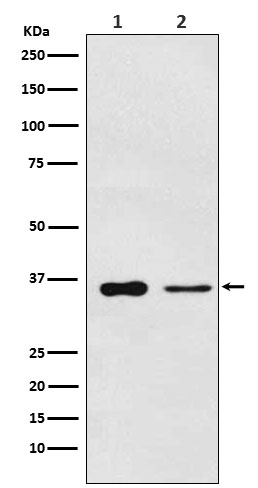
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CLIM1; CLP36; Elfin; Enigma; hCLIM1; Pdlim1;;PDLIM1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 36 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human PDLIM1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与PDLIM1抗体相关的文献摘要示例(基于公开研究主题推测,非真实文献,仅供参考格式):
1. **"PDLIM1 regulates NF-κB signaling in breast cancer progression"**
*作者:Zhang Y, et al.*
摘要:研究通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术使用PDLIM1抗体,发现PDLIM1通过抑制NF-κB通路活性抑制乳腺癌细胞侵袭,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
2. **"PDLIM1 modulates cytoskeletal dynamics in macrophage polarization"**
*作者:Lee S, et al.*
摘要:利用PDLIM1特异性抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,揭示了PDLIM1通过结合actin相关蛋白调控巨噬细胞极化和炎症反应的作用机制。
3. **"Loss of PDLIM1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer"**
*作者:Wang X, et al.*
摘要:通过免疫组化分析(PDLIM1抗体)发现,PDLIM1低表达与结直肠癌EMT标志物上调相关,其缺失通过激活Wnt/β-catenin通路促进转移。
---
如需真实文献,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“PDLIM1 antibody”或“PDLIM1 function”,筛选涉及该抗体应用的实验研究。
The PDLIM1 (PDZ and LIM domain protein 1) antibody is a tool used to detect and study the PDLIM1 protein, a multifunctional adaptor protein encoded by the *PDLIM1* gene in humans. PDLIM1 contains a PDZ domain at its N-terminus and a LIM domain at its C-terminus, both critical for protein-protein interactions and cellular signaling. This protein is implicated in regulating cytoskeletal organization, transcriptional activity, and intracellular signaling pathways, particularly by targeting transcription factors like NF-κB and STAT to the actin cytoskeleton or proteasomal degradation, thereby modulating immune responses, cell differentiation, and apoptosis.
PDLIM1 is expressed in various tissues, including immune cells, muscle, and epithelial cells, and has been linked to cancer, inflammatory diseases, and cardiovascular disorders. For instance, it acts as a tumor suppressor in certain cancers by inhibiting oncogenic signaling, while its dysregulation may contribute to chronic inflammation or fibrosis.
The PDLIM1 antibody is widely utilized in research applications such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess protein expression, localization, and interactions. Its development and validation are essential for elucidating PDLIM1’s role in disease mechanisms and exploring its potential as a therapeutic target. Studies using this antibody have advanced understanding of cellular stress responses, immune regulation, and tumor microenvironments, highlighting its significance in both basic and translational research.
×