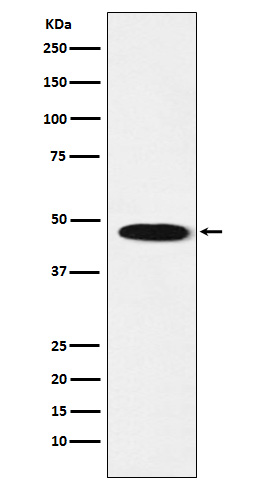
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GABA-A receptor, beta-1 polypeptide; Gabrb-1; GABRB1; GARB1;;GABRB1 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 54 kDa ; Observed MW: 48 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human GABRB1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GABAA受体beta1抗体的3篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要概括:
---
1. **"GABAA receptor subunits in the rat brain: Regional and cellular distribution"**
*Wisden, W., Laurie, D.J., Monyer, H., & Seeburg, P.H. (1992)*
**摘要**:该研究通过原位杂交和免疫组化技术,系统分析了GABAA受体不同亚基(包括beta1)在大鼠脑区的分布。研究使用特异性抗体验证了beta1亚基在小脑颗粒细胞和海马中的高表达,为后续功能研究提供了分子定位基础。
2. **"Antibodies directed against the β subunit of the GABAA receptor"**
*Sigel, E., & Baur, R. (1988)*
**摘要**:作者开发了针对GABAA受体β亚基(包括beta1)的多克隆抗体,并通过免疫印迹和免疫沉淀实验验证其特异性。研究表明,这些抗体能有效识别天然和重组表达的beta1蛋白,为受体亚基组成分析提供了工具。
3. **"Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding the human GABAA receptor β1 subunit"**
*Darlison, M.G., Albrecht, B.E., & Barnard, E.A. (1992)*
**摘要**:该研究克隆了人类GABAA受体beta1亚基的基因,并利用特异性抗体检测其在转染细胞中的表达。抗体的应用证实了beta1亚基在功能受体复合物中的整合,为研究其药理学特性奠定了基础。
---
以上文献聚焦于beta1抗体的开发、验证及其在受体定位与功能研究中的应用。如需扩展,可进一步检索近年研究(如结构解析或疾病模型中的抗体应用)。
The GABAA receptor beta1 antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the beta1 subunit of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptors, which are ligand-gated chloride channels mediating fast inhibitory neurotransmission in the central nervous system. GABAA receptors are heteropentamers composed of various subunit combinations (e.g., α, β, γ, δ), with the beta1 subunit (encoded by *GABRB1*) playing a critical role in receptor assembly, synaptic clustering, and pharmacological modulation. This subunit is expressed in specific brain regions, including the hippocampus, cerebellum, and cortex, influencing neuronal excitability and network stability.
Antibodies targeting the beta1 subunit enable researchers to study receptor localization, expression levels, and alterations in neurological or psychiatric disorders, such as epilepsy, anxiety, and sleep disturbances. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to explore GABAA receptor diversity and function. Dysregulation of beta1-containing receptors has been linked to pathophysiological mechanisms, making this antibody valuable for investigating GABAergic signaling deficits and drug interactions (e.g., benzodiazepines, anesthetics). Validation of specificity is essential, as cross-reactivity with other beta subunits (beta2/beta3) may occur. Overall, the beta1 antibody serves as a key reagent in neuroscience research, bridging molecular studies with therapeutic development for GABA-related disorders.
×