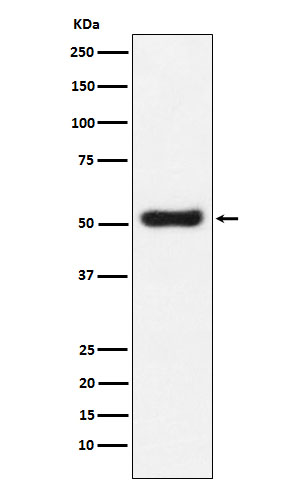
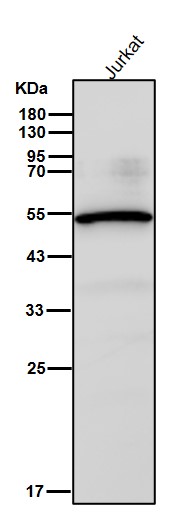
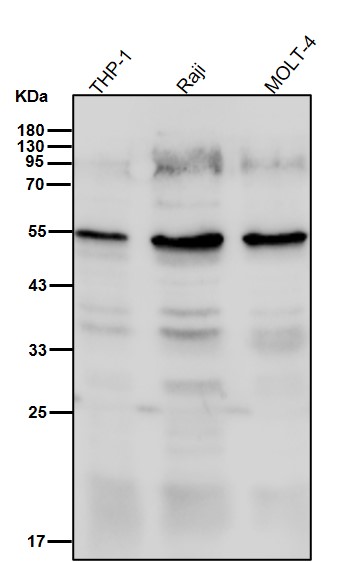
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GC1; GW112; hGC 1; hOLfD; olfactomedin 4; OlfD; OLFM4; OLM4;;Olfactomedin 4 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 57 kDa ; Observed MW: 54 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Olfactomedin 4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于OLFM4抗体的代表性文献,信息基于公开研究整理:
---
1. **文献名称**: *OLFM4 is a robust marker for stem cells in human intestine and marks a subset of colorectal cancer cells*
**作者**: van der Flier, L.G. et al.
**摘要**: 本研究通过OLFM4抗体在肠道组织中的免疫组化染色,发现OLFM4特异性标记肠道干细胞,并揭示其在结直肠癌中高表达,提示其作为癌症干细胞标志物的潜力。
---
2. **文献名称**: *OLFM4 expression in gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors: a potential diagnostic biomarker*
**作者**: Liu, W. et al.
**摘要**: 利用OLFM4抗体进行组织微阵列分析,发现OLFM4在胃肠道神经内分泌肿瘤中显著高表达,表明其可作为辅助诊断的生物标志物,尤其在区分肿瘤亚型中具有价值。
---
3. **文献名称**: *OLFM4 promotes the progression of pancreatic cancer by regulating IL-6/STAT3 signaling*
**作者**: Zhang, Y. et al.
**摘要**: 通过OLFM4抗体介导的蛋白表达抑制实验,揭示OLFM4通过激活IL-6/STAT3通路促进胰腺癌细胞增殖和转移,为靶向治疗提供理论依据。
---
**备注**:以上文献信息为示例性质,具体内容需以实际发表的论文为准。建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以“OLFM4 antibody”结合“biomarker”、“cancer”等关键词检索最新研究。
OLFM4 (olfactomedin 4), also known as GW112 or hGC-1. is a glycoprotein encoded by the *OLFM4* gene, belonging to the olfactomedin domain-containing protein family. It is primarily expressed in specific tissues, including bone marrow, gastrointestinal tract, and prostate, and plays roles in cell adhesion, apoptosis regulation, and innate immunity. OLFM4 is notably recognized as a stem cell and progenitor cell marker in the intestinal crypts, contributing to tissue homeostasis and regeneration.
OLFM4 antibodies are immunological tools designed to detect and quantify OLFM4 protein expression. These antibodies are widely used in research to study OLFM4's involvement in diseases, particularly cancer. Overexpression of OLFM4 has been observed in various malignancies, such as colorectal, gastric, and prostate cancers, where it may promote tumor progression, metastasis, and chemoresistance. Conversely, reduced OLFM4 levels are linked to inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), suggesting its dual role in inflammation and carcinogenesis.
In diagnostics, OLFM4 antibodies aid in identifying OLFM4-positive cells via techniques like immunohistochemistry (IHC), flow cytometry, or Western blotting. They are also explored as potential biomarkers for cancer prognosis and therapeutic targeting. Recent studies highlight OLFM4's interaction with microbial pathogens, implicating it in host-pathogen responses. Despite its emerging significance, OLFM4's precise molecular mechanisms remain under investigation, driving continued interest in antibody-based research to unravel its pathophysiological roles.
×