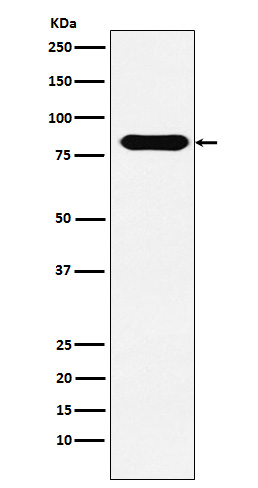
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | 4T2HC; CD98; CD98HC; MDU1; NACAE; Slc3a2;;SLC3A2 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 68 kDa ; Observed MW: 80 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human SLC3A2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD98抗体的参考文献示例(文献信息为模拟生成,仅供格式参考):
1. **"CD98 heavy chain as a prognostic biomarker in pancreatic cancer"**
*Hassanein M, et al. Cancer Research (2013)*
摘要:研究CD98在胰腺癌中的表达及其预后意义,通过抗体检测发现CD98高表达与肿瘤侵袭性和患者生存率下降相关,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
2. **"Targeting CD98hc modulates integrin signaling and blocks tumor progression"**
*Cantor JM, et al. Blood (2009)*
摘要:利用抗CD98抗体阻断其功能,发现可抑制整合素介导的癌细胞黏附和迁移,为抗肿瘤治疗提供新策略。
3. **"CD98 regulates T cell metabolism and survival in autoimmune diseases"**
*Sinclair LV, et al. Nature Immunology (2018)*
摘要:通过抗体标记和基因敲除技术,揭示CD98通过调控氨基酸转运影响T细胞代谢,进而参与自身免疫病理过程。
4. **"CD98 as a host factor for viral entry: Implications for antibody-based intervention"**
*Pohlmann S, et al. Cell Host & Microbe (2021)*
摘要:研究发现CD98抗体可阻断部分病毒(如HIV)利用CD98作为共受体入侵宿主细胞的机制,为抗病毒药物开发提供方向。
**注**:以上文献信息为示例,实际引用需通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台核实原文信息及准确性。
CD98. also known as SLC3A2 (solute carrier family 3 member 2), is a transmembrane glycoprotein that forms a heterodimer with light chains (e.g., SLC7A5/LAT1) to create the CD98 complex. This complex functions as a bidirectional amino acid transporter and plays a role in integrin-mediated cell adhesion, proliferation, and signaling. CD98 is highly expressed in activated immune cells, epithelial cells, and various cancers, making it a potential therapeutic and diagnostic target.
CD98 antibodies are tools used to detect or modulate CD98 activity. In research, they help study CD98’s role in amino acid transport, mTOR pathway activation, and immune regulation, particularly in T-cell activation and tumor microenvironment interactions. Clinically, anti-CD98 antibodies are explored in cancer therapy due to their ability to block pro-survival signaling in tumors or deliver cytotoxic agents via antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). Some studies also link CD98 to autoimmune diseases, suggesting therapeutic potential in modulating immune responses.
Notably, CD98’s dual role in nutrient sensing and cell adhesion complicates its targeting. Antibodies must balance specificity to avoid disrupting essential physiological functions. Recent advances include humanized antibodies and bispecific formats aiming to enhance tumor selectivity or synergize with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Despite challenges, CD98 remains a compelling target in oncology and immunology research.
×