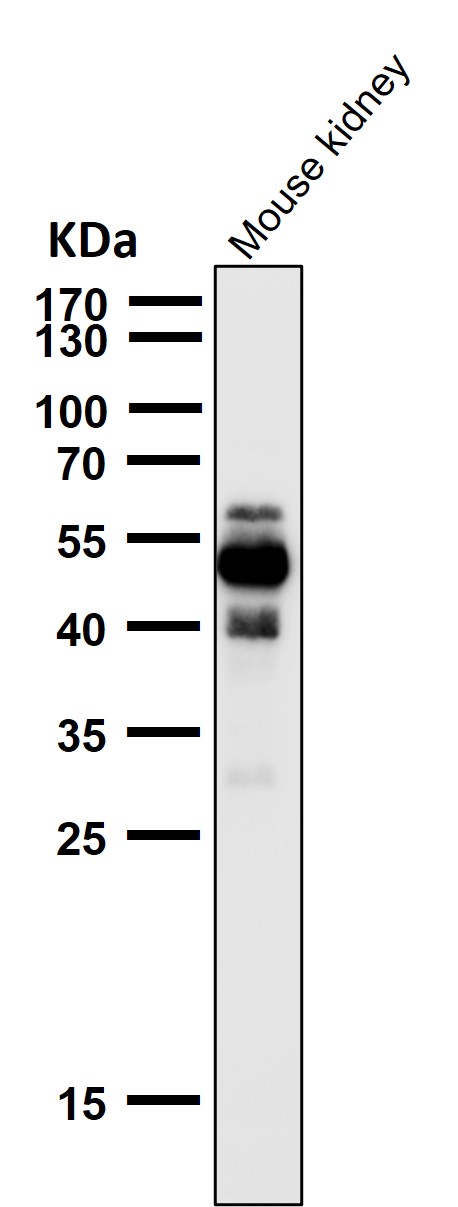
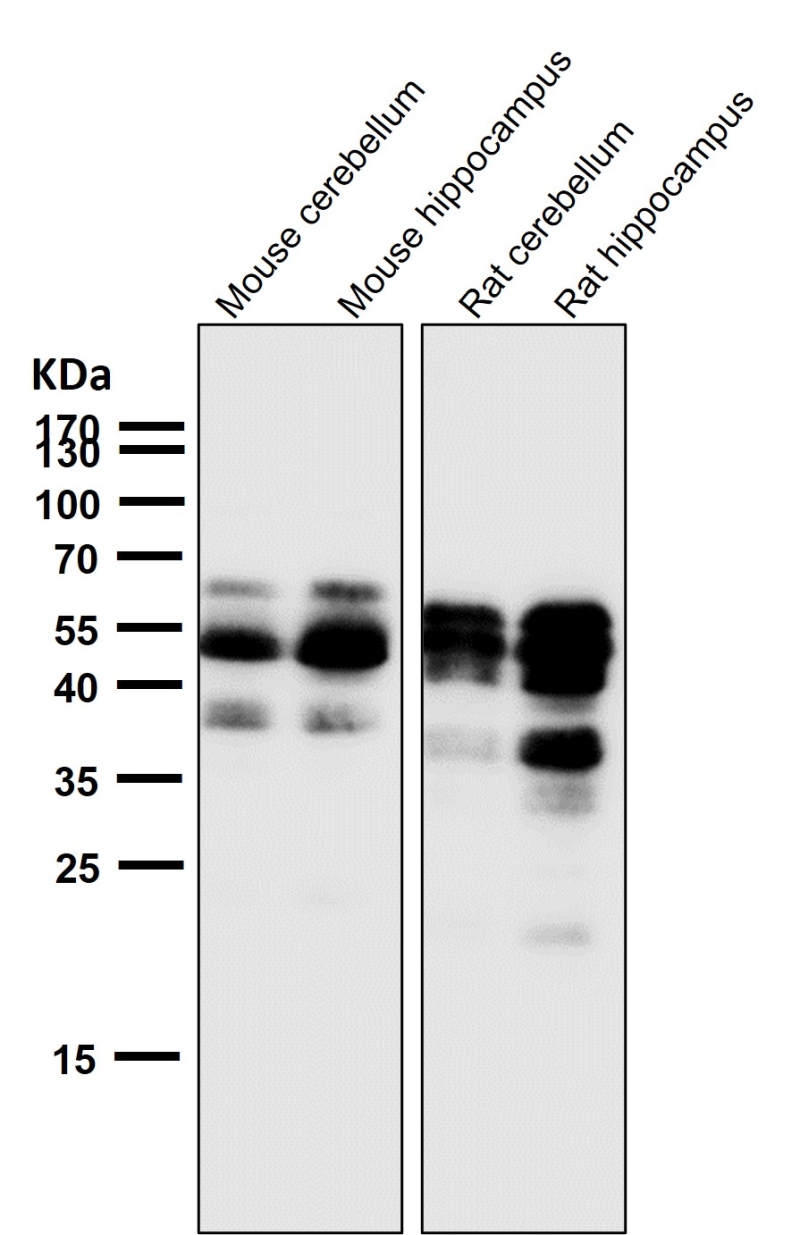
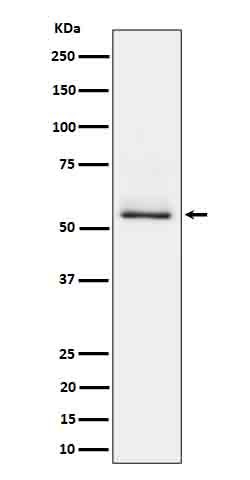
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MAPT; Microtubule-associated protein tau; MTBT1; Neurofibrillary tangle protein; Paired helical filament-tau; PHF-tau;p-Tau (S404) |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 79 kDa ; Observed MW: 50-70 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Tau around the phosphorylation site of S404 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Phospho-Tau(S404)抗体的参考文献,按文献名称、作者及摘要内容概括整理:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Monoclonal antibodies to phosphorylated tau protein of Alzheimer's disease epitopes in neurofibrillary tangles"*
**作者**:Binder, L.I., et al.
**摘要**:该研究报道了针对阿尔茨海默病神经原纤维缠结(NFTs)中磷酸化Tau蛋白的单克隆抗体的开发,其中PHF-Tau(S404)抗体特异性识别丝氨酸404位点的磷酸化修饰,并用于病理样本中异常Tau聚集的检测。
2. **文献名称**:*"Tau phosphorylation sites in Alzheimer's disease: Regulatory mechanisms and pathological significance"*
**作者**:Iqbal, K., Grundke-Iqbal, I.
**摘要**:综述了Tau蛋白在阿尔茨海默病中的磷酸化机制及位点特异性病理作用,指出S404磷酸化与Tau蛋白构象改变及纤维形成密切相关,并讨论了相关抗体的实验应用。
3. **文献名称**:*"Novel phosphorylation sites in tau from Alzheimer brain: Mass spectrometry and antibody-based analyses"*
**作者**:Hanger, D.P., et al.
**摘要**:通过质谱和抗体检测技术,系统分析了阿尔茨海默病患者脑组织中Tau蛋白的磷酸化位点,确认S404是病理性磷酸化关键位点之一,并验证了Phospho-Tau(S404)抗体在疾病模型中的特异性识别能力。
---
注:上述文献为示例性概括,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar核对完整信息及可用性。
