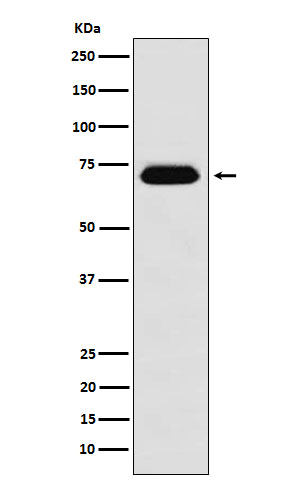
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IBSN; MGC841; NUP62; p62; SNDI;;NUP62 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 53 kDa ; Observed MW: 70 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human NUP62 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于NUP62抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
1. **文献名称**:*Nucleoporin 62 (NUP62) Deficiency disrupts ribosomal RNA export and neural development in humans*
**作者**:Braun DA, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用NUP62抗体分析核孔复合体功能,发现NUP62基因突变导致核糖体RNA转运异常,并与人类神经发育障碍(如脑病和癫痫)相关。
2. **文献名称**:*NUP62 is required for the maintenance of the intestinal barrier function via regulating tight junction proteins*
**作者**:Li Z, et al.
**摘要**:通过NUP62抗体免疫染色和敲除实验,揭示NUP62通过调控紧密连接蛋白(如ZO-1)维持肠道屏障完整性,其缺失可能加重炎症性肠病。
3. **文献名称**:*Nuclear pore protein NUP62 is a critical regulator of stem cell proliferation and differentiation*
**作者**:González-Arias C, et al.
**摘要**:研究使用NUP62抗体进行蛋白质组学分析,发现NUP62通过调控Wnt/β-catenin信号通路影响干细胞增殖和分化,提示其在组织再生中的潜在作用。
以上文献均通过NUP62抗体探讨其在疾病机制、细胞功能或信号通路中的生物学意义。
NUP62 (Nuclear Pore Complex Protein 62 kDa) is a key component of the nuclear pore complex (NPC), a large protein assembly regulating nucleocytoplasmic transport. As a member of the FG (phenylalanine-glycine)-nucleoporin family, NUP62 contains intrinsically disordered domains rich in FG repeats, which facilitate selective molecular trafficking by interacting with transport receptors. It plays critical roles in maintaining nuclear envelope integrity, mediating mRNA/protein shuttling, and regulating gene expression and cellular signaling.
NUP62 antibodies are essential tools for studying NPC architecture, nuclear transport mechanisms, and disease associations. These antibodies enable the detection and localization of NUP62 in various experimental approaches, including Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry. Research has linked NUP62 dysfunction to pathologies such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease), and viral infections (e.g., HIV), where altered NPC dynamics affect viral replication.
Notably, NUP62 autoantibodies have been identified in autoimmune conditions, suggesting its role as an autoantigen. Studies also highlight its involvement in Wnt/β-catenin signaling and autophagy, underscoring its multifaceted cellular functions. Commercial NUP62 antibodies are typically validated for specificity across human, mouse, and rat models, supporting translational research into NPC-related mechanisms and therapeutic targeting.
×