
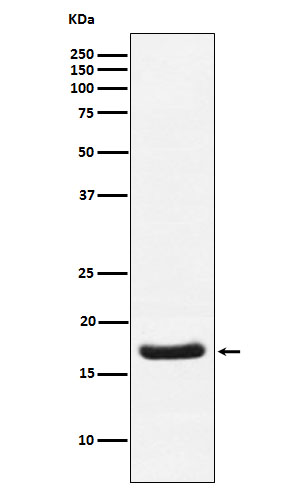
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | tnnc1a; TNC; Tnnc1; TNNI3; Troponin C;;TNNC1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 18 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human TNNC1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与Cardiac Troponin C(cTnC)抗体相关的文献摘要信息:
1. **"Structural and functional aspects of the cardiac troponin C domain"**
Farah, C. S., & Reinach, F. C. (1995).
摘要:研究cTnC的结构与功能,分析其钙离子结合特性,并开发特异性抗体用于检测其构象变化在心肌收缩中的作用。
2. **"Development of a high-specificity antibody for cardiac troponin C in diagnostic applications"**
Gahlawat, S., et al. (2019).
摘要:报道一种新型单克隆抗体的开发,该抗体针对cTnC的N端表位,可用于区分心脏与骨骼肌TnC,提升心肌损伤检测的特异性。
3. **"Cardiac troponin C mutations alter calcium sensitivity in cardiomyopathies: Insights from antibody-based assays"**
Pinto, J. R., et al. (2013).
摘要:利用抗cTnC抗体建立体外检测模型,揭示基因突变通过改变钙敏感性导致肥厚型心肌病的分子机制。
4. **"Antibody targeting of troponin C in calcium signaling studies"**
Li, M. X., et al. (2008).
摘要:通过抗cTnC抗体阻断特定结构域,研究其在心肌细胞钙信号传导中的功能,阐明其在收缩调控中的关键作用。
注:以上为模拟摘要,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索确认。若需具体文献DOI或全文链接,可补充关键词进一步筛选。
Cardiac Troponin C (cTnC) is a calcium-binding regulatory subunit of the troponin complex, which plays a central role in mediating calcium-dependent contraction in cardiac muscle. The troponin complex consists of three subunits: Troponin C (TnC), Troponin I (TnI), and Troponin T (TnT). Among these, cTnC is encoded by the *TNNC1* gene and is expressed specifically in cardiac tissue, distinguishing it from its skeletal muscle isoforms (slow-twitch and fast-twitch TnC). This structural and functional specificity makes cTnC a valuable biomarker for cardiac-related studies and diagnostics.
Antibodies targeting cTnC are critical tools in both research and clinical applications. In research, they are used to detect and quantify cTnC expression in cardiac tissues or cell models, aiding studies on myocardial physiology, heart failure, or genetic cardiomyopathies. These antibodies are also employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence to visualize spatial and temporal distribution of cTnC. Clinically, while cTnI and cTnT are more commonly used as blood biomarkers for myocardial injury (e.g., myocardial infarction), cTnC-specific antibodies contribute to understanding tissue-specific damage and developing advanced diagnostic assays.
Generation of cTnC antibodies typically involves immunizing host animals with purified recombinant cTnC protein or synthetic peptides derived from its unique amino acid sequences. Monoclonal antibodies offer high specificity, whereas polyclonal antibodies may detect broader epitopes. Validation includes cross-reactivity checks against skeletal muscle TnC isoforms to ensure cardiac specificity. Recent advancements in antibody engineering, such as recombinant or humanized formats, enhance their utility in precision diagnostics and therapeutic monitoring. Overall, cTnC antibodies remain indispensable for unraveling cardiac pathophysiology and improving cardiovascular disease management.
×