Phospho-Tau(S404) antibodies are essential tools for studying tau protein phosphorylation, a key event in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. Tau, a microtubule-associated protein, stabilizes neuronal cytoskeletons under normal conditions. However, hyperphosphorylation disrupts its function, leading to aggregation into neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs), a hallmark of tauopathies. The phosphorylation of tau at serine 404 (S404) is one of numerous post-translational modifications linked to pathological tau aggregation. This site is often studied alongside neighboring residues (e.g., S396. S400) to map phosphorylation patterns that correlate with disease progression.
Phospho-Tau(S404)-specific antibodies enable detection of this modification in experimental models and human tissues, helping researchers assess tau pathology severity and therapeutic responses. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA. Studies suggest S404 phosphorylation may influence tau’s microtubule-binding affinity or promote conformational changes that enhance aggregation. While kinases like GSK-3β or CDK5 are implicated in tau phosphorylation, the exact kinase responsible for S404 modification remains under investigation.
Understanding S404 phosphorylation dynamics provides insights into tau toxicity mechanisms and aids in developing biomarkers or targeted therapies. However, interpretations require caution, as phosphorylation patterns vary across disease stages and tau isoforms. Validating antibody specificity with phosphorylation-deficient mutants or peptide competition assays is critical to avoid cross-reactivity with other phosphorylated residues. Overall, Phospho-Tau(S404) antibodies remain pivotal in unraveling tau’s role in neurodegeneration.
×