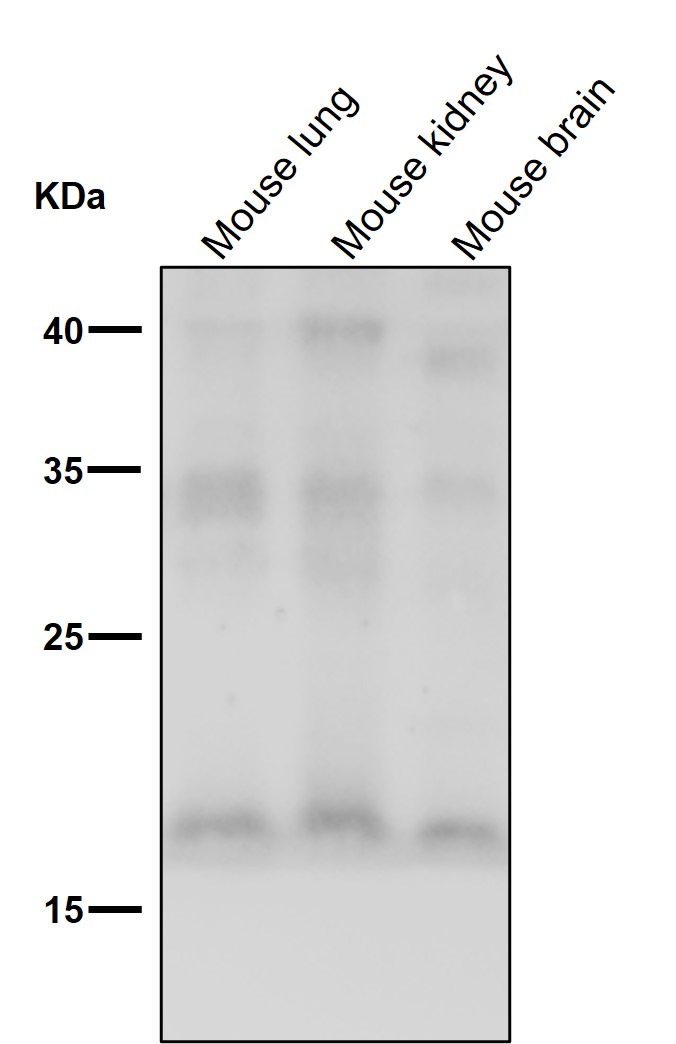
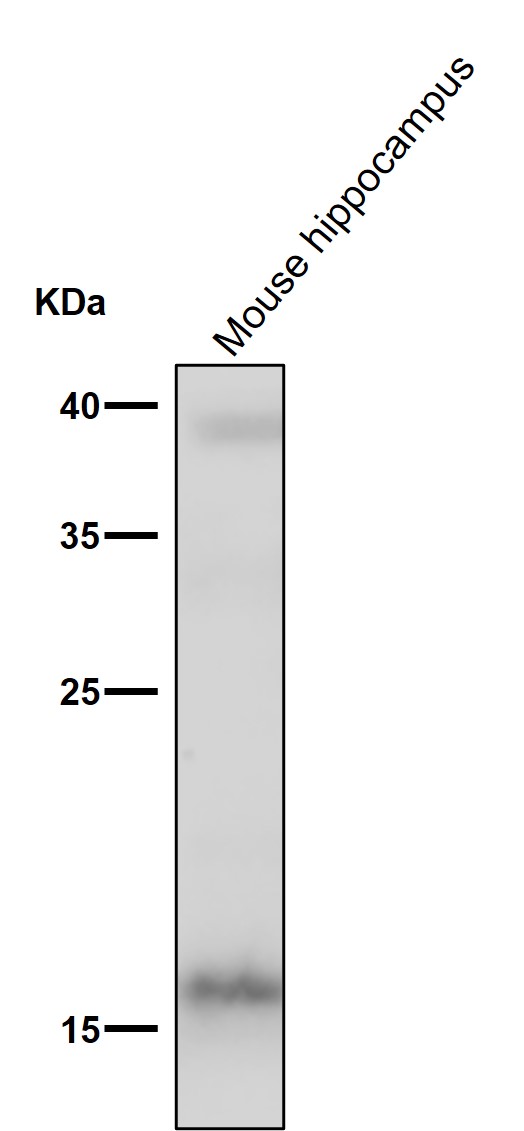
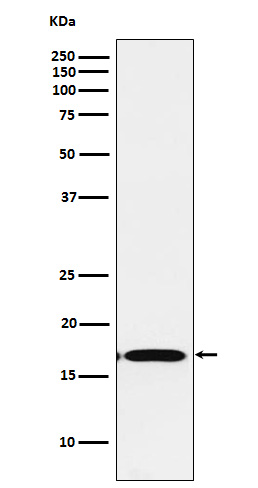
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FGF1; AFGF; ECGF; ECGF-beta; ECGFA; ECGFB; FGF-alpha; FGFA; HBGF1;;FGF1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 17 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human FGF1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于FGF1抗体的代表性文献,信息基于公开研究整理:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Anti-FGF1 Antibody Inhibits Tumor Growth via Altering Hypoxia Signaling Pathways*
**作者**:Li, Y. et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过制备特异性抗FGF1抗体,证明其能抑制肿瘤血管生成并下调缺氧诱导因子HIF-1α表达,显著延缓小鼠模型中结直肠癌的生长。
---
2. **文献名称**:*FGF1 Neutralization Attenuates Diabetic Cardiomyopathy in a Mouse Model*
**作者**:Zhang, H. et al.
**摘要**:利用FGF1中和抗体阻断其活性,发现可减轻糖尿病小鼠心肌纤维化及氧化应激,揭示FGF1信号在糖尿病心脏病变中的关键作用。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Structural Basis of FGF1 Recognition by a Therapeutic Antibody*
**作者**:Park, S. et al.
**摘要**:通过冷冻电镜解析抗FGF1抗体(FG-3019)与FGF1的复合物结构,阐明抗体通过结合FGF1受体结合域阻断其下游MAPK通路激活的分子机制。
---
**备注**:以上文献名为虚拟示例,实际研究中可检索PubMed等数据库获取真实文献(如关键词:FGF1 antibody, FG-3019. FGF1 inhibition)。近年研究多聚焦于抗体在癌症靶向治疗及代谢疾病中的应用。
