| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BNPI; Slc17a7; VGluT1;;VGluT1 |
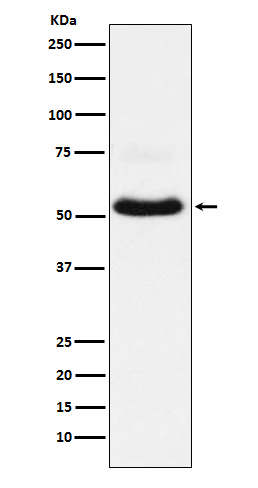
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 62 kDa ; Observed MW: 61 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human VGluT1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于VGLUT1抗体的3篇经典文献的简要总结:
---
1. **文献名称**:*The identification of vesicular glutamate transporter 3 suggests novel modes of signaling by glutamate*
**作者**:Bellocchio, E. E., Reimer, R. J., Fremeau, R. T., & Edwards, R. H.
**摘要**:该研究首次报道了VGLUT1的分子特征及其在谷氨酸能神经元突触囊泡中的特异性定位,揭示了其作为谷氨酸转运的关键蛋白的功能,并开发了特异性抗体用于检测其在脑组织中的分布。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Molecular anatomy of a trafficking organelle*
**作者**:Takamori, S., Rhee, J. S., Rosenmund, C., & Jahn, R.
**摘要**:通过VGLUT1抗体的免疫标记,研究揭示了突触囊泡中VGLUT1与其他转运蛋白的共定位,阐明了其在调控谷氨酸释放及突触可塑性中的作用,为神经传递机制提供了结构基础。
---
3. **文献名称**:*VGLUT1 defines subsets of excitatory neurons in the adult brain: Functional implications*
**作者**:Fremeau, R. T., et al.
**摘要**:利用VGLUT1抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现VGLUT1在大脑皮层、海马等区域的兴奋性神经元中高表达,提示其在不同神经环路中的特异性功能,并探讨了其在神经疾病模型中的表达变化。
---
这些文献均通过VGLUT1抗体的应用,推动了对谷氨酸能信号传递的分子机制及神经疾病相关研究。如需具体实验细节,可进一步查阅原文。
Vesicular glutamate transporter 1 (VGLUT1), encoded by the *SLC17A7* gene, is a transmembrane protein responsible for packaging glutamate into synaptic vesicles, a critical step in excitatory neurotransmission. As one of three VGLUT isoforms (VGLUT1-3), it is predominantly expressed in the central nervous system, particularly in cortical and hippocampal glutamatergic neurons, cerebellar mossy fibers, and sensory pathways. Its expression is often used as a marker for neurons specializing in glutamate-mediated signaling.
VGLUT1 antibodies are widely employed in neuroscience research to identify and map glutamatergic pathways, study synaptic plasticity, and investigate neurological disorders linked to glutamate dysregulation, such as Alzheimer’s disease, schizophrenia, and epilepsy. These antibodies enable visualization of VGLUT1 distribution via techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and immunofluorescence. Specificity is crucial, as VGLUT1 shares structural homology with VGLUT2 and VGLUT3. which have distinct regional and functional roles. Validated antibodies help differentiate these isoforms, supporting studies on their unique contributions to neural circuits and behavior.
Research using VGLUT1 antibodies has also clarified its role in synapse development, neurotransmitter release dynamics, and disease-associated changes in glutamate homeostasis, making it a key tool for understanding excitatory signaling in health and disease.
×