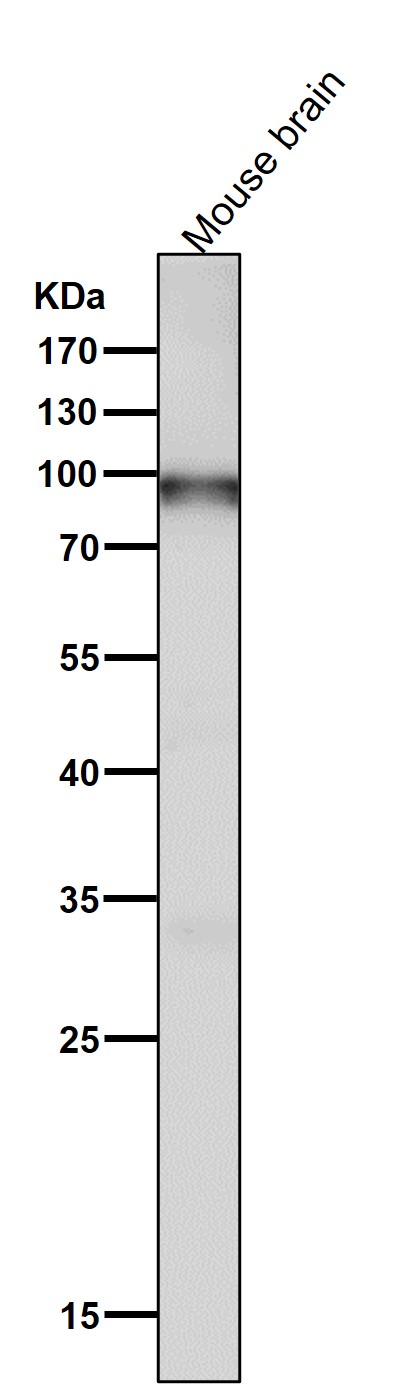

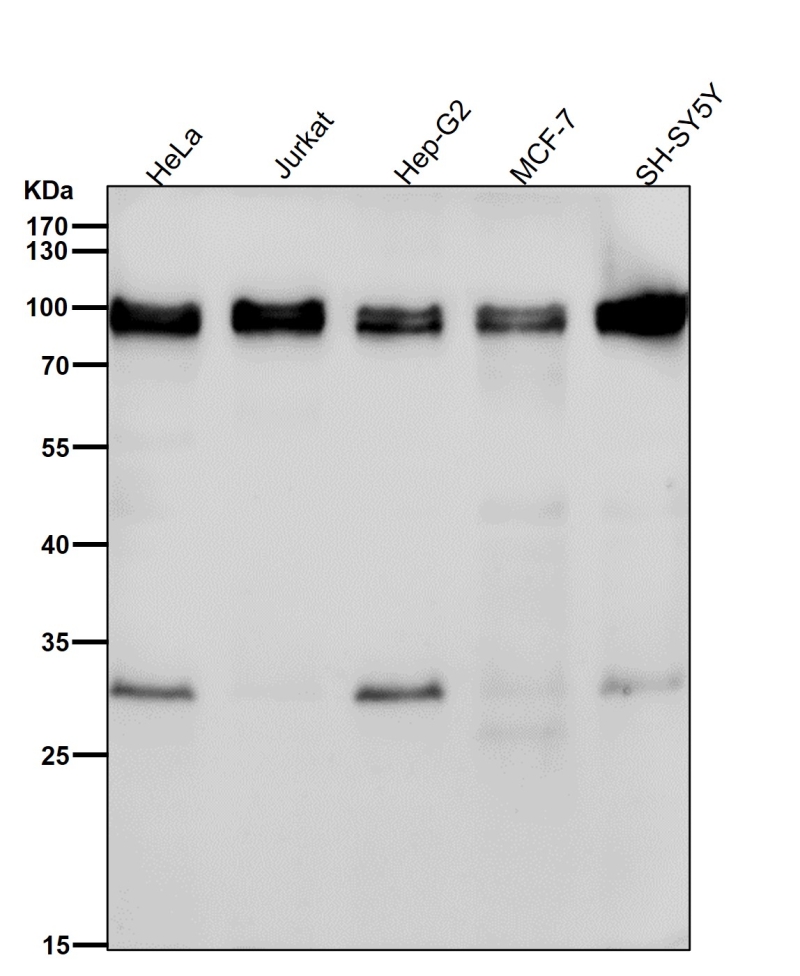
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NOR 90; UBF; Ubtf;;UBTF |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 89 kDa ; Observed MW: 94,97 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human UBTF |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于UBF1抗体的3篇参考文献,涵盖功能研究和实验应用方向:
1. **文献名称**:*"Cloning and characterization of UBF1. a human transcription factor involved in ribosomal RNA synthesis"*
**作者**:O’Mahony DJ, et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次克隆了人类UBF1基因,并制备了特异性抗体,证实UBF1在核仁中的定位及其在rRNA转录调控中的核心作用,抗体被用于免疫荧光和Western blot分析。
2. **文献名称**:*"The RNA polymerase I transcription factor UBF regulates the dynamics of chromatin structure"*
**作者**:Bell SP, et al.
**摘要**:通过抗体介导的染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)实验,揭示UBF1通过重塑染色质构象促进rRNA基因转录起始复合物形成,证明其在维持核仁结构中的功能。
3. **文献名称**:*"p53-mediated repression of rRNA synthesis by binding to UBF1 and blocking its interaction with RNA polymerase I"*
**作者**:Crighton D, et al.
**摘要**:利用UBF1抗体进行共免疫沉淀实验,发现p53通过直接结合UBF1抑制rRNA转录,阐明UBF1在细胞应激反应中协调生长抑制的关键机制。
---
**选择依据**:覆盖UBF1抗体在定位(免疫荧光)、功能验证(Western blot/ChIP)和互作研究(Co-IP)中的典型应用场景,适合实验设计参考。如需扩展,可补充其在疾病模型(如癌症)中的研究文献。
The UBF1 (Upstream Binding Factor 1) antibody is a critical tool for studying the role of UBF1. a nucleolar transcription factor essential for ribosomal RNA (rRNA) synthesis. UBF1 binds to the upstream control element of rRNA gene promoters, facilitating the assembly of the RNA polymerase I (Pol I) pre-initiation complex and regulating ribosome biogenesis. It contains multiple HMG (high mobility group) box domains, enabling DNA bending and nucleolar chromatin remodeling. UBF1 is dynamically phosphorylated during the cell cycle, influencing its activity and interactions with other Pol I machinery components, such as SL1/TIF-IB.
Antibodies against UBF1 are widely used to investigate its expression, localization, and function in diverse biological contexts, including cancer (where dysregulated rRNA synthesis promotes tumor growth), developmental biology, and cellular stress responses. These antibodies enable techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), and co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) to explore UBF1’s role in nucleolar organization, cell proliferation, and diseases linked to ribosomopathies.
Commercial UBF1 antibodies are typically raised against epitopes in conserved regions (e.g., the N-terminal HMG boxes) and validated for specificity in human, mouse, or rat samples. Researchers rely on these antibodies to dissect mechanisms underlying Pol I transcription and its therapeutic targeting in pathologies like cancer.
×