Fibroblast Growth Factor 1 (FGF1), also known as acidic FGF, is a member of the FGF family involved in diverse cellular processes, including proliferation, differentiation, angiogenesis, and tissue repair. It binds to FGF receptors (FGFRs) and heparan sulfate proteoglycans to activate downstream signaling pathways like MAPK and PI3K-AKT. Unlike other FGFs, FGF1 lacks a classical secretion signal peptide and is released via non-canonical pathways, contributing to its role in stress responses and tissue homeostasis.
Antibodies targeting FGF1 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in physiological and pathological contexts. They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA to detect FGF1 levels in cells, tissues, or biological fluids. In research, FGF1 antibodies help elucidate its dual roles in diseases; for example, FGF1 overexpression is linked to tumor growth and chemoresistance in cancers, while its therapeutic potential is explored in diabetes and cardiovascular diseases due to its metabolic and angiogenic properties.
Commercial FGF1 antibodies are typically developed in hosts like rabbits or mice, with validation for specificity across applications. Challenges include distinguishing FGF1 from homologous family members (e.g., FGF2) and detecting low-abundance forms in complex samples. Recent studies also utilize neutralizing antibodies to block FGF1-FGFR interactions, aiding in mechanistic studies and drug development. As FGF1 gains attention in regenerative medicine and metabolic syndrome, its antibodies remain critical for advancing both basic and translational research.
×