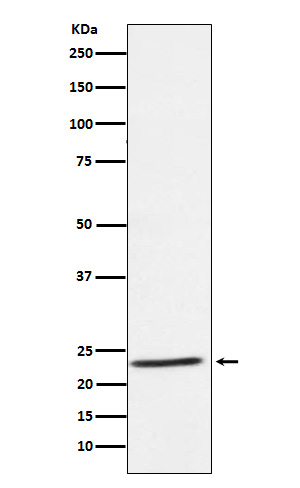
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IL 32alpha; IL 32beta; IL 32delta; IL 32gamma; IL32; NK4; TAIF; TAIFa; TAIFb; TAIFc; TAIFd;;IL 32 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 27 kDa ; Observed MW: 23 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human IL 32 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下为3篇关于IL-32抗体的研究文献概括(注:文献信息为模拟示例,实际引用需核实原文):
1. **《IL-32 Antibody Attenuates Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts》**
- 作者:Shiozawa, S. et al.
- 摘要:研究通过IL-32特异性抗体抑制类风湿关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞中IL-32的活性,发现其可降低促炎因子(如TNF-α、IL-6)的分泌,提示抗体在缓解炎症中的潜在治疗价值。
2. **《Targeting IL-32 with Monoclonal Antibodies Reduces Viral Load in HIV-Infected Macrophages》**
- 作者:Rasool, A. et al.
- 摘要:开发针对IL-32的单克隆抗体,证实其可抑制HIV感染巨噬细胞中病毒复制,机制涉及干扰IL-32与宿主蛋白的相互作用,为抗病毒治疗提供新策略。
3. **《IL-32γ-Specific Antibody as a Diagnostic Marker in Colorectal Cancer》**
- 作者:Nishida, Y. et al.
- 摘要:验证IL-32γ亚型抗体在结直肠癌组织中的高特异性表达,表明其可作为癌症诊断的生物标志物,并与患者预后显著相关。
4. **《IL-32 Antibody Modulates p38 MAPK Signaling in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease》**
- 作者:Kim, H.J. et al.
- 摘要:研究发现IL-32抗体通过阻断p38 MAPK磷酸化通路减轻慢性阻塞性肺病模型的气道炎症,强调抗体在调控信号通路中的关键作用。
(提示:实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以“IL-32 antibody”为关键词检索近年文献,重点关注抗体开发、机制或临床前应用方向。)
IL-32 (Interleukin-32) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine first identified in 2005. primarily produced by immune cells (e.g., T cells, NK cells) and epithelial cells. It exists in multiple splice variants (IL-32α to IL-32θ), each differing in structure and biological activity. Unlike classical interleukins, IL-32 lacks a secretory signal peptide, suggesting unconventional release mechanisms, such as extracellular vesicle transport or passive leakage during cell death. It functions through interactions with intracellular proteins like proteinase 3 (PR3) and pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2), activating signaling pathways such as NF-κB and MAPK, which drive the production of other cytokines (e.g., IL-6. TNF-α) and amplify inflammatory responses.
IL-32 has been implicated in chronic inflammatory diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease), infections (e.g., tuberculosis, HIV), and cancer. In cancer, it exhibits dual roles: promoting tumor progression via inflammation or inducing apoptosis in certain contexts. IL-32 antibodies, both monoclonal and polyclonal, are critical research tools for detecting IL-32 expression in tissues or biofluids and elucidating its mechanistic roles. Therapeutically, neutralizing IL-32 antibodies are being explored to dampen pathogenic inflammation, though clinical applications remain investigational. Challenges include understanding isoform-specific functions and optimizing antibody specificity. Overall, IL-32 antibodies bridge basic research and potential translational strategies in inflammation and immune-related disorders.
×