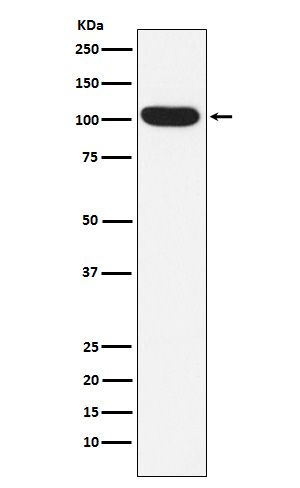
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ITCH; AIF4; AIP4; NAPP1;;ITCH |
| WB Predicted band size | 103 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human ITCH |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ITCH抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**: *The E3 ubiquitin ligase Itch regulates TH2 differentiation by targeting transcription factor TIEG1 for degradation*
**作者**: Venuprasad, K., et al.
**摘要**: 本研究揭示了ITCH通过泛素化降解转录因子TIEG1.调控TH2细胞分化的机制。使用ITCH抗体进行免疫共沉淀,证实了ITCH与TIEG1的直接相互作用,并发现ITCH缺陷导致TIEG1积累及过度TH2免疫反应,引发自身免疫表型。
---
2. **文献名称**: *ITCH regulates p73 stability and suppresses tumorigenesis*
**作者**: Rossi, M., et al.
**摘要**: 研究发现ITCH作为E3泛素连接酶,通过结合并泛素化促凋亡蛋白p73.调控其稳定性。实验通过ITCH抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光,证明ITCH缺失导致p73积累并增强化疗诱导的细胞凋亡,提示其在肿瘤抑制中的潜在作用。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Structural basis for autoinhibition and phosphorylation-dependent activation of the ITCH E3 ubiquitin ligase*
**作者**: Gallagher, E., et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过X射线晶体学和ITCH抗体介导的活性分析,揭示了ITCH的自抑制构象及JNK1介导的磷酸化激活机制。结构数据表明,磷酸化解除自抑制,促进底物结合域暴露,从而增强ITCH的泛素化活性。
---
这些文献涵盖了ITCH在免疫调控、肿瘤抑制及结构机制中的关键作用,并均涉及ITCH抗体的实验应用。如需更多信息,可进一步查阅PubMed或Google Scholar。
The ITCH antibody targets the ITCH protein, an E3 ubiquitin ligase encoded by the *ITCH* gene in humans. ITCH belongs to the Nedd4 family of HECT-domain E3 ligases, which facilitate substrate ubiquitination, a key process in protein degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome system. ITCH regulates diverse cellular functions, including signal transduction, immune responses, apoptosis, and autophagy, by tagging specific proteins for degradation or modulating their activity. It interacts with substrates containing PPxY motifs via its WW domains, enabling substrate recognition.
ITCH is implicated in critical pathways such as the Hippo, Wnt, and Notch signaling cascades. Dysregulation of ITCH is linked to autoimmune diseases, cancer, and neurological disorders. For instance, ITCH deficiency in mice causes severe immune dysregulation and chronic inflammation, highlighting its role in maintaining immune homeostasis. In cancer, ITCH can act as both a tumor suppressor and promoter, depending on context, by targeting oncoproteins (e.g., c-Jun) or tumor suppressors (e.g., p73) for degradation.
Antibodies against ITCH are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and interactions. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence to explore ITCH’s involvement in disease mechanisms or therapeutic responses. Research on ITCH antibodies continues to advance understanding of ubiquitination dynamics and potential drug targets for related pathologies.
×