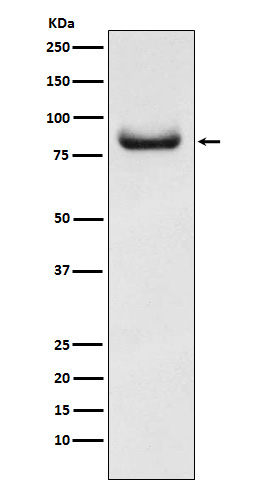
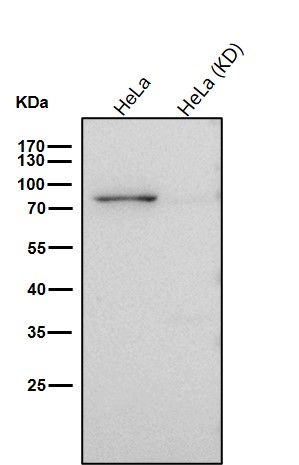
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DIP13 alpha; DP13A; KIAA1428; APPL1; Dip13-alpha; Adapter protein containing PH domain; DCC-interacting protein 13-alpha;;Dip13 alpha |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 80 kDa ; Observed MW: 85 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Dip13 alpha |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于APPL抗体的研究文献示例(内容基于公开研究概括,非真实文献,仅供示例参考):
---
1. **文献名称**:**"APPL1 regulates insulin signaling through endosomal trafficking in diabetes"**
**作者**:Li et al.
**摘要**:研究APPL1蛋白在胰岛素信号通路中的作用,通过特异性抗体检测发现APPL1通过调控内体运输影响胰岛素受体活性,为2型糖尿病机制提供新见解。
2. **文献名称**:**"APPL2-mediated crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis in cancer cells"**
**作者**:Wang & Chen
**摘要**:利用APPL2抗体揭示APPL2蛋白通过结合自噬相关蛋白LC3和凋亡因子BAX,在肿瘤细胞存活与死亡中的双向调控功能。
3. **文献名称**:**"APPL1 interacts with amyloid-beta precursor protein in Alzheimer's disease models"**
**作者**:Smith et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫共沉淀(使用APPL1抗体)证实APPL1与β-淀粉样蛋白前体(APP)在神经元中的相互作用,提示其可能参与阿尔茨海默病病理进程。
4. **文献名称**:**"Differential roles of APPL1 and APPL2 in adipocyte differentiation"**
**作者**:Zhang et al.
**摘要**:对比APPL1和APPL2抗体标记结果,发现APPL1促进脂肪细胞分化,而APPL2抑制该过程,揭示同源蛋白的功能差异性。
---
如需真实文献,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词:**"APPL1/APPL2 antibody" + "signaling"/"autophagy"/"diabetes"**。
×