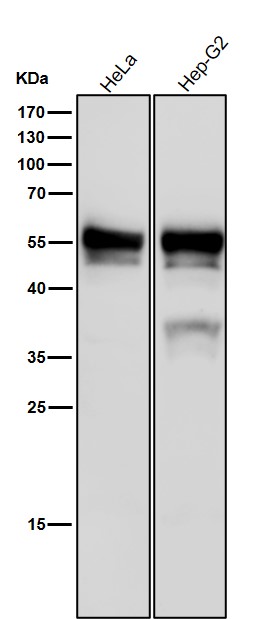
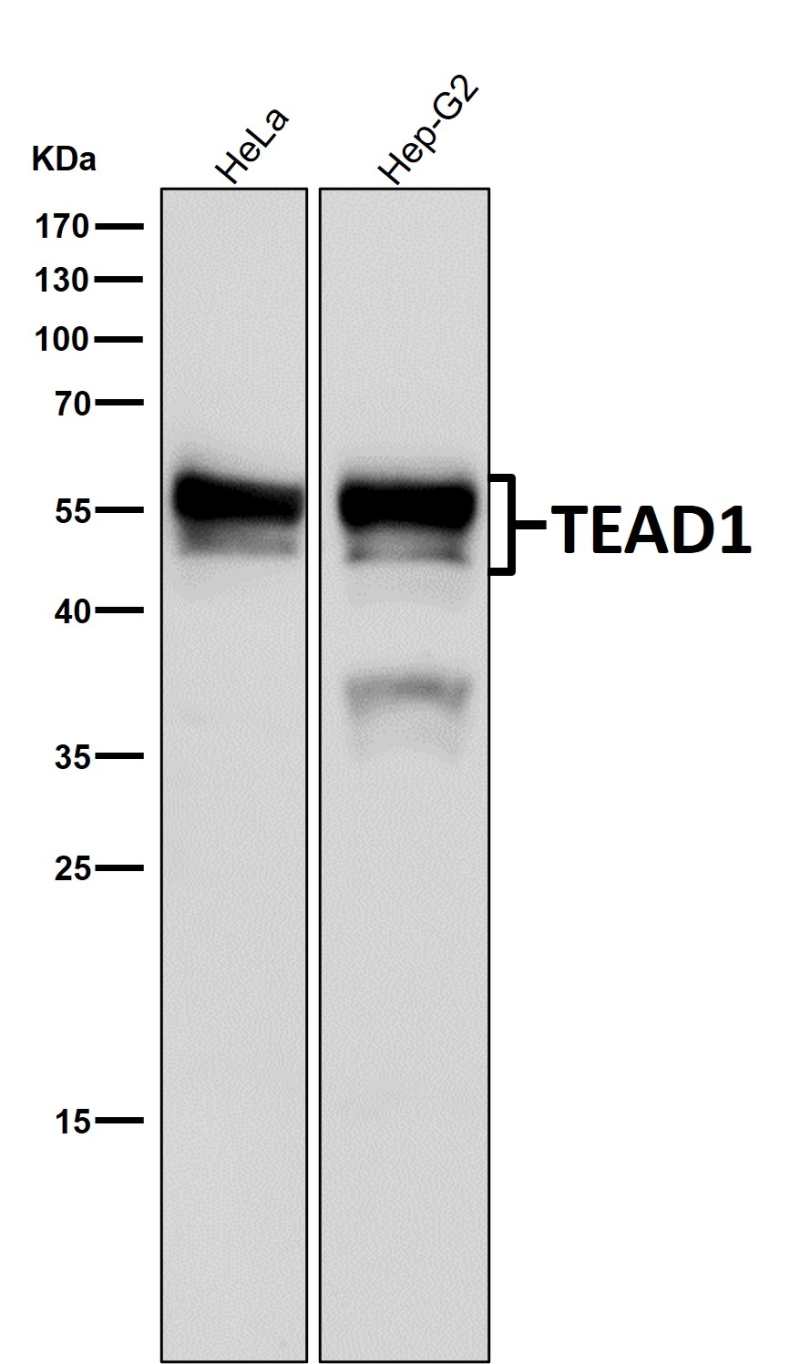
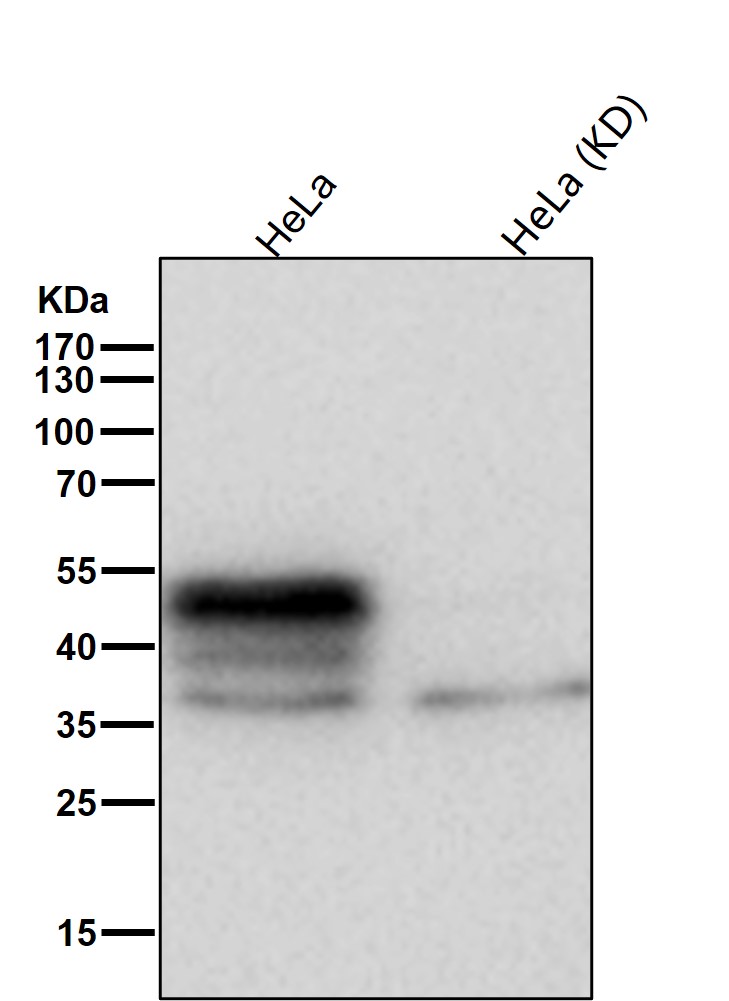
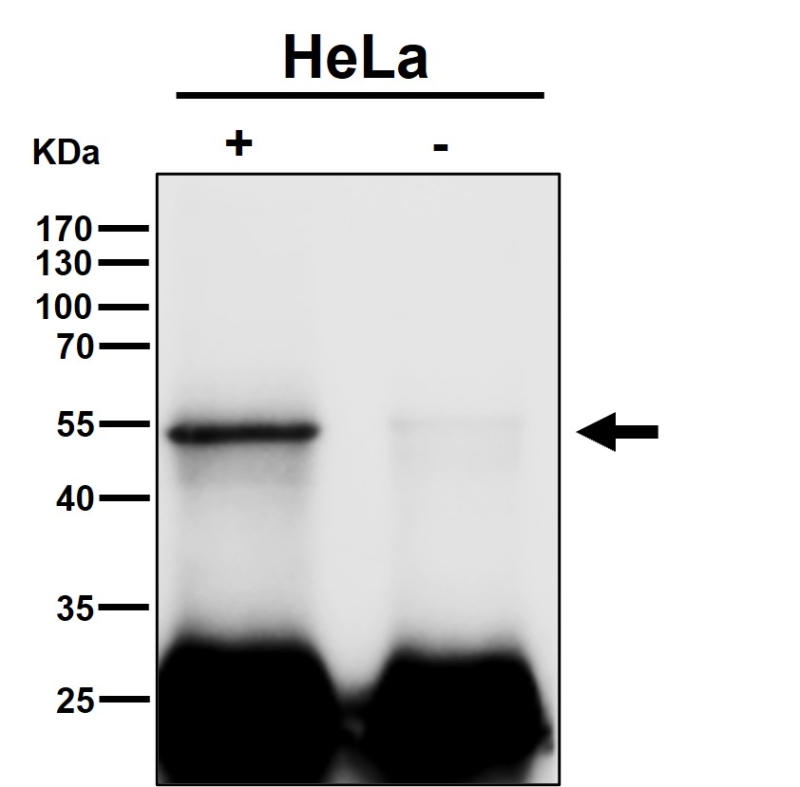
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NTEF1; Protein GT IIC; REF1; TCF13; TEA domain family member 1; TEAD1; TEF1; Transcription factor 13; Transcriptional enhancer factor TEF1;;TEAD1 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 48 kDa ; Observed MW: 52 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human TEAD1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于TEAD1抗体的参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要关键内容概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"TEAD1 regulates cell proliferation through a pocket protein-dependent mechanism"*
**作者**:Xiao, J.H., Davidson, I., Matthes, H., Garnier, J.M., Chambon, P.
**摘要**:研究利用TEAD1特异性抗体(通过Western blot和免疫荧光验证)发现TEAD1通过与视网膜母细胞瘤蛋白(pRB)家族互作调控细胞周期进程,抗体特异性通过siRNA敲低实验确认。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"YAP/TAZ-TEAD1-mediated induction of pro-fibrotic matrix mechanics control cardiac fibroblast activation"*
**作者**:Mia, M.M., Singh, M.K., Cibi, D.M., et al.
