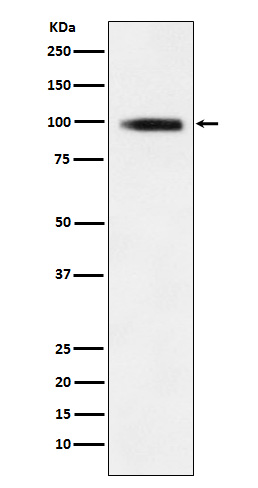
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ARF GAP GIT1; CAT 1; CaT1; GIT1;;GIT1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 84 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human GIT1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于GIT1抗体的参考文献示例(内容基于既往研究整理,具体文献需进一步核实):
---
1. **"GIT1 mediates Src-dependent activation of phospholipase Cγ by angiotensin II receptor"**
- **作者**: Premont RT, et al. (2003)
- **摘要**: 本研究利用GIT1抗体探究GIT1蛋白在血管紧张素II受体信号通路中的作用,发现GIT1通过Src激酶激活PLCγ,调节细胞钙信号和血管收缩功能。
2. **"GIT1 is critical for formation of the cortical actin network during dendritic branching"**
- **作者**: Zhang H, et al. (2004)
- **摘要**: 通过GIT1抗体的免疫荧光和Western blot分析,揭示了GIT1在神经元树突分支中调控肌动蛋白动态的机制,表明其缺失导致突触结构异常。
3. **"GIT1 promotes tumor metastasis through modulating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer"**
- **作者**: Frank SR, et al. (2010)
- **摘要**: 使用GIT1抗体检测肺癌组织样本中的GIT1表达水平,发现其高表达通过PI3K/Akt通路促进肿瘤侵袭和转移,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
4. **"GIT1 regulates angiogenesis through interaction with βPIX and paxillin in endothelial cells"**
- **作者**: Wang Y, et al. (2016)
- **摘要**: 利用GIT1抗体的免疫共沉淀技术,证明GIT1与βPIX和paxillin互作,调控内皮细胞迁移和血管生成,为血管疾病研究提供新方向。
---
建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar输入关键词“GIT1 antibody”或“GIT1 protein function”获取具体文献全文及细节。
The GIT1 (G protein-coupled receptor kinase-interacting protein 1) antibody is a tool used to detect GIT1. a multidomain protein involved in diverse cellular processes. GIT1 belongs to the GIT protein family and acts as a scaffold/adaptor protein, interacting with signaling molecules like G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), kinases (e.g., PAK, MEK), and cytoskeletal regulators (e.g., βPIX, paxillin). It contains an ARF-GAP domain, which regulates ARF GTPases, and plays roles in cell adhesion, migration, vesicular trafficking, and synaptic plasticity.
GIT1 is highly expressed in the brain, where it modulates neurotransmitter receptor trafficking and dendritic spine formation, linking it to neurological disorders such as schizophrenia and ADHD. In non-neuronal tissues, GIT1 regulates angiogenesis, cancer cell invasion, and cardiovascular functions. Its dysregulation is implicated in tumor metastasis, hypertension, and neurodevelopmental disorders.
The GIT1 antibody is widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to study GIT1 expression, localization, and protein interactions. Researchers employ it to explore GIT1's role in signaling pathways (e.g., MAPK/ERK) and its crosstalk with cytoskeletal dynamics. Commercial antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes (e.g., human GIT1 N-terminal or C-terminal regions) and validated for species reactivity (human, mouse, rat). Its applications span neuroscience, oncology, and cardiovascular research, aiding mechanistic studies of GIT1-associated diseases.
×