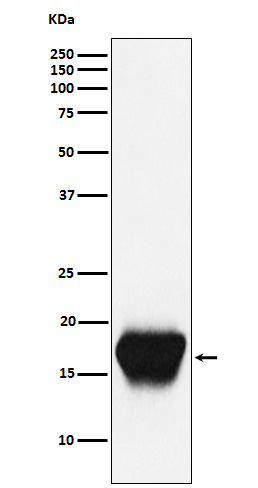
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CAMPATH 1; CD52; CDw52; He5;;CD52 |
| WB Predicted band size | 8 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from mouse CD52 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD52抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要信息:
1. **文献名称**: *"CD52 antibodies for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia"*
**作者**: Hale G, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究探讨了抗CD52单克隆抗体(如阿仑单抗)在慢性淋巴细胞白血病(CLL)治疗中的作用,显示其通过靶向CD52高表达的淋巴细胞,有效清除恶性B细胞并改善患者预后。
2. **文献名称**: *"Alemtuzumab versus interferon beta-1a in early multiple sclerosis"*
**作者**: Coles AJ, et al.
**摘要**: 这项临床试验比较了抗CD52抗体阿仑单抗与干扰素β-1a治疗早期多发性硬化症(MS)的效果,发现阿仑单抗显著降低复发率并延缓疾病进展,但伴随自身免疫副作用风险。
3. **文献名称**: *"CD52 as a regulator of T-cell function in inflammatory diseases"*
**作者**: Watanabe T, et al.
**摘要**: 研究揭示了CD52分子通过释放可溶性信号(如sCD52)调控T细胞活化和炎症反应,提示抗CD52抗体可能通过双重机制(耗竭细胞和信号调节)发挥治疗作用。
4. **文献名称**: *"Mechanisms of anti-CD52 antibody-mediated cell killing"*
**作者**: Cragg MS, et al.
**摘要**: 该文献系统分析了抗CD52抗体(如阿仑单抗)诱导细胞死亡的机制,包括补体依赖性细胞毒性(CDC)、抗体依赖性细胞介导的细胞毒性(ADCC)以及直接凋亡信号激活。
这些文献覆盖了CD52抗体的治疗应用、机制研究及临床效果,主要发表于血液学、神经免疫学领域期刊。
CD52 is a small, glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored cell surface glycoprotein expressed abundantly on lymphocytes, monocytes, and macrophages, with lower levels on eosinophils and dendritic cells. Discovered in the 1980s, its gene maps to chromosome 1p36. The CD52 antigen comprises a 12-amino acid peptide linked to a complex carbohydrate moiety, though its precise physiological role remains unclear, potentially involving immune modulation.
The CD52 antibody, notably alemtuzumab (Campath-1H), is a humanized monoclonal antibody targeting CD52. Developed in the 1990s, alemtuzumab initially treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) by depleting malignant B cells via antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and complement activation. Its potent lymphodepleting effects later expanded applications to autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis (MS) and organ transplant rejection prophylaxis.
Despite efficacy, CD52 antibody therapy risks severe immunosuppression, increasing susceptibility to infections and secondary autoimmune disorders. Research continues to refine dosing strategies and explore novel anti-CD52 agents with improved safety profiles. CD52 remains a pivotal therapeutic target, illustrating the dual role of immune-targeted therapies in balancing clinical benefits against systemic immunomodulatory risks.
×