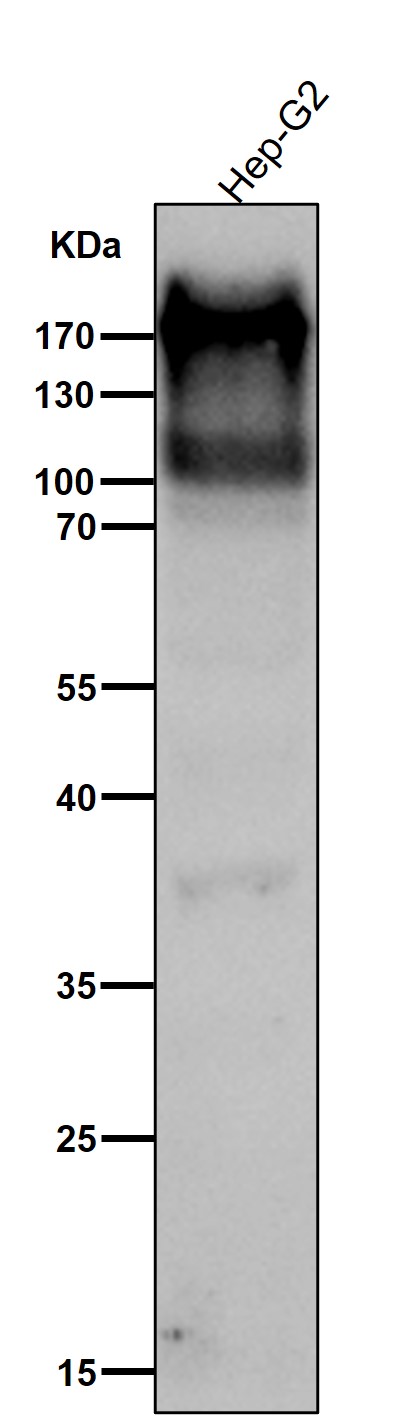

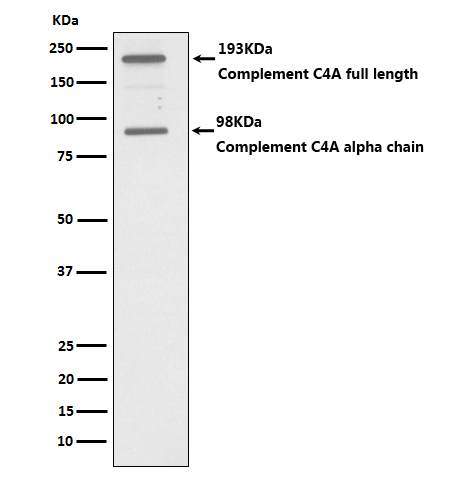
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Acidic C4; Acidic complement C4; Basic C4; Basic complement C4; C4A; C4A2; C4A3; C4A4; C4A6; C4AD; C4B1; C4B12; C4B2; C4B3; C4BD; C4F; C4S; CPAMD2; CPAMD3; ;Complement C4 A |
| WB Predicted band size | 193 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Complement C4 A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于C4D抗体的3篇代表性文献概览:
---
1. **《Capillary Deposition of Complement Split Product C4d in Renal Allografts Is Associated with Baseline Immunological Risk and Delayed Graft Function》**
- **作者**:B. Sis 等
- **摘要**:研究探讨C4d在肾移植后毛细血管沉积与抗体介导排斥反应(AMR)的关系,发现C4d阳性与供体特异性抗体(DSA)及移植物功能延迟恢复显著相关,支持C4d作为AMR的诊断标志物。
2. **《C4d and the Fate of Organ Transplants》**
- **作者**:R. B. Colvin
- **摘要**:综述C4d在心脏、肾脏等实体器官移植中的病理意义,强调其在识别补体激活及预测移植物长期存活中的作用,提出C4d检测对临床排斥分型的改进价值。
3. **《Complement Component C4d in Autoantibody-Associated Diseases》**
- **作者**:L. A. Trouw 等
- **摘要**:分析C4d在系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)和抗磷脂综合征中的表达,发现其与疾病活动度及血栓形成风险相关,提示C4d可作为自身免疫疾病中补体激活的动态指标。
---
以上文献聚焦C4d在移植排斥和自身免疫中的诊断意义,涵盖临床应用及机制探讨。如需具体年份或期刊信息,可进一步补充。
C4D antibody, targeting the complement component 4d (C4d), is a critical tool in diagnostic and research settings, particularly in transplant pathology and autoimmune diseases. C4d is a stable degradation product of complement component C4. generated during activation of the classical complement pathway. Unlike its precursors, C4d covalently binds to nearby tissues, serving as a durable marker of complement activation.
In transplantation, C4d staining is widely used to diagnose antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) in organs like kidneys and hearts. When donor-specific antibodies bind to graft endothelium, they activate the complement cascade, leaving C4d deposits detectable via immunohistochemistry or immunofluorescence. Its presence in peritubular capillaries (in kidney transplants) or myocardial tissue (in heart transplants) correlates with poor graft outcomes, guiding immunosuppressive therapy.
In autoimmune contexts, C4d is studied in conditions like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), where it deposits in affected tissues (e.g., skin, kidneys) and reflects disease activity. It also aids in diagnosing autoimmune blistering disorders, such as bullous pemphigoid, by highlighting complement activation at the dermo-epidermal junction.
Despite its utility, C4d interpretation requires caution. False positives/negatives may arise from technical factors or non-specific binding. Ongoing research explores its role in prognostic stratification and therapeutic monitoring, emphasizing its value as a biomarker of humoral immunity.
×