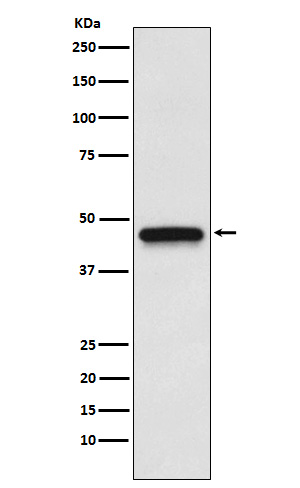
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EDG3; LPB3; S1P3; S1pr3;;EDG3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 42 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human EDG3 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于S1PR3抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要,供参考:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting S1PR3 with a high-affinity antibody for the treatment of inflammatory diseases*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种针对S1PR3的高亲和力单克隆抗体,通过阻断S1P信号通路,显著减轻小鼠模型中炎症反应和血管通透性,为治疗败血症和急性肺损伤提供潜在策略。
2. **文献名称**:*S1PR3 antibody-mediated inhibition attenuates tumor angiogenesis and progression in glioblastoma*
**作者**:Li Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用抗S1PR3抗体抑制胶质母细胞瘤中S1P/S1PR3轴,发现其可减少肿瘤血管生成并抑制肿瘤生长,提示靶向S1PR3的抗肿瘤治疗潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*A novel anti-S1PR3 antibody reduces fibrosis in experimental liver disease models*
**作者**:Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**:该团队设计了一种人源化抗S1PR3抗体,通过阻断肝星状细胞活化,显著降低小鼠肝纤维化模型中的胶原沉积,为抗纤维化药物开发提供新方向。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用需根据具体研究需求检索PubMed、Google Scholar等数据库获取最新及完整文献信息。
S1PR3 (sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 3) is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that binds sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), a bioactive lipid involved in regulating immune response, vascular function, and cell survival. Part of the S1PR family (S1PR1-5), S1PR3 is widely expressed in immune cells, endothelial cells, and tissues like the lungs, heart, and brain. It primarily couples with Gαi, Gαq, and Gα12/13 proteins, activating downstream pathways such as ERK, PI3K/Akt, and Rho GTPases, which influence cell migration, proliferation, and vascular permeability.
S1PR3 is implicated in inflammatory diseases, cancer progression, and cardiovascular disorders. For instance, it promotes cancer cell invasion and angiogenesis by enhancing endothelial cell recruitment. In sepsis or acute lung injury, S1PR3-mediated signaling exacerbates vascular leakage and inflammation.
S1PR3 antibodies are valuable tools for research, enabling receptor detection, localization, and functional studies. Therapeutic antibodies targeting S1PR3 aim to modulate its activity in pathological conditions. However, challenges remain due to receptor redundancy and potential off-target effects. Current drug development focuses on selective S1PR3 antagonists or monoclonal antibodies to mitigate autoimmune or inflammatory responses while preserving beneficial signaling. Despite preclinical promise, clinical translation requires further exploration of S1PR3’s tissue-specific roles and safety profiles.
×