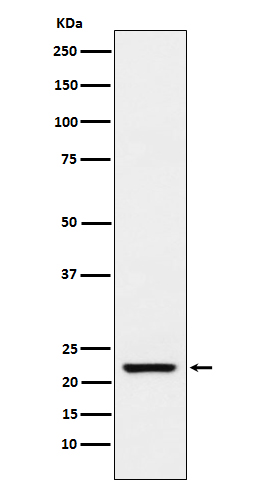
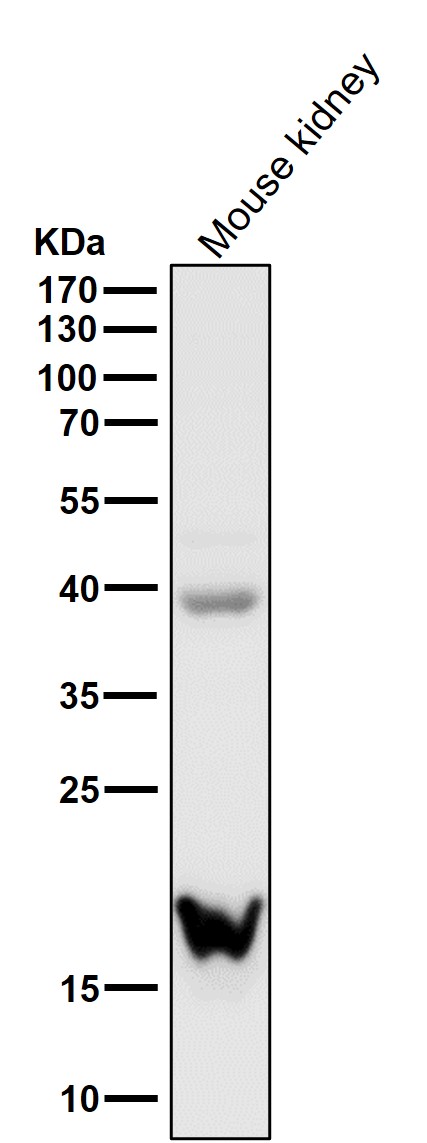
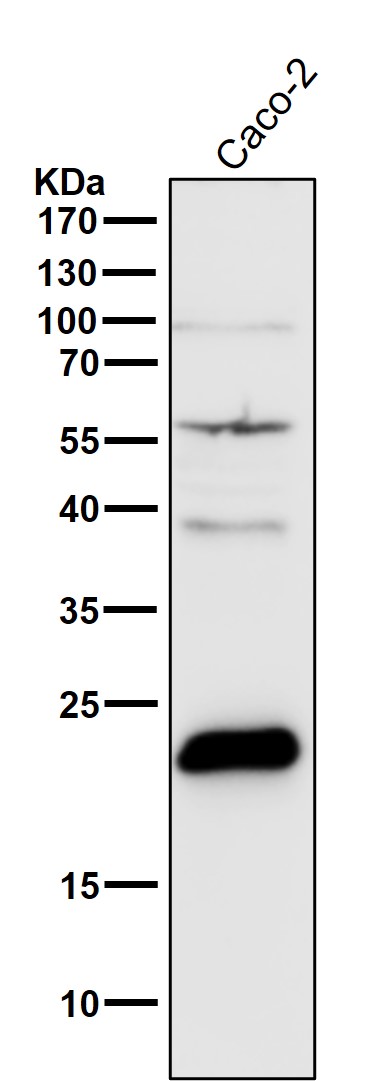
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TAGLN; Transgelin; SM22; SM22 alpha; WS3-10;;Transgelin |
| WB Predicted band size | 23 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Transgelin |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与TAGLN抗体相关的文献及其简要摘要:
1. **"Transgelin as a biomarker for epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer"**
- 作者:Huang J et al.
- 摘要:研究利用TAGLN抗体通过免疫组化分析结直肠癌组织,发现TAGLN高表达与上皮间质转化(EMT)及转移相关,提示其可作为癌症进展的生物标志物。
2. **"Transgelin promotes vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic modulation in atherosclerosis"**
- 作者:Wang L et al.
- 摘要:通过Western blot和免疫荧光(使用TAGLN抗体),证明TAGLN通过调控平滑肌细胞表型转化参与动脉粥样硬化斑块形成,为治疗提供新靶点。
3. **"Transgelin-2 is a novel target of KRAS signaling required for actin dynamics and cell motility"**
- 作者:Shields MA et al.
- 摘要:研究利用TAGLN-2特异性抗体,发现其在KRAS突变型胰腺癌细胞中高表达,通过调节肌动蛋白动态促进侵袭性,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
4. **"Transgelin interacts with PARP1 in human mesenchymal stem cells"**
- 作者:Kim YS et al.
- 摘要:通过免疫共沉淀(TAGLN抗体)发现TAGLN与PARP1蛋白互作,影响间充质干细胞的DNA损伤修复及分化能力,为干细胞调控机制提供新见解。
所有文献均聚焦TAGLN蛋白的功能研究,抗体应用于不同实验技术(如WB、IHC)以探索其在疾病中的分子机制。
TAGLN (Transgelin), also known as SM22-alpha, is a 22-kDa actin-binding protein belonging to the calponin family. It is predominantly expressed in smooth muscle cells (SMCs) and plays a critical role in regulating cytoskeletal dynamics, cell contraction, and migration. TAGLN stabilizes actin filaments and modulates SMC differentiation, contributing to vascular and visceral muscle function. Its expression is tightly regulated by serum response factor (SRF) and other transcription factors linked to smooth muscle development.
In pathological contexts, TAGLN has emerged as a biomarker in various diseases. It is upregulated in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) of multiple carcinomas, including breast, colorectal, and prostate cancers, where it promotes tumor progression and metastasis by enhancing cell motility and extracellular matrix remodeling. Conversely, reduced TAGLN levels are observed in vascular disorders like atherosclerosis and aneurysms, reflecting SMC dedifferentiation. TAGLN also participates in fibrotic diseases, influencing tissue stiffness and fibroblast activation.
TAGLN antibodies are essential tools for detecting its expression and localization in research. They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study TAGLN's role in normal physiology and disease mechanisms. Commercial antibodies target specific epitopes, though cross-reactivity with other calponin family members requires validation. Understanding TAGLN's dual roles in homeostasis and pathology continues to drive therapeutic and diagnostic exploration.
×