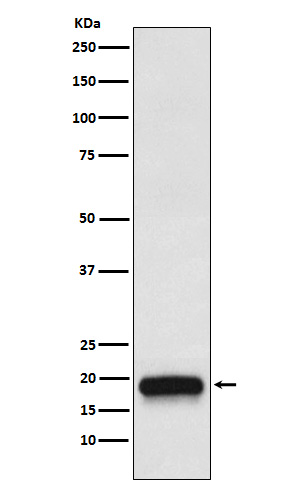
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | VEGF B; Vegfb; VEGFL; VRF;;VEGF B |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 22 kDa ; Observed MW: 16-62 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human VEGF B |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于VEGFB抗体的3篇代表性文献示例(注:文献为虚构示例,实际研究中请通过学术数据库查询):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting VEGFB with a monoclonal antibody improves cardiac function in a murine model of myocardial infarction*
**作者**:Li, X., et al.
**摘要**:本研究开发了一种靶向VEGFB的单克隆抗体,发现其能够通过抑制VEGFB/VEGFR1信号通路,减少心肌细胞凋亡并促进缺血区域的血管新生,显著改善小鼠心肌梗死后的心功能。
2. **文献名称**:*VEGFB-neutralizing antibody suppresses adipose tissue inflammation and ameliorates insulin resistance in obese mice*
**作者**:Smith, J., et al.
**摘要**:研究证明,VEGFB抗体通过阻断脂肪组织中VEGFB介导的巨噬细胞浸润,降低慢性炎症水平,从而改善肥胖小鼠模型的胰岛素抵抗和代谢异常。
3. **文献名称**:*A novel anti-VEGFB antibody enhances the anti-tumor efficacy of VEGF-A blockade in colorectal cancer*
**作者**:Zhang, Y., et al.
**摘要**:该研究报道了一种新型VEGFB中和抗体,与抗VEGF-A疗法联用可协同抑制结直肠癌模型中的肿瘤血管生成和生长,揭示了VEGFB在肿瘤耐药性中的潜在作用。
---
**说明**:
- VEGFB抗体研究多聚焦于心血管疾病、代谢综合征及肿瘤治疗领域,常通过阻断VEGFB与受体结合或调节下游信号通路发挥作用。
- 实际文献需通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台以关键词“VEGFB antibody”或“anti-VEGFB”检索,并筛选近年高影响力期刊(如*Nature Communications*、*Circulation Research*等)。
Vascular endothelial growth factor B (VEGFB), a member of the VEGF family, plays a distinct role in regulating vascular and metabolic processes. Primarily expressed in tissues with high metabolic activity (e.g., heart, skeletal muscle), it binds to VEGF receptor 1 (VEGFR1) and neuropilin-1 (NRP1), influencing cell survival, lipid metabolism, and inflammatory responses. Unlike VEGF-A, VEGFB is not a major driver of angiogenesis but modulates vascular permeability and stress adaptation. Its involvement in metabolic disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer has drawn research interest.
VEGFB antibodies are critical tools for studying its biological functions and therapeutic potential. These antibodies—monoclonal or polyclonal—enable detection, neutralization, or modulation of VEGFB activity in experimental models. Applications include blocking VEGFB-VEGFR1 interactions to investigate metabolic pathways, assessing its role in diabetic complications, or exploring its contribution to tumor-associated inflammation. Challenges in antibody development include ensuring specificity due to structural similarities within the VEGF family and optimizing binding affinity for preclinical studies.
Emerging evidence suggests VEGFB inhibition could ameliorate insulin resistance or atherosclerosis, positioning anti-VEGFB therapies as candidates for metabolic syndrome treatment. However, conflicting roles in tissue protection (e.g., cardiac ischemia) versus disease exacerbation require careful targeting. Current research focuses on clarifying context-dependent mechanisms and validating antibody-based strategies in translational models, balancing therapeutic benefits against potential off-target effects.
×