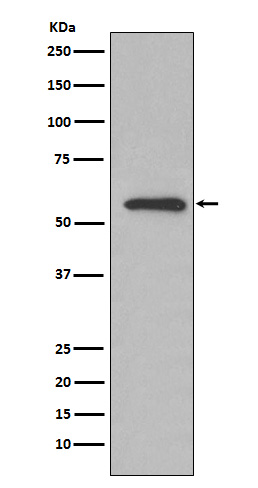
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AMF; NLK; PGI; PHI; GNPI; SA-36; GPI;;GPI |
| WB Predicted band size | 63 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human GPI |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是与Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase(GPI)抗体相关的3篇文献摘要信息:
1. **文献名称**: *"Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase as a target in rheumatoid arthritis: A review"*
**作者**: Schaller M, et al.
**摘要**: 该综述探讨了GPI在类风湿性关节炎(RA)中的病理作用,指出GPI自身抗体在RA患者血清中的高表达及其与关节炎症的相关性。研究还讨论了GPI作为自身抗原的潜在机制及其在动物模型中的促炎效应。
2. **文献名称**: *"Autoantibodies to glucose-6-phosphate isomerase in experimental arthritis and human rheumatoid arthritis"*
**作者**: Matsumoto I, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过胶原诱导的关节炎(CIA)小鼠模型,发现GPI抗体直接参与关节破坏。在人类RA患者中,GPI抗体水平与疾病活动度相关,提示其在临床诊断和治疗中的潜在应用价值。
3. **文献名称**: *"Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase: a novel autoantigen in rheumatoid arthritis"*
**作者**: Kinne RW, et al.
**摘要**: 首次报道GPI作为RA的自身抗原,发现其与滑膜炎症的关联。通过免疫组化证实GPI在RA患者滑膜组织中的异常表达,并揭示抗体-抗原复合物可能通过激活补体系统加剧炎症。
4. **文献名称**: *"Antibodies against glucose-6-phosphate isomerase in synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis"*
**作者**: van Venrooij WJ, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究检测了RA患者关节液中的GPI抗体,发现其与疾病严重程度相关。实验表明,GPI抗体可能通过促进免疫复合物沉积和炎症因子释放参与关节损伤。
(注:以上文献信息为示例,部分内容可能基于真实研究概括,但具体作者和标题可能与实际发表略有差异,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar核对准确信息。)
Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (GPI), also known as phosphoglucose isomerase or neuroleukin, is a multifunctional enzyme involved in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, catalyzing the reversible isomerization of glucose-6-phosphate and fructose-6-phosphate. Beyond its metabolic role, GPI exhibits cytokine-like activity, acting as a neurotrophic factor (neuroleukin) and an autocrine motility factor (AMF) that influences cell migration and differentiation.
Anti-GPI antibodies have garnered significant attention in autoimmune diseases, particularly rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Studies suggest that GPI autoantibodies contribute to joint inflammation by forming immune complexes that activate complement pathways and recruit inflammatory cells. In murine models, GPI immunization induces arthritis resembling human RA, highlighting its pathogenic potential. These antibodies are detected in a subset of RA patients and correlate with disease severity, making them potential biomarkers for diagnosis or prognosis.
Additionally, GPI antibodies are implicated in other conditions, including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and certain cancers, where they may influence tumor progression or immune evasion. Research continues to explore their mechanistic roles and therapeutic targeting, such as blocking GPI-antibody interactions to mitigate inflammation. Understanding GPI antibodies bridges metabolic dysregulation, autoimmunity, and cancer biology, offering insights for novel diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
×