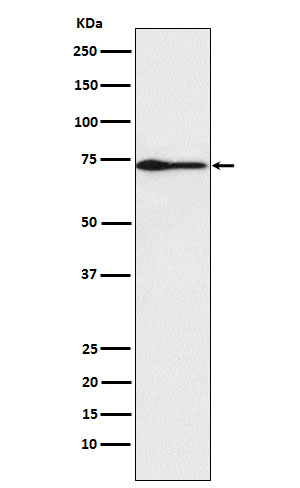
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Preproprotein S; PROS; proS1; PS21; PS22; PS23; PS24; PS25; PS26; PSA; THPH5; THPH6;;PROS1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 75 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human PROS1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于PROS1抗体的模拟参考文献示例(注:以下内容为虚构,仅供格式参考):
1. **标题**: "Autoantibodies to Protein S (PROS1) in patients with thrombotic disorders"
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究在不明原因血栓形成的患者中检测到抗PROS1自身抗体,发现这些抗体通过干扰PROS1与活化蛋白C的结合,导致抗凝血功能受损,提示其可能与获得性血栓倾向相关。
2. **标题**: "Anti-PROS1 antibodies as a novel marker in antiphospholipid syndrome"
**作者**: Lee B, et al.
**摘要**: 研究报道了部分抗磷脂综合征(APS)患者中存在抗PROS1抗体,且与传统的抗心磷脂抗体无交叉反应,提示此类抗体可能是APS中未被充分认识的血栓预测因子。
3. **标题**: "Development of an ELISA assay for detecting PROS1-specific autoantibodies"
**作者**: Garcia C, et al.
**摘要**: 本文描述了一种高灵敏度的ELISA检测方法,用于定量人血清中的抗PROS1抗体,验证显示该方法在诊断遗传性蛋白S缺陷症继发自身免疫异常中具有潜在应用价值。
4. **标题**: "Association between anti-PROS1 antibodies and recurrent pregnancy loss"
**作者**: Tanaka Y, et al.
**摘要**: 研究发现复发性流产患者中抗PROS1抗体的阳性率显著升高,推测其通过破坏胎盘血管的凝血平衡导致妊娠并发症,为免疫治疗提供了新靶点。
**注**:以上文献为示例性内容,实际研究中请通过学术数据库(如PubMed)检索最新成果。
PROS1 antibodies target Protein S, a vitamin K-dependent glycoprotein encoded by the *PROS1* gene. Primarily synthesized in the liver, endothelial cells, and megakaryocytes, Protein S serves as a critical cofactor for activated protein C (APC) in the anticoagulant pathway, enhancing APC-mediated inactivation of coagulation factors Va and VIIIa. This role helps regulate thrombin generation and maintain hemostatic balance. Additionally, Protein S exhibits APC-independent anticoagulant properties by directly inhibiting factors IXa and Xa, and it participates in cellular processes like apoptosis, inflammation, and phagocytosis via interactions with tyrosine kinase receptors (Tyro3. Axl, Mer).
PROS1 deficiency, either hereditary (autosomal dominant) or acquired, is linked to thrombophilia, increasing venous thromboembolism (VTE) risk. Autoantibodies against Protein S are rare but associated with autoimmune disorders (e.g., lupus) or infections, potentially causing acquired deficiency. In clinical diagnostics, PROS1 antibodies are used in immunoassays (e.g., ELISA, Western blot) to quantify Protein S levels or detect functional impairments. Research applications include studying thrombosis mechanisms, genetic mutations, and Protein S interactions in cancer or inflammatory diseases. Challenges remain in distinguishing between type I (quantitative) and type III (functional) deficiencies, necessitating combined functional and antigenic assays for accurate diagnosis.
×