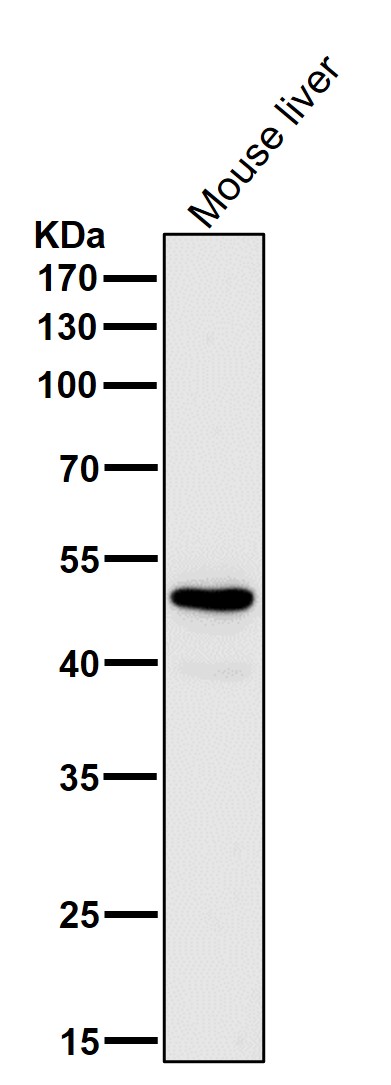
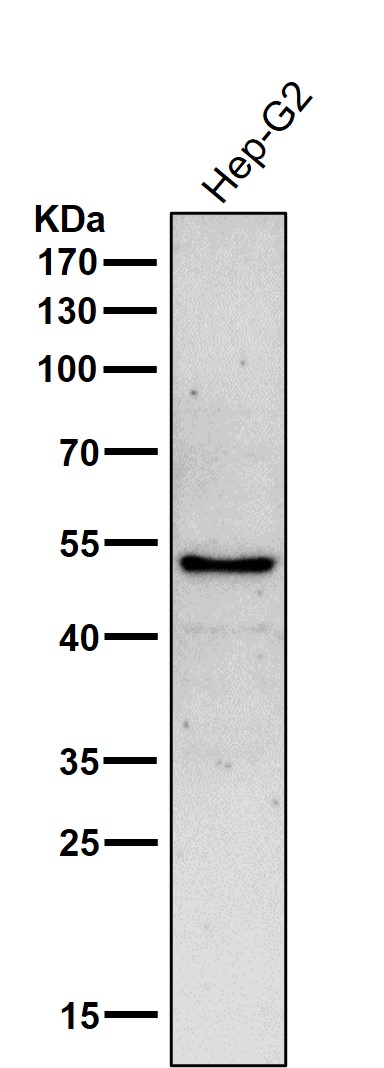
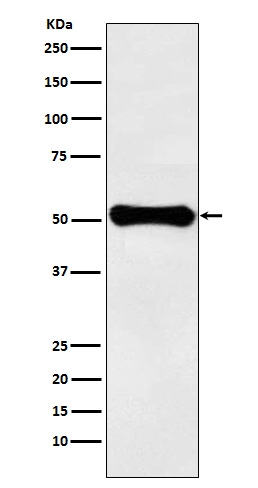
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GDH; Gdh-X; GDH1; GLUD; Glud1; Glud1a; Glud1b; Gludl; MRG-2;;Glutamate dehydrogenase 1 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 61 kDa ; Observed MW: 50 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Glutamate dehydrogenase 1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GLUD1抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要的简要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*"Overexpression of GLUD1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its clinical significance"*
**作者**:Li Y, et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过免疫组化及Western blot分析,发现GLUD1在肝癌组织中显著高表达,且与患者预后不良相关。研究使用特异性GLUD1抗体验证其表达水平,提示GLUD1可能作为肝癌潜在生物标志物。
2. **文献名称**:*"A novel hyperinsulinism/hyperammonemia syndrome mutation in GLUD1 alters mitochondrial enzyme activity and protein stability"*
**作者**:Stanley CA, et al.
**摘要**:本文报道了一种GLUD1基因突变导致的高胰岛素血症/高血氨综合征。通过患者样本的Western blot分析(使用GLUD1抗体),发现突变体蛋白稳定性降低,揭示了该疾病的分子机制。
3. **文献名称**:*"Glutamate dehydrogenase deficiency alters mitochondrial dynamics in Alzheimer's disease models"*
**作者**:Burbulla LF, et al.
**摘要**:研究探讨了阿尔茨海默病模型中GLUD1功能缺陷对线粒体功能的影响。利用GLUD1抗体进行免疫荧光染色,发现疾病相关β-淀粉样蛋白积累导致GLUD1表达下调,进而影响神经元代谢平衡。
4. **文献名称**:*"Validation of a high-specificity monoclonal antibody for GLUD1 in human tissue samples"*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:该文献描述了一种新型GLUD1单克隆抗体的开发与验证,通过免疫印迹和免疫组化实验证明其高度特异性,为GLUD1相关研究提供了可靠工具。
这些文献涵盖了GLUD1在疾病机制、诊断标志物及实验工具开发中的应用,均依赖GLUD1抗体进行蛋白水平分析。
The glutamate dehydrogenase 1 (GLUD1) antibody is a critical tool for studying the function and expression of GLUD1. a mitochondrial enzyme encoded by the GLUD1 gene. GLUD1 catalyzes the conversion of glutamate to α-ketoglutarate, linking amino acid metabolism to the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and energy production. It plays a vital role in insulin secretion, neurotransmission, and ammonia detoxification. Dysregulation of GLUD1 is implicated in metabolic disorders, hyperinsulinism-hyperammonemia syndrome (HI/HA), and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
GLUD1 antibodies are widely used in research to detect protein expression levels, subcellular localization, and interactions in tissues or cell lines. They are essential in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF). Monoclonal antibodies offer high specificity, while polyclonal antibodies may detect multiple epitopes, enhancing sensitivity. Validation via knockdown/knockout controls or peptide blocking is crucial to ensure antibody reliability.
Recent studies utilize GLUD1 antibodies to explore its role in cancer metabolism, where altered GLUD1 activity affects tumor growth and drug resistance. Additionally, these antibodies aid in investigating neurological conditions linked to glutamate excitotoxicity. Researchers prioritize antibodies with proven cross-reactivity across species (e.g., human, mouse, rat) to support translational studies. As GLUD1 gains attention in precision medicine, its antibody remains a cornerstone for mechanistic and diagnostic research.
×