
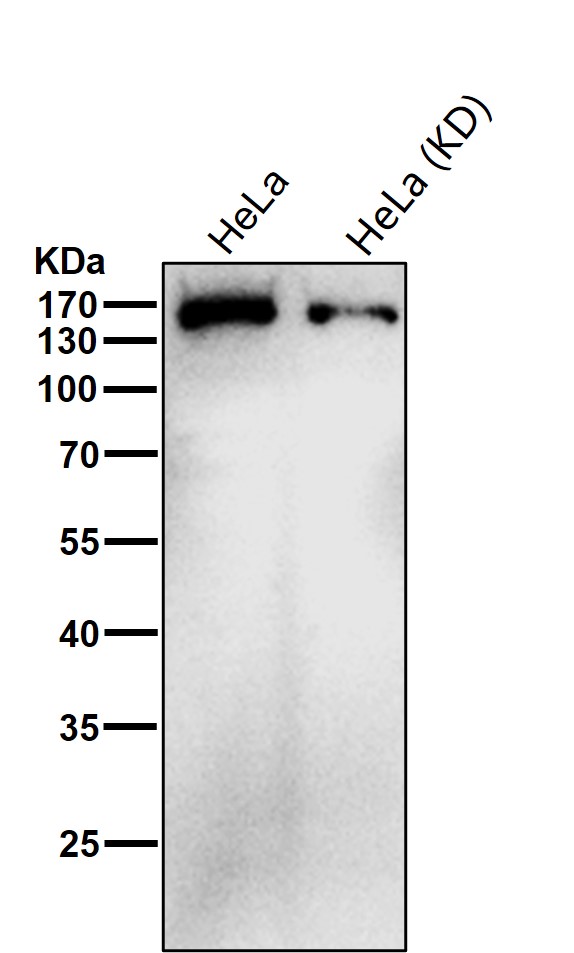
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Aminopeptidase A; APA; bp1; CD249; EAP; Enpep; Gp160; Ly51;;Glutamyl aminopeptidase |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 109 kDa ; Observed MW: 160 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Glutamyl aminopeptidase |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Aminopeptidase A/CD249抗体的代表性文献摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Aminopeptidase A: A key regulator of blood pressure through angiotensin III metabolism"*
**作者**:Reaux-Le Goazigo et al.
**摘要**:研究利用特异性抗体制备,证实APA在脑干心血管中枢的分布,并揭示其通过降解Ang III调控血压的机制,为高血压治疗提供潜在靶点。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Monoclonal antibody targeting renal aminopeptidase A ameliorates hypertension in rodent models"*
**作者**:Balavoine et al.
**摘要**:开发靶向肾脏APA的单克隆抗体,通过抑制APA活性减少血管紧张素II转化,显著降低自发性高血压大鼠的血压,提出抗体疗法的新策略。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"CD249 (aminopeptidase A) expression in tumor vasculature: A novel biomarker for anti-angiogenic therapy"*
**作者**:Mina-Osorio et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化分析CD249抗体标记的肿瘤血管,发现APA在实体瘤血管内皮特异性高表达,提示其作为抗血管生成治疗生物标志物的潜力。
---
如需更多文献或扩展应用领域(如免疫疾病),可进一步补充。
Aminopeptidase A (APA), also known as CD249 or angiotensinase, is a membrane-bound metalloprotease belonging to the M1 family of zinc-dependent enzymes. It catalyzes the cleavage of N-terminal acidic residues from peptides, notably converting angiotensin II to angiotensin III, thereby playing a role in blood pressure regulation and the renin-angiotensin system. APA is expressed on the surface of various cell types, including renal proximal tubules, vascular endothelial cells, and specific immune cells.
Antibodies targeting APA/CD249 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in physiological and pathological contexts. In research, these antibodies are utilized in techniques such as immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry, and Western blotting to investigate APA's involvement in hypertension, inflammation, and cancer. For example, elevated APA levels have been linked to tumor progression in certain cancers, such as glioblastoma, where it may influence angiogenesis and immune evasion.
Additionally, APA's role in modulating bioactive peptides highlights its potential as a therapeutic target. Anti-APA antibodies have been explored in preclinical studies for conditions like preeclampsia and hypertension. Understanding APA's regulatory mechanisms and tissue-specific expression through antibody-based assays continues to advance insights into its dual roles in homeostasis and disease, underscoring its relevance in both basic research and clinical applications.
×