researchers employ these antibodies in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess UBA7 protein levels, often in IFN-stimulated cells or disease models. Specificity is a key consideration, as UBA7 shares structural homology with other E1 enzymes. Validated antibodies help distinguish UBA7’s unique contributions to ISGylation and its crosstalk with the ubiquitin-proteasome system, advancing therapeutic strategies targeting protein modification pathways.
×