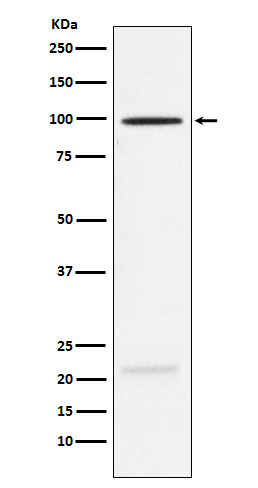
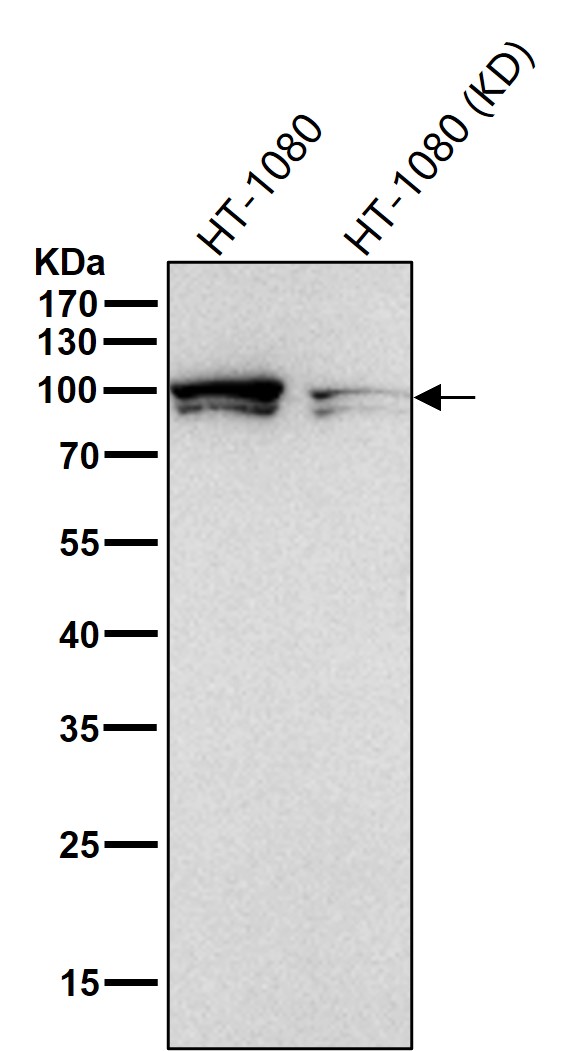
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GMA; MAG; S MAG; SIGLEC4A; SPG75;;MAG |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 69 kDa ; Observed MW: 100 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human MAG |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于MAG抗体的3篇参考文献,包括文献名称、作者及摘要内容概括:
1. **文献名称**: *"Peripheral neuropathy and anti-MAG antibodies."*
**作者**: Latov N, Hays AP, Sherman WH.
**摘要**: 该研究首次报道了IgM单克隆丙种球蛋白病患者中存在抗MAG抗体,揭示了其与慢性脱髓鞘性周围神经病的关联,患者主要表现为感觉性共济失调和运动障碍。
2. **文献名称**: *"Experimental autoimmune neuropathy with anti-MAG IgM antibodies and electrophysiological changes."*
**作者**: Willison HJ, Trapp BD, Bunge RP.
**摘要**: 通过将抗MAG抗体被动转移至动物模型,证实了这些抗体可直接导致周围神经脱髓鞘和神经传导阻滞,支持了抗MAG抗体在神经病变中的致病作用。
3. **文献名称**: *"Rituximab in anti-MAG antibody-associated polyneuropathy: a retrospective study."*
**作者**: Léger JM, Viala K, Nicolas G, et al.
**摘要**: 回顾性分析显示,利妥昔单抗治疗可显著改善部分抗MAG抗体相关周围神经病患者的临床症状和神经电生理指标,提示B细胞靶向治疗的有效性。
4. **文献名称**: *"Antibodies to myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) in neuropathy: clinical correlations and disease mechanisms."*
**作者**: Pestronk A, Choksi R, Blume G.
**摘要**: 探讨了抗MAG抗体滴度与疾病严重程度的关系,指出高抗体水平与更严重的感觉障碍相关,并提出抗体可能通过干扰轴突-施万细胞相互作用致病。
这些文献涵盖了抗MAG抗体的发现、致病机制、治疗及临床意义,为理解其在周围神经病中的作用提供了重要依据。
Anti-MAG (myelin-associated glycoprotein) antibodies are autoantibodies targeting MAG, a glycoprotein found in the myelin sheaths of peripheral nerves. MAG is expressed by Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes, playing a critical role in maintaining myelin integrity and facilitating axon-glial interactions. In autoimmune neuropathies, particularly IgM monoclonal gammopathy-associated demyelinating neuropathy, these antibodies bind to MAG’s carbohydrate epitopes, disrupting myelin stability and impairing nerve conduction.
The condition, often linked to monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), manifests as chronic sensorimotor neuropathy with symptoms like sensory ataxia, tremor, and progressive weakness. Diagnosis involves detecting serum anti-MAG IgM antibodies via ELISA or Western blot, alongside clinical and electrophysiological evidence of demyelination.
While the exact trigger remains unclear, molecular mimicry between MAG and infectious antigens is hypothesized. Treatment focuses on reducing antibody levels through immunotherapy (e.g., rituximab, IVIG) or targeting underlying clonal B-cell disorders. Prognosis varies, with some patients stabilizing on therapy, while others experience gradual decline. Research continues to clarify pathogenetic mechanisms and optimize therapeutic strategies.
×