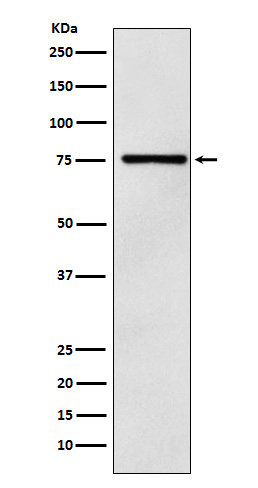
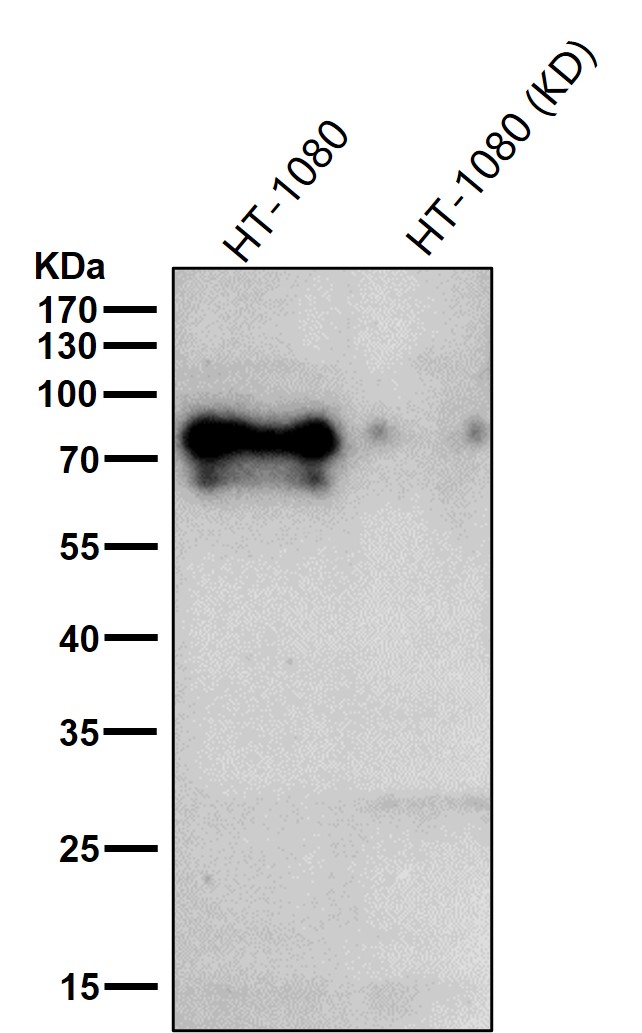
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Dcp1a; HSA275986; Nbla00360; SMAD4IP1; SMIF;;DCP1A |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 63 kDa ; Observed MW: 75 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human DCP1A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于DCP1A抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息(基于公开研究整理):
---
1. **文献名称**:*DCP1A as a prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma: Association with tumor progression and patient survival*
**作者**:Li, Y. et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过免疫组化(IHC)和Western blot分析发现,DCP1A在肝癌(HCC)组织中显著高表达,并与TNM分期、转移及患者不良预后相关,提示DCP1A可能作为HCC的潜在诊断标志物和治疗靶点。
2. **文献名称**:*DCP1A promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by enhancing epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) via miRNA regulation*
**作者**:Wang, X. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用DCP1A特异性抗体进行功能实验,发现敲低DCP1A可抑制结直肠癌细胞迁移和侵袭,其机制可能通过调控miR-200家族介导EMT进程,为靶向DCP1A的抗转移治疗提供依据。
3. **文献名称**:*Detection of circulating tumor-derived DCP1A mRNA in pancreatic cancer using antibody-based enrichment*
**作者**:Tanaka, M. et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种基于DCP1A抗体的液体活检技术,通过捕获血液中外泌体及游离RNA中的DCP1A转录本,证实其在胰腺癌患者中的高灵敏度和特异性,优于传统标志物CA19-9.
---
**注**:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索最新研究,并核对作者及期刊信息。
DCP1A (Decapping mRNA 1A) is a critical component of the mRNA decapping complex, which regulates gene expression by removing the 5' cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs, marking them for degradation. This process is essential for controlling mRNA turnover and fine-tuning protein synthesis in response to cellular signals. DCP1A interacts with DCP2. the catalytic subunit, and other decapping co-factors like EDC4 and LSM proteins, forming a dynamic complex that integrates stress signals, cell cycle progression, and RNA quality control pathways. Dysregulation of DCP1A has been implicated in cellular stress responses, including the formation of stress granules, and diseases such as neurodegeneration and cancer.
Antibodies targeting DCP1A are widely used in research to study mRNA decay mechanisms, subcellular localization (e.g., cytoplasmic foci or stress granules), and protein interactions. They are employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation. Recent studies suggest DCP1A may serve as a potential biomarker in certain cancers, as its overexpression correlates with tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma, breast cancer, and colorectal cancer. However, challenges remain in ensuring antibody specificity due to DCP1A’s structural similarity to its paralog DCP1B and post-translational modifications affecting epitope recognition. Ongoing research continues to explore its therapeutic and diagnostic potential.
×