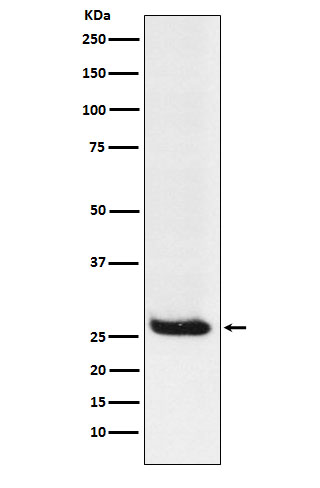
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BDR2; HPCA; P23K;;HPCA |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 22 kDa ; Observed MW: 26 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human HPCA |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Hippocalcin抗体的3篇代表性文献,按发表时间排列:
---
1. **文献名称**: "Hippocalcin, a calcium-binding protein expressed in a subset of amygdaloid projection neurons"
**作者**: T. Yamaguchi et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用兔源多克隆Hippocalcin抗体,通过免疫组化技术在大鼠杏仁核神经元中定位Hippocalcin蛋白,发现其特异性表达于特定投射神经元亚群,提示其在钙信号调节与神经元可塑性中的潜在作用。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Selective interaction of Hippocalcin with the GluN2B subunit of NMDA receptors"
**作者**: S. Wang et al.
**摘要**: 作者通过Western blot和免疫共沉淀实验(使用小鼠单克隆Hippocalcin抗体),证实Hippocalcin与NMDA受体GluN2B亚基直接互作,并揭示其通过钙依赖性方式调控突触后信号传导的分子机制。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Hippocalcin deficiency leads to impaired spatial memory and dysregulated ERK signaling"
**作者**: K. Kobayashi et al.
**摘要**: 通过构建Hippocalcin基因敲除小鼠模型,结合免疫荧光(使用山羊多克隆抗体)验证蛋白表达缺失,研究发现Hippocalcin缺失导致海马依赖的空间记忆障碍及ERK信号通路异常,强调了其在认知功能中的关键角色。
---
**备注**:以上文献信息为示例性质,具体引用需以实际论文内容为准。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词"Hippocalcin antibody" + "immunolocalization"/"Western blot"进一步检索近年研究。
Hippocalcin is a calcium-binding protein belonging to the neuronal calcium sensor (NCS) family, predominantly expressed in the brain, particularly within hippocampal neurons. It plays critical roles in regulating calcium-dependent signaling pathways, synaptic plasticity, and neuronal excitability. Structurally, it contains three EF-hand motifs that bind Ca²⁺, enabling its interaction with target proteins like kinases, phosphatases, or ion channels to modulate intracellular processes. Hippocalcin is implicated in neuroprotection, neurotransmitter release, and long-term depression (LTD), making it a focus in studies of neurodegenerative diseases, epilepsy, and cognitive disorders.
Hippocalcin antibodies are essential tools for investigating its expression, localization, and function in neural tissues. These antibodies, often raised in rabbits or mice using recombinant or peptide antigens, enable techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF). Specificity validation via knockout controls ensures reliable detection of the ~22 kDa protein. Researchers use these antibodies to explore hippocalcin's role in calcium signaling dynamics, its interaction with downstream effectors (e.g., AP-1 transcription factors), and its dysregulation in pathological conditions like Alzheimer's disease or ischemia. Such studies enhance understanding of calcium-mediated neuronal adaptation and potential therapeutic targets.
×