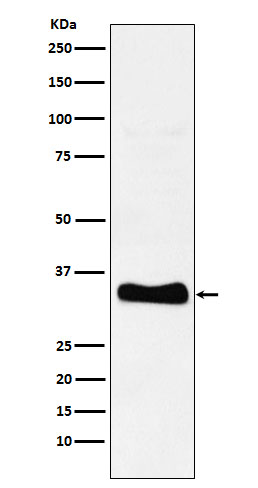
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HUK5; Lysophospholipase homolog; Lysophospholipase like; MAGL; MGL; MGLL;Monoacylglycerol lipase;;Monoglyceride lipase |
| WB Predicted band size | 33 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Monoglyceride lipase |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Monoacylglycerol Lipase(MAGL)抗体的代表性文献概览:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Monoacylglycerol Lipase Regulates 2-Arachidonoylglycerol Action and Inflammatory Pain"*
**作者**: Schlosburg, J.E. 等 (2010)
**摘要**: 本文利用MAGL抗体研究其在神经炎症中的表达调控,发现抑制MAGL可减少花生四烯酸释放,从而缓解小鼠慢性炎症疼痛。抗体用于验证组织中的酶表达水平。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Chemical Proteomics Maps Brain Region Specific Activity of Endocannabinoid Inhibitors"*
**作者**: Niphakis, S.K. 等 (2013)
**摘要**: 开发基于MAGL抗体的化学探针,结合质谱分析,揭示小鼠脑区中MAGL的活性分布,并验证抗体在脑组织免疫沉淀中的特异性应用。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Development and Characterization of Monoclonal Antibodies Against Human Monoacylglycerol Lipase"*
**作者**: Kociełkiewicz, A. 等 (2009)
**摘要**: 首次报道了针对人源MAGL的单克隆抗体制备,通过Western blot和免疫荧光验证抗体特异性,为后续酶功能研究提供关键工具。
---
这些文献涵盖了抗体的开发、验证及在疾病机制研究中的应用。如需具体文章,建议通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索标题或作者进一步获取全文。
Monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) is a serine hydrolase enzyme that plays a critical role in lipid metabolism by catalyzing the hydrolysis of monoacylglycerols into free fatty acids and glycerol. It is particularly notable for breaking down the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), a key signaling molecule in the endogenous cannabinoid system. MAGL’s activity influences various physiological and pathological processes, including neurotransmission, inflammation, energy homeostasis, and cancer progression. Dysregulation of MAGL has been linked to neurological disorders (e.g., neurodegeneration, pain), metabolic syndromes, and tumorigenesis, making it a therapeutic target of interest.
MAGL antibodies are essential tools for studying the enzyme’s expression, localization, and function in biological systems. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to quantify MAGL levels in tissues or cells, map its distribution in the nervous system, or assess its role in disease models. Specific MAGL antibodies help distinguish its activity from other lipases and validate genetic or pharmacological manipulations (e.g., CRISPR knockout, inhibitor studies). Recent research also focuses on MAGL’s dual role in cancer—promoting tumor growth via lipid signaling while suppressing cancer spread through metabolic remodeling—highlighting the need for reliable antibodies to explore these mechanisms. As MAGL-targeted therapies advance, such antibodies remain vital for preclinical validation and biomarker development.
×