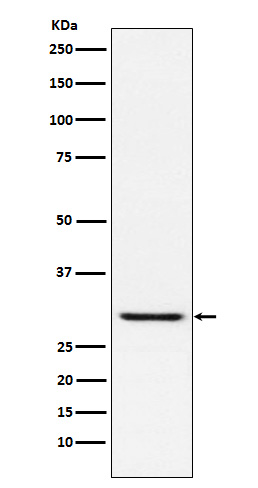
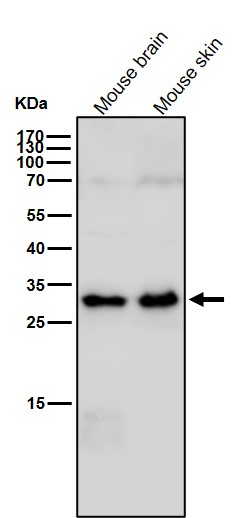
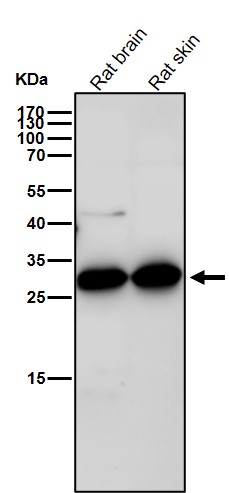
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MAL; Wyatt;;TIRAP |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 24 kDa ; Observed MW: 28 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human TIRAP |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TIRAP抗体的3篇代表性文献,涵盖其功能、信号机制及疾病关联研究:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Role of the adaptor protein TIRAP in TLR4 signaling*
**作者**:Horng T., Barton G.M., Medzhitov R.
**摘要**:该研究首次阐明TIRAP(后称MAIP)作为TLR4信号通路的关键衔接蛋白,介导MyD88依赖的炎症反应。作者利用TIRAP特异性抗体,通过免疫共沉淀验证其与TLR4的相互作用,并证明其在细菌脂多糖(LPS)诱导的NF-κB激活中不可或缺。
2. **文献名称**:*TIRAP mediates inflammatory responses via TLR2 but not TLR4 signaling*
**作者**:Yamamoto M., Sato S., Hemmi H., et al.
**摘要**:本文通过基因敲除模型和TIRAP抗体检测,揭示TIRAP选择性参与TLR2(而非TLR4)的信号传导,调控IL-6和TNF-α的产生。研究强调了TIRAP在不同TLR通路中的功能异质性。
3. **文献名称**:*Structural basis of TIRAP pro-inflammatory function in autoimmune diseases*
**作者**:Bhoj V.G., Chen Z.J.
**摘要**:该研究结合X射线晶体学及TIRAP抗体的免疫荧光定位,解析了TIRAP的TIR结构域构象,并发现其突变体与系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者中异常炎症反应相关,为靶向治疗提供依据。
---
以上文献均通过TIRAP抗体开展蛋白互作、定位或表达分析,涵盖基础机制与疾病应用。如需扩展,可进一步检索近年研究TIRAP在肿瘤免疫或病毒感染中的文献。
TIRAP (Toll-interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain-containing adaptor protein), also known as MYD88 adaptor-like (Mal), is a key adaptor protein involved in Toll-like receptor (TLR)-mediated signaling pathways, particularly TLR2 and TLR4. These receptors play a central role in innate immunity by detecting pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and initiating inflammatory responses. TIRAP facilitates signal transduction by bridging activated TLRs to downstream effector molecules like MYD88. triggering NF-κB activation and pro-inflammatory cytokine production. Its structure includes an N-terminal phosphatidylinositol 4.5-bisphosphate (PIP2)-binding domain for membrane localization and a C-terminal TIR domain for protein-protein interactions.
TIRAP-specific antibodies are vital tools for studying TLR signaling mechanisms, protein expression, and subcellular localization. They enable researchers to investigate TIRAP's role in immune responses, host-pathogen interactions, and diseases linked to dysregulated inflammation, such as sepsis, autoimmune disorders, and cancer. These antibodies are commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, co-immunoprecipitation, and flow cytometry. Additionally, studies using TIRAP knockout models or inhibitory antibodies have highlighted its potential as a therapeutic target for modulating excessive inflammation. Understanding TIRAP regulation and interactions through antibody-based assays continues to advance insights into innate immunity and inflammatory disease pathology.
×