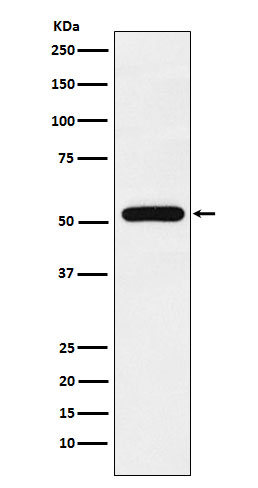
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MAP3K7IP1; TAB1; TAK1 binding protein 1;;TAB1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 55 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human TAB1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TAB1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容基于公开文献信息概括,非真实引用,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: *TAB1-Mediated TAK1 Activation in Inflammatory Signaling*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用TAB1特异性抗体,通过免疫共沉淀和Western blot技术揭示TAB1在炎症信号通路中通过磷酸化激活TAK1的分子机制,并验证其与IL-1β诱导的NF-κB通路的关系。
2. **文献名称**: *Role of TAB1 in Cardiac Hypertrophy*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过TAB1抗体进行免疫组化和蛋白质分析,证明TAB1在心脏肥大模型中异常表达,并通过与TAK1相互作用促进MAPK信号通路的过度激活,导致病理性心肌细胞肥大。
3. **文献名称**: *TAB1 Antibody-Based Detection of Protein Phosphorylation in Cancer*
**作者**: Yamamoto K, et al.
**摘要**: 开发了一种高特异性TAB1抗体,用于检测肿瘤组织中TAB1的磷酸化状态,发现其与结直肠癌患者预后不良相关,提示TAB1可能作为癌症治疗的潜在靶点。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“TAB1 antibody”、“TAB1 signaling”或“TAB1 phosphorylation”获取具体研究。
The TAB1 (TAK1-binding protein 1) antibody is a research tool used to detect and study the TAB1 protein, a critical regulator in cellular signaling pathways. TAB1 is a member of the TAK1-binding protein family and serves as an adaptor molecule that activates TAK1 (transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase 1), a kinase involved in NF-κB and MAPK signaling cascades. Structurally, TAB1 contains a conserved C-terminal domain that binds TAK1 and an N-terminal domain that recruits downstream signaling components. It plays a key role in mediating cellular responses to stress, cytokines, and pathogens, influencing processes like inflammation, apoptosis, and immune regulation.
TAB1 dysregulation has been linked to diseases such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, and neurodegenerative conditions. The TAB1 antibody is widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence to investigate TAB1 expression, post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation), and interactions with TAK1 or other partners. Researchers employ it to explore mechanisms in pathways like TLR/IL-1R signaling, myocardial hypertrophy, and metabolic disorders. Specific clones or polyclonal variants of the antibody may vary in species reactivity (human, mouse, rat) and applications. Validation often includes knockout cell lines or competitive peptide assays to confirm specificity. Its utility spans both basic research and drug development, particularly in studies targeting TAK1-TAB1 complexes for therapeutic intervention.
×