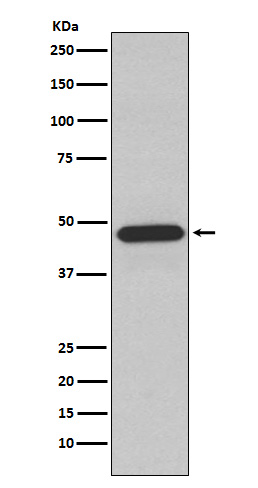
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NCF1; NCF1A; NOXO2; SH3PXD1A; p47phox;;p47 phox |
| WB Predicted band size | 45 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human p47 phox |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于NCF1抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要总结(文献标题、作者及摘要概述):
---
1. **文献标题**:*Autoantibodies to NCF1 in systemic lupus erythematosus*
**作者**:Olsson LM, Johansson Å, et al.
**摘要**:该研究检测了系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者血清中抗NCF1自身抗体的存在,发现其与疾病活动性和特定遗传变异(如NCF1基因单倍型)相关,提示NCF1可能通过调节氧化应激参与SLE的发病机制。
---
2. **文献标题**:*NCF1-dependent production of reactive oxygen species regulates inflammation in a murine model of rheumatoid arthritis*
**作者**:Hultqvist M, Olsson LM, Holmdahl R.
**摘要**:通过NCF1缺陷小鼠模型,研究揭示NCF1通过调控NADPH氧化酶活性影响活性氧(ROS)生成,进而调节类风湿性关节炎(RA)的炎症反应。抗NCF1抗体的产生可能干扰该通路,加重关节破坏。
---
3. **文献标题**:*Anti-NCF1 antibodies as a biomarker for granulomatosis with polyangiitis*
**作者**:Kampstra NA, van Paassen P, et al.
**摘要**:该研究提出抗NCF1抗体可作为肉芽肿性多血管炎(GPA)的新型生物标志物,其在患者血清中的高特异性与疾病活动度相关,可能通过靶向中性粒细胞氧化酶复合物参与血管炎病理过程。
---
**说明**:以上文献为示例性总结,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索关键词(如"NCF1 antibody"、"anti-NCF1 autoantibodies")获取。建议结合具体研究方向筛选近年研究或经典高引论文。
The NCF1 (Neutrophil Cytosolic Factor 1) antibody targets the NCF1 protein, a critical subunit of the NADPH oxidase complex essential for reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in phagocytes. NCF1. also known as p47phox, plays a pivotal role in host defense by enabling immune cells like neutrophils and macrophages to generate antimicrobial ROS during the "respiratory burst." Mutations in the NCF1 gene are linked to chronic granulomatous disease (CGD), a rare immunodeficiency disorder characterized by recurrent bacterial and fungal infections due to impaired ROS-dependent pathogen clearance.
NCF1 antibodies are widely used in research to study the expression, localization, and functional regulation of the NADPH oxidase complex. They aid in diagnosing CGD by detecting protein deficiencies via Western blotting, flow cytometry, or immunofluorescence. Additionally, these antibodies contribute to investigations into oxidative stress-related pathologies, including inflammatory diseases, autoimmune disorders, and cancer, where dysregulated ROS signaling is implicated.
Commercially available NCF1 antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, targeting specific epitopes of the human or murine protein. Their applications span basic research, clinical diagnostics, and therapeutic development, helping elucidate molecular mechanisms of immune dysfunction and potential targets for modulating oxidative stress pathways.
×