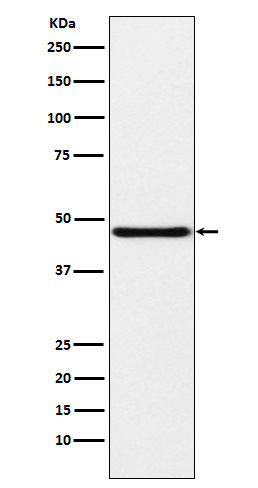
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NPHS2; PDCN; Podocin; SRN1;;Podocin |
| WB Predicted band size | 42 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Podocin |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于NPHS2抗体的参考文献及其摘要内容:
1. **"Podocin, a raft-associated component of the glomerular slit diaphragm, interacts with CD2AP and nephrin"**
- **作者**: Huber TB, Kottgen M, Schilling B, Walz G, Benzing T
- **摘要**: 该研究通过免疫共沉淀和免疫荧光技术,使用NPHS2抗体揭示了podocin在肾小球裂孔隔膜中的定位,并发现其与CD2AP、nephrin的相互作用,强调了其在足细胞结构和功能中的关键作用。
2. **"Mutations in the human laminin β2 (LAMB2) gene and the associated phenotypic spectrum"**
- **作者**: Hasselbacher K, Wiggins RC, Matejas V, Hinkes B, Schlötzer-Schrehardt U, Lemmink HH, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究在分析遗传性肾病综合征时,使用NPHS2抗体检测患者肾组织中的podocin表达,结合基因测序发现部分病例存在LAMB2基因突变,提示足细胞蛋白异常与肾病的关联。
3. **"Clinical and epidemiological assessment of steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome associated with the NPHS2 R229Q variant"**
- **作者**: Pereira AC, Pereira AB, Mota GF, Cunha RS, Herkenhoff FL, Pollak MR, et al.
- **摘要**: 通过NPHS2抗体进行免疫组化分析,评估携带R229Q突变的患者肾活检样本中podocin的表达模式,发现该变异可能导致足细胞功能障碍,进而引发激素抵抗型肾病综合征。
4. **"Nephrin and podocin synergize to induce kidney podocyte-specific gene expression"**
- **作者**: Schwarz K, Simons M, Reiser J, Saleem MA, Faul C, Kriz W, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究利用NPHS2抗体及nephrin抗体共转染细胞模型,证明两者协同调控足细胞特异性基因表达,为理解NPHS2在肾病发生中的分子机制提供了实验依据。
这些文献涵盖了NPHS2抗体在基础研究(蛋白互作、基因表达调控)及临床诊断(突变分析、表型关联)中的应用,反映了其在肾病机制探索中的重要性。
**Background of NPHS2 Antibody**
The NPHS2 antibody targets podocin, a critical protein encoded by the *NPHS2* gene, which is predominantly expressed in glomerular podocytes—specialized cells in the kidney responsible for maintaining filtration barriers. Podocin plays a structural and regulatory role in the slit diaphragm, a junctional complex essential for preventing proteinuria. Mutations in *NPHS2* are linked to autosomal recessive steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS), often manifesting in childhood as focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS).
NPHS2 antibodies are widely used in research and diagnostics to study podocyte biology and kidney diseases. They help detect podocin expression in tissues via immunohistochemistry (IHC) or immunofluorescence (IF), aiding in the identification of podocyte injury or loss. In experimental models, these antibodies are employed to validate *NPHS2* knockout or knockdown efficiency and assess podocin localization, which is crucial for understanding slit diaphragm integrity.
Clinically, NPHS2 antibodies contribute to differentiating genetic forms of SRNS from other glomerulopathies. Podocin expression levels, measured using these antibodies, may correlate with disease severity or progression. Additionally, they are used alongside other podocyte markers (e.g., nephrin, synaptopodin) to investigate crosstalk in signaling pathways underlying podocyte dysfunction. Their utility extends to transgenic animal studies, where podocin-specific staining helps evaluate experimental FSGS models and potential therapies. Overall, NPHS2 antibodies serve as vital tools in nephrology research and diagnostics.
×