
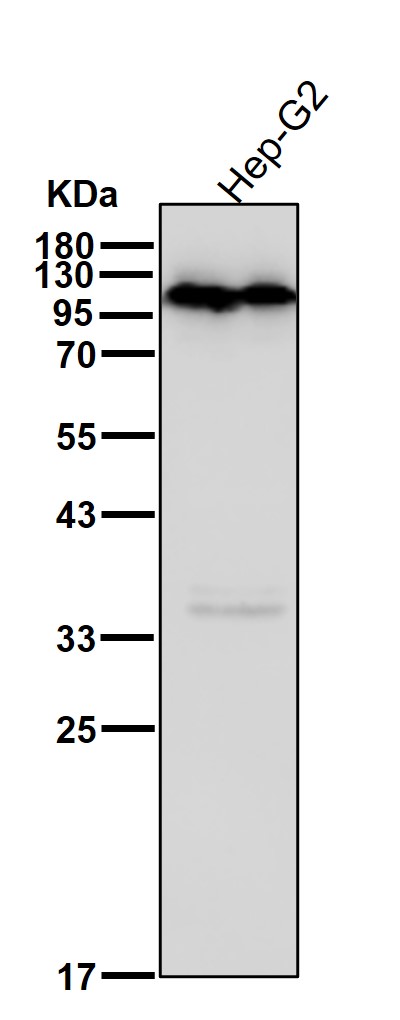
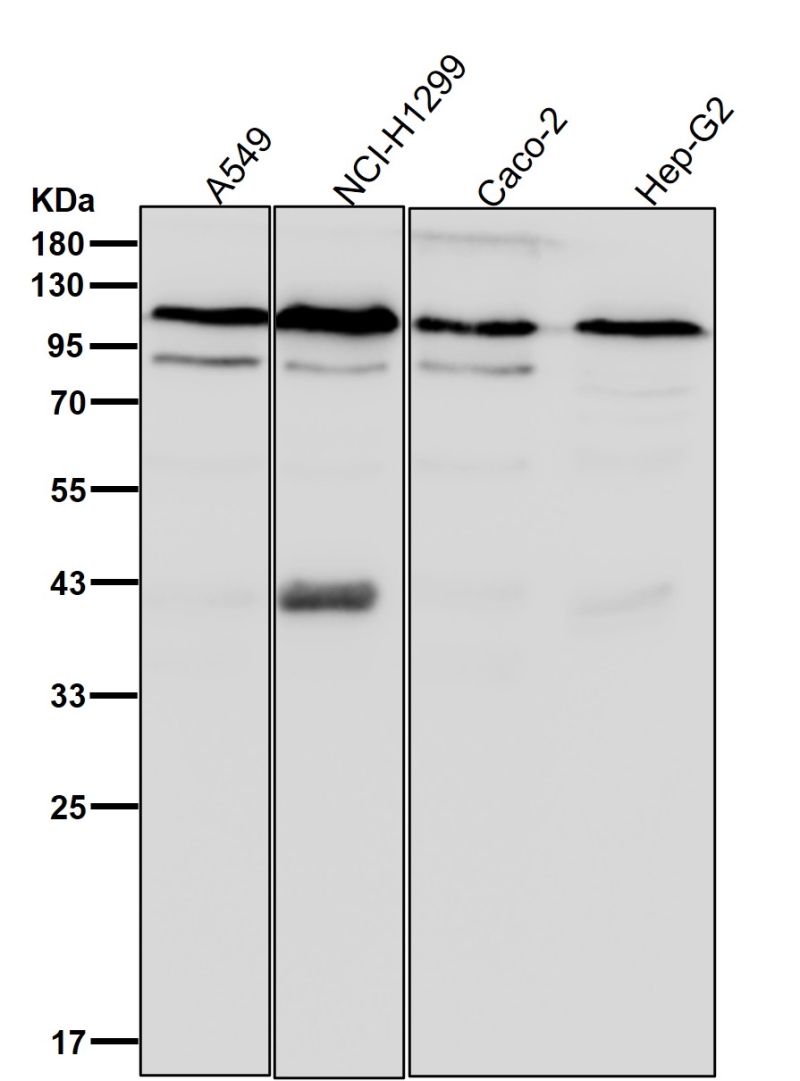
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | hPOMp100; POMP100; PPP1R140; PSF; Sfpq; Splicing factor;;SFPQ |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 76 kDa ; Observed MW: 100 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human SFPQ |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
1. **"SFPQ and its binding partners in neuronal RNA granules in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis" - Ito D. et al.**
摘要:研究探讨SFPQ蛋白在肌萎缩侧索硬化症(ALS)患者神经元RNA颗粒中的异常聚集,通过SFPQ抗体检测发现其与TDP-43共定位,提示其在神经退行性疾病中的病理作用。
2. **"The role of SFPQ in DNA damage response and genomic stability" - Bladen C.L. et al.**
摘要:利用SFPQ抗体进行免疫沉淀和染色质分析,揭示SFPQ在DNA双链断裂修复中与ATM激酶通路相互作用,维持基因组稳定性。
3. **"SFPQ modulates HIV-1 replication by binding viral RNA and regulating transcription" - Yedavalli V.S. et al.**
摘要:研究通过SFPQ抗体阻断实验,发现SFPQ蛋白直接结合HIV-1 RNA,抑制病毒转录复合体形成,影响病毒复制效率。
4. **"Nuclear paraspeckle assembly mediated by SFPQ-NONO complex" - Hirose T. et al.**
摘要:采用SFPQ抗体进行免疫荧光定位,阐明SFPQ与NONO蛋白共同调控核内paraspeckles结构的形成,并参与长链非编码RNA(如NEAT1)的功能。
The SFPQ (Splicing Factor Proline and Glutamine Rich) antibody is a key tool for studying the multifunctional SFPQ protein, also known as PSF (PTB-associated Splicing Factor). SFPQ is a ubiquitously expressed RNA/DNA-binding protein involved in critical cellular processes, including pre-mRNA splicing, transcriptional regulation, DNA repair, and paraspeckle formation. It often forms heterodimers with NONO or PSPC1. contributing to large molecular complexes (∼700-800 kDa) that mediate RNA processing and genomic stability. SFPQ is essential for neuronal development, immune responses, and cell cycle control, with dysregulation linked to neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., ALS), viral infections, and cancers.
SFPQ antibodies, typically monoclonal or polyclonal, are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to investigate its localization, expression levels, and interactions. These antibodies help identify SFPQ’s dual roles in gene expression—acting as a splicing repressor or activator depending on cellular context—and its involvement in DNA damage response pathways. Researchers also utilize SFPQ antibodies to explore its pathological roles, such as forming toxic aggregates in ALS or modulating oncogenic signaling in tumors. Validated specificity for target epitopes ensures reliability in both basic research and clinical studies aiming to dissect SFPQ-related molecular mechanisms or therapeutic targets.
×