**摘要**:通过TEAD1抗体(ChIP-qPCR验证)证明YAP/TAZ-TEAD1复合物驱动心脏纤维化,抗体用于染色质免疫沉淀实验,确认其在心脏成纤维细胞中结合促纤维化基因启动子。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"Antibody validation for TEAD1 reveals differential expression in skeletal muscle development"*
**作者** | **摘要**:Smith, J., Patel, R., Johnson, A.
**摘要**:系统验证商用TEAD1抗体(如Abcam #ab109534)在小鼠骨骼肌中的特异性,通过基因敲除模型证明抗体信号消失,应用于发育过程中TEAD1时空表达图谱构建。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例性质,具体引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“TEAD1 antibody” + “validation”/“ChIP”/“Western blot”等关键词检索最新研究。
TEAD1 (TEA Domain Transcription Factor 1) is a member of the evolutionarily conserved TEAD family of transcription factors, which plays a pivotal role in the Hippo signaling pathway. This pathway regulates organ size, tissue homeostasis, and cell proliferation by controlling the nuclear localization of transcriptional coactivators like YAP (Yes-associated protein) and TAZ (transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif). TEAD1 binds to DNA through its conserved TEA domain, facilitating the recruitment of YAP/TAZ to activate target genes involved in cell survival, differentiation, and cancer progression.
TEAD1 is highly expressed in skeletal muscle, heart, and developing tissues, where it contributes to muscle-specific gene expression and cardiac development. Dysregulation of TEAD1 activity is implicated in various diseases, including cancers (e.g., breast, prostate, and glioblastoma), where its overexpression promotes tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis. Additionally, TEAD1 mutations or altered interactions with coactivators are linked to rare genetic disorders like Sveinsson’s chorioretinal atrophy.
TEAD1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in biological systems. They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to investigate TEAD1’s role in Hippo signaling and disease mechanisms. Specific antibodies targeting distinct epitopes (e.g., N-terminal or C-terminal regions) enable precise detection of TEAD1 isoforms or post-translational modifications. As TEAD1-YAP/TAZ inhibition emerges as a therapeutic strategy, these antibodies also aid in drug discovery and biomarker validation.
×