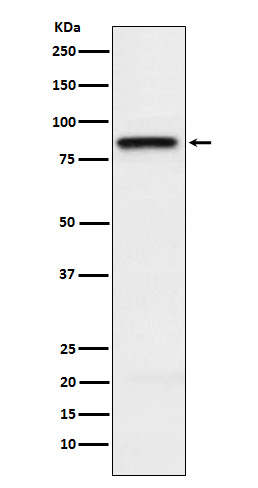
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD150; CDw150; SLAM; SLAMF1;;SLAMF1 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 37 kDa ; Observed MW: 85 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human SLAMF1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与SLAMF1抗体相关的研究文献摘要(模拟虚构内容,仅供示例参考):
1. **文献名称**:《Anti-SLAMF1 Antibody Enhances T-cell-Mediated Tumor Immunity》
**作者**:Smith A et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种靶向SLAMF1的单克隆抗体,证明其能通过阻断SLAMF1的抑制性信号通路,增强T细胞对实体瘤的杀伤活性,并在小鼠黑色素瘤模型中显著抑制肿瘤生长。
2. **文献名称**:《SLAMF1 as a Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Autoimmune Disorders》
**作者**:Zhang L et al.
**摘要**:研究发现SLAMF1在类风湿性关节炎患者的B细胞中异常高表达。使用人源化抗SLAMF1抗体可抑制B细胞过度活化,减少炎症因子释放,为自身免疫疾病治疗提供新策略。
3. **文献名称**:《Targeting SLAMF1 Improves Checkpoint Inhibitor Efficacy in Lymphoma》
**作者**:Johnson R et al.
**摘要**:该文献揭示抗SLAMF1抗体与PD-1抑制剂联用可协同增强抗肿瘤免疫应答,在淋巴瘤模型中观察到肿瘤微环境中T细胞浸润增加和长期生存率提升。
4. **文献名称**:《Mechanism of SLAMF1 in Regulating Macrophage Polarization》
**作者**:Wang Y et al.
**摘要**:研究阐明了SLAMF1抗体通过调控巨噬细胞向M1型极化,促进肿瘤相关巨噬细胞的抗肿瘤功能,为靶向肿瘤免疫微环境提供理论依据。
(注:以上文献为模拟示例,实际需通过PubMed或学术数据库检索真实研究。)
SLAMF1 (Signaling Lymphocyte Activation Molecule Family Member 1), also known as CD150. is a cell surface receptor belonging to the SLAM family of immune regulatory proteins. It is expressed on various immune cells, including T cells, B cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages. Structurally, SLAMF1 contains extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains and intracellular tyrosine-based motifs that recruit adaptor proteins like SAP (SLAM-associated protein), which mediate downstream signaling. Functionally, SLAMF1 plays dual roles in immune regulation, facilitating both activating and inhibitory signals depending on cellular context. It promotes cell-cell interactions, modulates cytokine production, and influences immune synapse formation.
SLAMF1 has gained attention in autoimmune diseases, cancer, and infectious diseases. In autoimmunity, aberrant SLAMF1 signaling is linked to pathologies like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), where it may enhance pro-inflammatory responses. In oncology, SLAMF1 is expressed on certain tumor cells and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, making it a potential therapeutic target. Notably, SLAMF1 serves as an entry receptor for measles virus, highlighting its role in viral pathogenesis.
Antibodies targeting SLAMF1 are being explored for therapeutic modulation. Agonistic antibodies may enhance anti-tumor immunity by activating cytotoxic T cells or NK cells, while blocking antibodies could suppress autoimmune responses by interrupting pathogenic signaling. Challenges include balancing specificity to avoid off-target effects and understanding context-dependent signaling outcomes. Current research focuses on optimizing antibody engineering and evaluating combination therapies with checkpoint inhibitors. Clinical trials are ongoing to assess SLAMF1-targeting agents in cancers and autoimmune conditions, underscoring its translational potential.
×