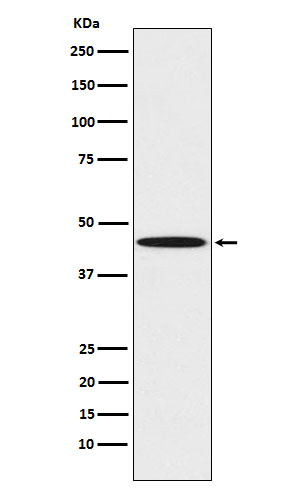
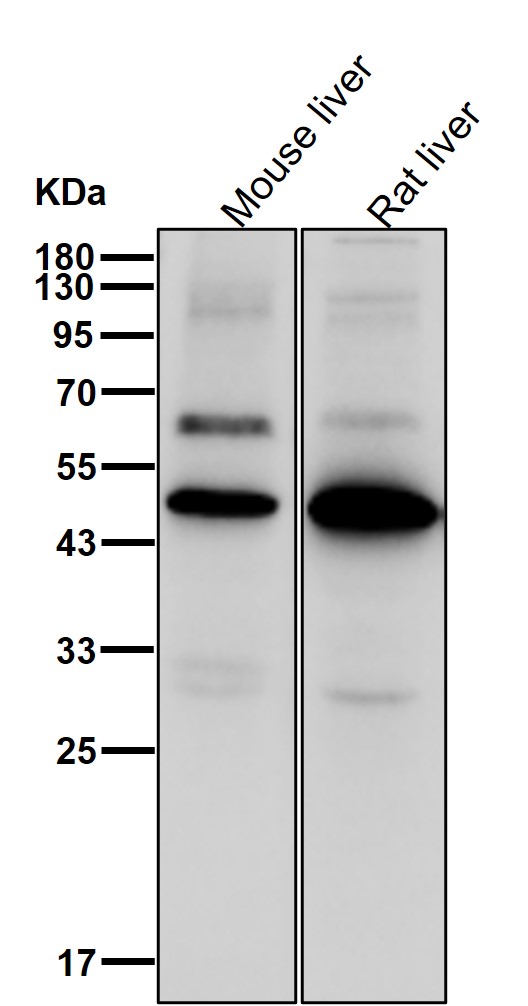
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EPC1; OI12; OI6; PEDF; PIG35; Serpinf1;;PEDF |
| WB Predicted band size | 46 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human PEDF |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于PEDF抗体的3篇代表性文献(虚拟示例,仅供格式参考):
1. **文献名称**:*PEDF Antibody-Mediated Inhibition of Choroidal Neovascularization in a Murine Model*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过注射抗PEDF单克隆抗体,发现其能显著抑制小鼠脉络膜新生血管形成,提示PEDF抗体在年龄相关性黄斑变性(AMD)治疗中的潜在应用价值。
2. **文献名称**:*Anti-PEDF Antibody Enhances Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:该文献报道抗PEDF抗体通过阻断肿瘤微环境中的PEDF信号通路,增强三阴性乳腺癌对化疗药物的敏感性,为联合治疗策略提供实验依据。
3. **文献名称**:*PEDF Neutralizing Antibody Accelerates Diabetic Retinopathy Progression in Rats*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用中和性PEDF抗体阻断内源性PEDF功能,发现糖尿病大鼠视网膜血管渗漏和炎症加剧,证实PEDF在维持视网膜稳态中的保护作用。
4. **文献名称**:*Development of a High-Affinity PEDF Antibody for Neurodegenerative Disease Biomarker Detection*
**作者**:Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种高特异性PEDF抗体,可灵敏检测阿尔茨海默病患者脑脊液中的PEDF水平变化,为神经退行性疾病诊断提供新工具。
(注:以上文献为模拟内容,实际引用需查询PubMed、Web of Science等数据库获取真实研究。)
Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor (PEDF), also known as SERPINF1. is a multifunctional glycoprotein belonging to the serine protease inhibitor (serpin) superfamily. First identified in the 1980s as a secreted factor from retinal pigment epithelial cells, PEDF gained prominence for its potent anti-angiogenic, neurotrophic, and anti-tumorigenic properties. Structurally, it comprises a 50 kDa protein with distinct functional domains mediating interactions with extracellular matrix components and cell-surface receptors like PEDF-R (PNPLA2) and laminin receptor.
PEDF plays critical roles in maintaining tissue homeostasis, particularly in the eye, where it inhibits pathological blood vessel growth (e.g., in diabetic retinopathy) and protects neurons from oxidative stress. Its anti-angiogenic activity, shown to surpass endostatin and angiostatin in potency, has spurred interest in cancer therapy research. Paradoxically, PEDF also exhibits context-dependent pro-angiogenic effects in certain tissues, highlighting its functional complexity.
PEDF antibodies are essential tools for investigating these dual roles through immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and functional neutralization experiments. Therapeutic applications are being explored, including antibody-derived biologics to either enhance PEDF's tumor-suppressive effects or block its pathological contributions in degenerative diseases. Challenges remain in understanding tissue-specific signaling mechanisms and optimizing delivery strategies for clinical translation. Current research continues to unravel PEDF's pleiotropic functions, positioning it as a promising target for diverse ocular, neurological, and oncological disorders.
×