
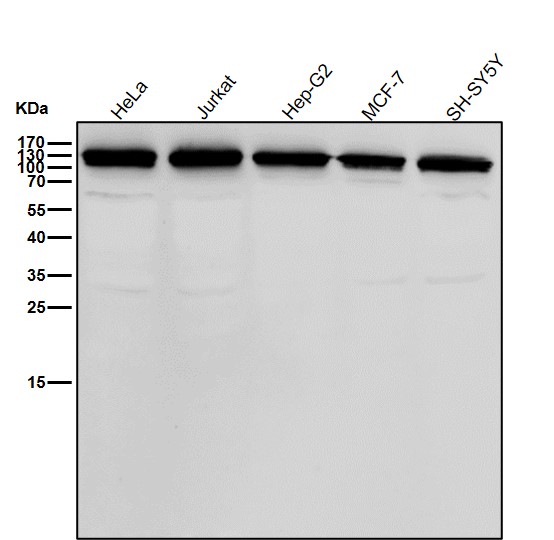
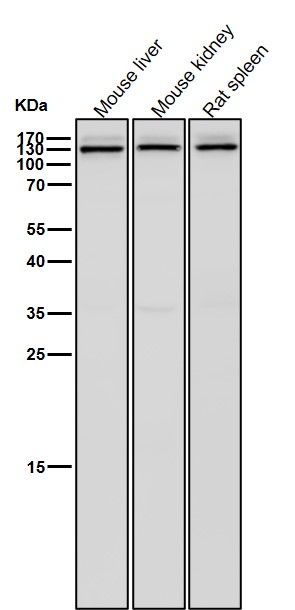
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Alpha RLC; ITGA4L; ITGA9; RLC;;Integrin alpha 9 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 114 kDa ; Observed MW: 140 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Integrin alpha 9 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Integrin alpha9(ITGA9)抗体的参考文献摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Targeting integrin α9 as a novel therapeutic strategy for inflammatory diseases"*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究开发了一种人源化抗ITGA9单克隆抗体,通过阻断α9β1整合素与VCAM-1的相互作用,显著抑制了小鼠模型中中性粒细胞迁移和炎症反应,为治疗类风湿性关节炎等炎症疾病提供了新策略。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Integrin α9β1 in cancer progression: Therapeutic targeting with a function-blocking antibody"*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 文章报道了一种阻断ITGA9的功能性抗体(mAb-A9),该抗体通过抑制肿瘤细胞与细胞外基质的粘附,降低乳腺癌和黑色素瘤小鼠模型的转移能力,揭示了α9在肿瘤微环境中的关键作用。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Integrin α9 regulates smooth muscle cell phenotype via mechanical signaling"*
**作者**: Yamamoto K, et al.
**摘要**: 利用抗ITGA9抗体阻断实验,研究发现α9整合素通过调控机械信号通路影响血管平滑肌细胞的分化,为动脉粥样硬化中血管重塑的机制提供了新见解。
---
如需具体文献链接或补充年份/期刊信息,可进一步说明。
Integrin alpha-9 (ITGA9) is a subunit of the α9β1 integrin heterodimer, a cell surface receptor involved in mediating cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix interactions. Unlike many integrins, α9β1 binds ligands such as vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), tenascin-C, and osteopontin, playing critical roles in immune regulation, angiogenesis, and tissue repair. It is highly expressed in immune cells (e.g., neutrophils, lymphocytes), endothelial cells, and certain epithelial cells, and is implicated in inflammatory responses, lymphatic development, and cancer progression.
ITGA9 antibodies are research tools or therapeutic candidates designed to target this subunit. In research, they help study α9β1's functional roles—for example, in leukocyte trafficking during inflammation or tumor cell metastasis. Therapeutically, blocking ITGA9 may inhibit pathological processes: preclinical studies suggest anti-ITGA9 antibodies could suppress cancer invasion (e.g., melanoma, lung cancer) by disrupting cell adhesion and signaling. They also show potential in treating fibrotic diseases (e.g., pulmonary fibrosis) or autoimmune disorders (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis) by modulating immune cell infiltration. Challenges include optimizing specificity to avoid off-target effects and understanding context-dependent roles, as ITGA9 has dual functions in both promoting and suppressing disease depending on the microenvironment. Current efforts focus on antibody engineering and validating clinical relevance across disease models.
×